Understanding inverter voltage
Choosing the optimal inverter voltage depends on various factors, including the inverter''s design, the power requirements of connected devices, and the available power source.
Get Price
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
Choosing the best inverter voltage depends on several factors, including the design of the inverter, the power requirements of the connected equipment, and the available
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition, Functions,
Based on that, it can be seen that the higher the voltage, the greater the power generated and the energy obtained by an inverter. With a
Get Price
Why DC supply voltage is increasing when inverter is connected
However, if a powerful induction motor is connected, the DC supply voltage gradually increases. The gradual increment might be due to the soft starting feature that
Get Price
Operational Amplifiers
When the + input is higher voltage than the – input, the output drives hard up to the voltage of the positive power supply rail. When the – input of the op amp is
Get Price
High Density Auxiliary Power Supply Using a SiC MOSFET
As automotive applications continue to trend in the direction of increased safety, it has become more common to include a high-voltage to low-voltage backup supply in the traction inverter
Get Price
Grid Tie Inverter Working Principle
A DC link to the output AC inverter is provided, and its value must be higher than the peak of utility AC voltage. For example, for 120VAC the
Get Price
power engineering
By Kirchhoff''s Voltage Law (KVL), the voltage across Rload is equal to the voltage supplied by V1. The amount of current that I1 is capable of supplying has no bearing upon the
Get Price
9. Inverter Settings
4. To set the voltage at which the inverter restarts after low voltage shut-down. - To prevent rapid fluctuation between shut-down and start up, it is recommended that this value be set at least
Get Price
Solar Voltage Rise – why you should care
In the ideal situation, the voltage rise is not a problem: the inverter increases the grid voltage from 240 volts to 242 volts. The problem arises
Get Price
Understanding High DC Bus Voltage in Inverters
Learn why your inverter''s DC bus voltage may be higher than expected and how to diagnose the issue effectively.
Get Price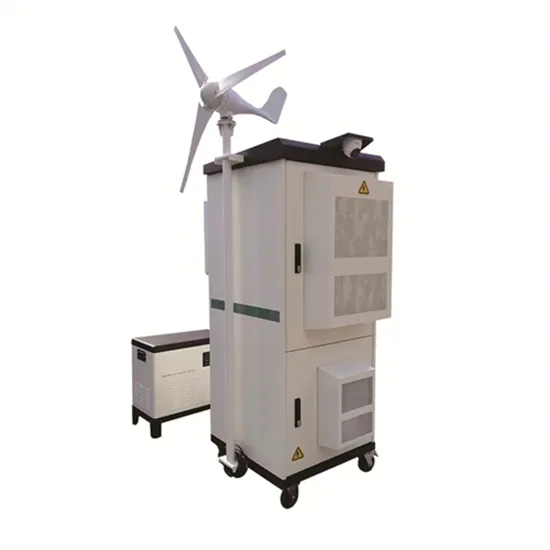
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar
Get Price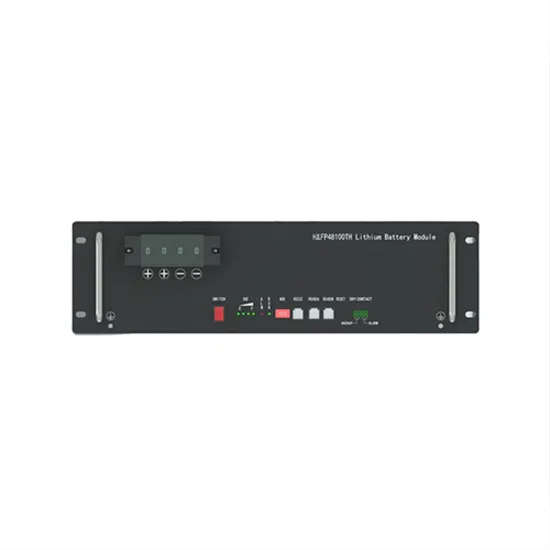
How Grid Voltage Affects Solar Production | Infinite
The higher the amount of electricity you are trying to export, the greater the "voltage rise" between your inverter and the grid will be. If the
Get Price
Op Amp Input and Output Swing Limitations
The practical output voltage range of an op-amp circuit is limited by the power supply voltage, internal op-amp design, and circuit configuration. The output range is always less than the
Get Price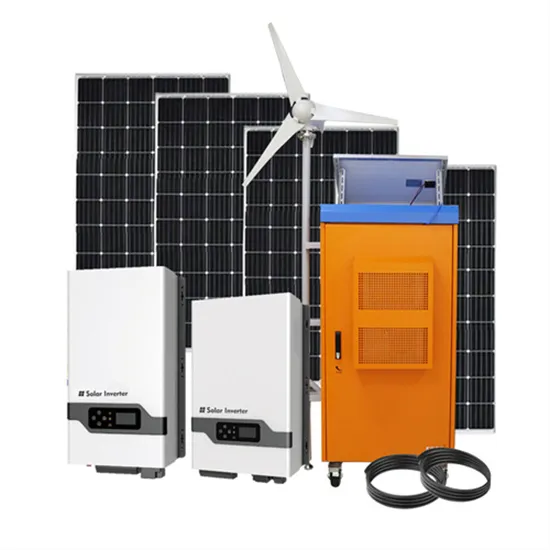
Understanding inverter voltage
Choosing the optimal inverter voltage depends on various factors, including the inverter''s design, the power requirements of connected devices,
Get Price
Wattage vs Voltage vs Current on Inverter Ratings
When sizing out a system, if you look at the specs on a lot of off-grid inverters, there will be a max Voltage, a max current and a max wattage. In strict math terms without factoring
Get Price
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
Choosing the best inverter voltage depends on several factors, including the design of the inverter, the power requirements of the connected
Get Price
Solar Voltage Rise – why you should care
In the ideal situation, the voltage rise is not a problem: the inverter increases the grid voltage from 240 volts to 242 volts. The problem arises when the customer''s cables
Get Price
The starting voltage of the inverter is higher than the minimum voltage
When the inverter starts, the modules are in a working state and the voltage will decrease. In order to prevent the inverter from restarting repeatedly, the starting voltage of the inverter is
Get Price
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings
Typically, residential inverters have a maximum input voltage between 500V and 1000V. Choosing one with a higher rating ensures greater flexibility and better
Get Price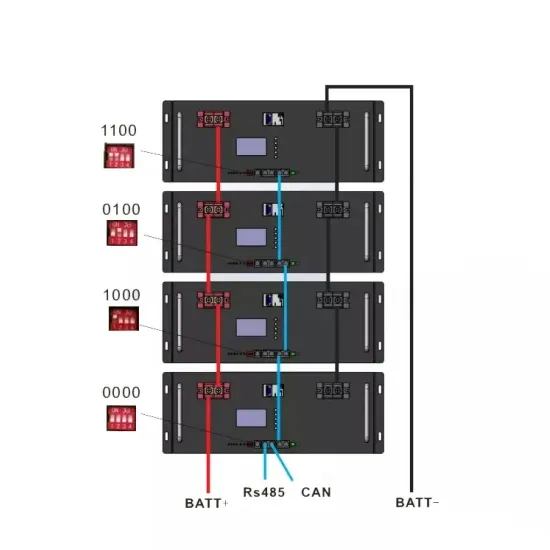
voltage
I suspect that the inverter monitors the grid voltage and produces an output voltage that is just a few volts higher. Is that all that is needed for the loads in the house to use all the
Get Price
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings should you pay
Typically, residential inverters have a maximum input voltage between 500V and 1000V. Choosing one with a higher rating ensures greater flexibility and better performance in different
Get Price
Interpreting inverter datasheet and main parameters | AE 868
Inverter Start-up voltage Aside from the operating voltage range, another main parameter is the start-up voltage. It is the lowest acceptable voltage that is needed for the inverter to kick on.
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power
Get Price
Grid Voltage Rise Is Getting Worse. That''s A Problem
The inverter has to be running at a higher voltage than the grid, so it can push power out (current flows from a point of higher voltage towards a
Get Price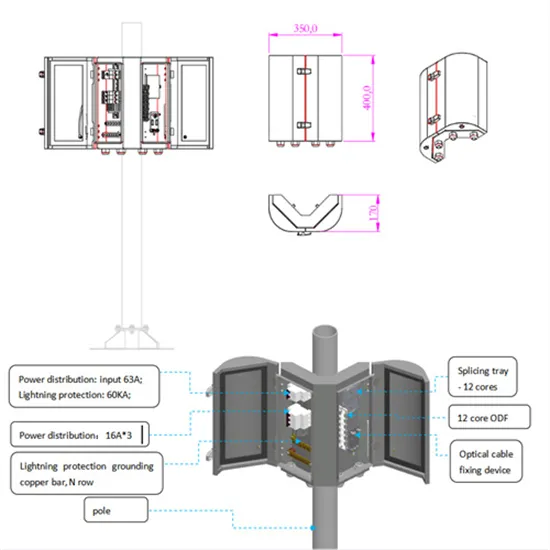
Inverter showing higher voltage than batteries
We''re confused about why our sungoldpower 6000 watt 48v inverter is showing a higher charge ( by 4 volts) than our battery bank.
Get Price
Harmonics and Inverters
Introduction Static UPS are almost perfect electric generators. They have high reliability and, by nature, ensure (within the battery operation limits) the uninterrupted power supply. Regarding
Get Price
INVERTERS
The word ''inverter'' in the context of power-electronics denotes a class of power conversion (or power conditioning) circuits that operates from a dc voltage source or a dc current source and
Get Price
Demystifying high-voltage power electronics for solar inverters
For a grid direct inverter, the input voltage usually needs to be above the output AC voltage (grid voltage). For example, generating a sinusoidal waveform of 230VAC requires an input voltage
Get Price
The truth about five common VFD myths
At higher speeds, the VFD must supply more voltage to overcome the back-EMF so that current can still flow into the motor as current is
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Inverter voltage is higher than the power supply voltage]
Why is inverter voltage important?
In the realm of power electronics, the inverter voltage is a critical parameter that dictates its performance, compatibility, and safety. Understanding the intricacies of inverter voltage is essential for anyone seeking a reliable and efficient power supply.
Should a power inverter be lowered if resistance is high?
To keep the equation balanced, if the resistance in your property’s cable is high, either the voltage from your inverter will have to be higher, or the current to the street will have to be lower. But reducing the current is a stupid idea. If your inverter wants to send 20 amps back to the grid, then we should “let it flow”.
Does a solar inverter increase a grid voltage?
In order for power to flow from your home to the grid, the voltage from the solar inverter has to produce a voltage that is a couple of volts higher than the grid voltage. Voila, Solar Voltage Rise. In the ideal situation, the voltage rise is not a problem: the inverter increases the grid voltage from 240 volts to 242 volts.
What voltage is a 12V inverter?
Inverters come in various configurations, each designed for specific power systems. Common rated input voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V. The choice depends on the application, the size of the power system, and the available power source. A 12V inverter is commonly used for smaller applications, such as in vehicles or small off-grid setups.
How many volts does a solar inverter produce?
Let's say it produces 10 amperes, and the grid has a resistance of 1 ohm. In this case, the voltage will rise to 220 volts at the inverter. If the solar inverter sees a high grid voltage of let's say 250 volts, it does the same. Only when the grid voltage exceeds some sane limit, will the solar inverter stop production.
What is the input voltage of an inverter?
Understanding the inverter voltage is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your power system. Inverter voltage typically falls into three main categories: 12V, 24V, and 48V. These values signify the nominal direct current (DC) input voltage required for the inverter to function optimally. What is the rated input voltage of an inverter?
More related information
-
 What size inverter power supply should I use for 220v voltage
What size inverter power supply should I use for 220v voltage
-
 Power supply voltage inverter function
Power supply voltage inverter function
-
 5v power supply to 12v inverter
5v power supply to 12v inverter
-
 Inverter as outdoor power supply
Inverter as outdoor power supply
-
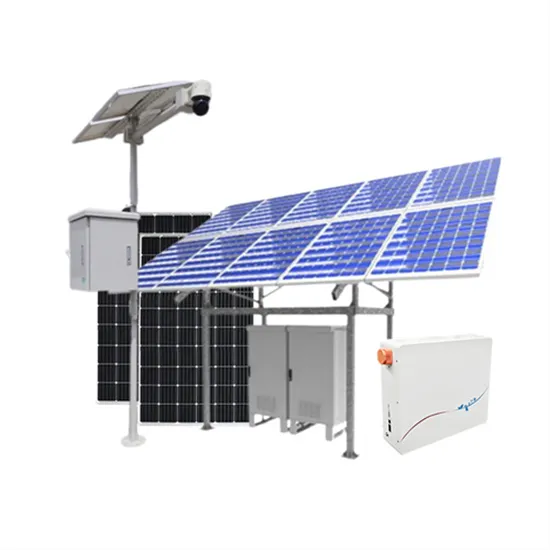 Does the photovoltaic inverter need power supply
Does the photovoltaic inverter need power supply
-
 Inverter for outdoor power supply
Inverter for outdoor power supply
-
 How to supply power to communication high voltage energy storage cabinet
How to supply power to communication high voltage energy storage cabinet
-
 Wide voltage inverter power generation system
Wide voltage inverter power generation system
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


