BS (Base Station)
At the heart of wireless communication networks are base stations, which act as the gateway between wireless devices and the network infrastructure. Base stations are
Get Price
Multiuser Communications with Movable-Antenna Base Station
This paper studies the deployment of multiple movable antennas (MAs) at the base station (BS) for enhancing the multiuser communication performance. First, we model
Get Price
What Is the Role of a Base Station in Wireless Communication?
Base stations are critical components in wireless communication networks, serving as the intermediary between mobile devices and the core network. They play a vital role in
Get Price
Multiuser Communications With Movable-Antenna Base Station:
Movable antenna (MA) is an innovative technology that facilitates the repositioning of antennas within the transmitter/receiver area to enhance channel conditions and communication
Get Price
What Is the Role of a Base Station in Wireless Communication?
Introduction to Base Stations in Wireless Communication Base stations are critical components in wireless communication networks, serving as the intermediary between mobile
Get Price
Multiuser Communications with Movable-Antenna Base
Abstract—Movable antenna (MA) is an emerging technol-ogy which enables a local movement of the antenna in the transmitter/receiver region for improving the channel condition and
Get Price
Base Stations
Base stations form a key part of modern wireless communication networks because they offer some crucial advantages, such as wide coverage, continuous communications and
Get Price
The Base Station in Wireless Communications: The
Equipped with an electromagnetic wave antenna, often placed on a tall mast, the base station enables communication between mobile terminals
Get Price
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile Connectivity
Base stations and cell towers are critical components of cellular communication systems, serving as the infrastructure that supports seamless mobile connectivity. These
Get Price
The Positioning of Base Station in Wireless Communication
The placement of base stations depends on the traffic density, channel conditions, interference scenario, the number of base stations, and the other network planning parameters; as a result,
Get Price
What Is A Base Station?
A base station is an integral component of wireless communication networks, serving as a central point that manages the transmission and reception of signals between
Get Price
What is a Base Station in Telecommunications?
Discover the role and functionality of a base station in telecommunications networks. Learn how these critical components manage communication between mobile devices and the network,
Get Price
What is a base station?
In telecommunications, a base station is a fixed transceiver that is the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile client devices.
Get Price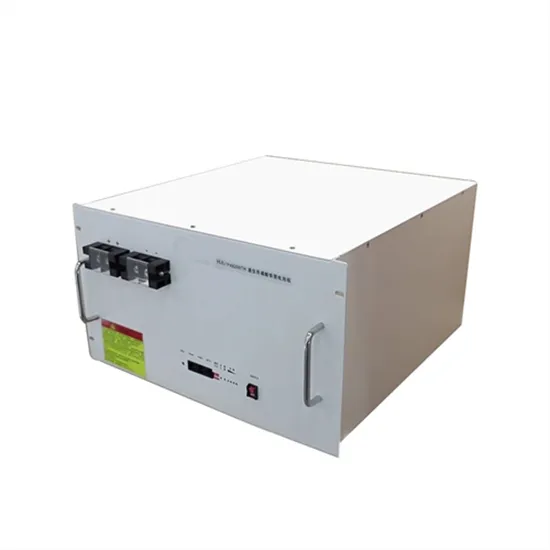
The Evolution of Base Station Antennas for Mobile Communications
This paper gives a general overview of the design of base station antennas for mobile communications. It explains underlying theoretical and practical implementation aspects in
Get Price
A tutorial on AI-powered 3D deployment of drone base stations:
The literature has several high quality surveys that analyze UAV-assisted communication networks from various standpoints. For instance, Zhang et al. in [24] present a
Get Price
5g base station
A 5G base station, also known as a 5G cell site or 5G NodeB, is a critical component of a 5G wireless network. It serves as the interface between the mobile devices
Get Price
The Global Network of Satellite Ground Stations
The intricate web of satellite ground stations forms a critical backbone in the realm of satellite communications, serving as the linchpin for
Get Price
(PDF) Accurate Base Station Placement in 4G LTE
Accurate Base Station Placement in 4G LTE Networks Using Multiobjective Genetic Algorithm Optimization February 2023 Wireless
Get Price
Base station
The term is used in the context of mobile telephony, wireless computer networking and other wireless communications and in land surveying. In surveying, it is a GPS receiver at a known
Get Price
What is a base station?
In telecommunications, a base station is a fixed transceiver that is the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile client devices. A base station serves as
Get Price
Types of Base Stations
Base stations are one of the widely used components in the field of wireless communication and networks. It is an access point or base point of a
Get Price
What is a Base Station in Telecommunications?
Discover the role and functionality of a base station in telecommunications networks. Learn how these critical components manage communication
Get Price
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile
Base stations and cell towers are critical components of cellular communication systems, serving as the infrastructure that supports seamless
Get Price
Cellular Networks, Cells, and Base Stations — EITC
These base stations provide the cell with the network coverage which can be used for transmission of voice, data, and other types of content. In radio communications, a
Get Price
The Base Station in Wireless Communications: The Key to
Equipped with an electromagnetic wave antenna, often placed on a tall mast, the base station enables communication between mobile terminals (such as mobile phones or
Get Price
6 FAQs about [The position of base stations in communications]
What is a base station in a telecommunications network?
A base station is a critical component in a telecommunications network. A fixed transceiver that acts as the central communication hub for one or more wireless mobile client devices. In the context of cellular networks, it facilitates wireless communication between mobile devices and the core network.
What does a base station do?
Base stations are responsible for transmitting and receiving data to and from wireless devices, as well as managing network resources and ensuring reliable and efficient communication. The basic function of a base station is to convert wireless signals into digital signals that can be transmitted over a wired network infrastructure.
Why are base stations important for modern telecommunications?
In summary, base stations are critical for modern telecommunications as they serve as the link between mobile devices and the extensive network infrastructure that spans the globe. The strategic deployment and ongoing improvement of these stations are essential for maintaining global connectivity.
How does a wireless device communicate with a base station?
When a wireless device, such as a mobile phone, communicates with a base station, the device sends a signal to the base station, which converts the signal into digital form and sends it to the network. Similarly, when the network sends data to the device, the base station converts the digital data into a wireless signal that the device can receive.
Is a base station a transmitter or broadcast point?
Base stations are generally a transceiver, capable of sending and receiving wireless signals; otherwise, if they only transmitted signals out, they would be considered a transmitter or broadcast point. A base station will have one or more radio frequency (RF) antennas to transmit and receive RF signals to other devices.
How does a base station communicate with a client device?
Generally, if client devices wanted to communicate to each other, they would communicate both directly with the base station and do so by routing all traffic through it for transmission to another device. Base stations in cellular telephone networks are more commonly referred to as cell towers.
More related information
-
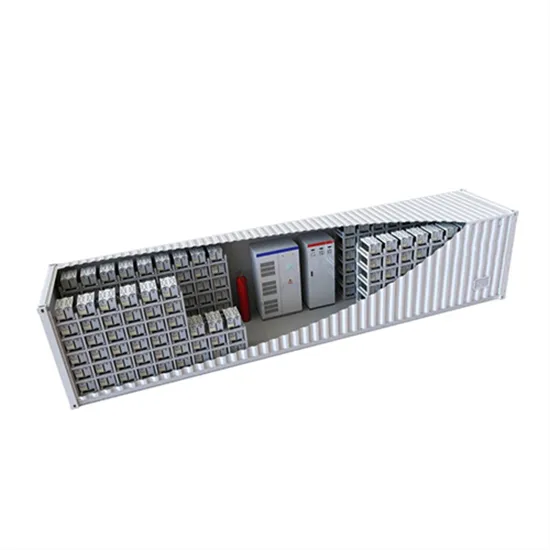 Timor-Leste supports green base stations for communications
Timor-Leste supports green base stations for communications
-
 China Communications has 2MWH5g base stations
China Communications has 2MWH5g base stations
-
 How many base stations are there in Guinea s 5G communications operations
How many base stations are there in Guinea s 5G communications operations
-
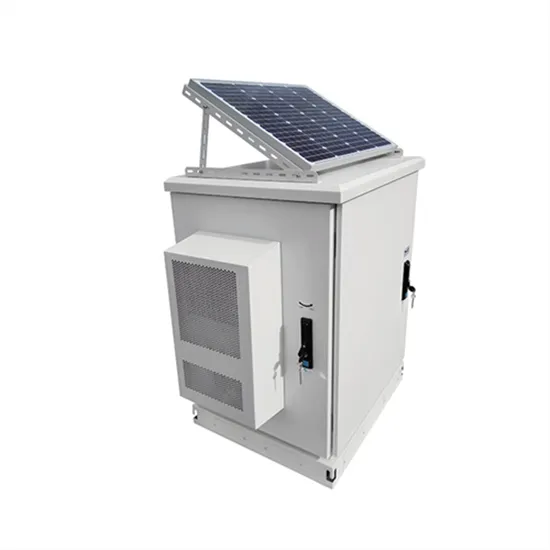 Are there green base stations for domestic communications abroad
Are there green base stations for domestic communications abroad
-
 Are operator base stations considered national communications facilities
Are operator base stations considered national communications facilities
-
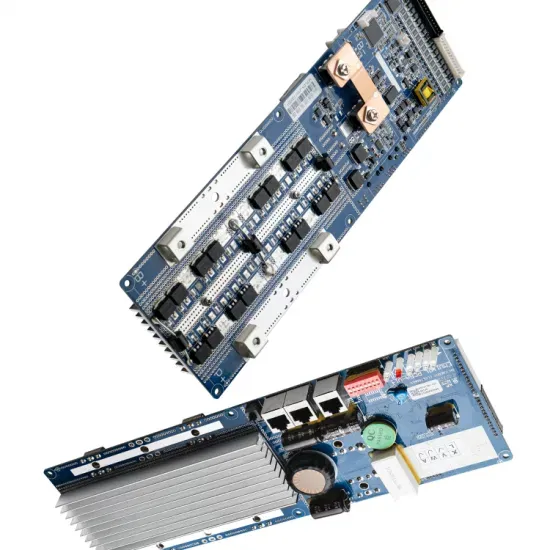 How many 5G base stations does Estonia Communications have
How many 5G base stations does Estonia Communications have
-
 What are the 5G base stations of Lesotho Communications Company
What are the 5G base stations of Lesotho Communications Company
-
 Communications are compensated according to 5G small base stations
Communications are compensated according to 5G small base stations
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


