Solar radio emission as a disturbance of radiomobile networks
This article, for the first time, studies the solar radio disturbance of LTE services by means of innovative 3GPP4 MDT (Minimization of Drive Test) standard radio measures and the richness
Get Price
Microsoft Word
Introduction: Exponential growth of mobile communications has increased interest in many topics in radio propagation. Much effort is now devoted to refi ne radio propagation path-loss models
Get Price
The Hybrid Solar-RF Energy for Base Transceiver Stations
In this work, we propose a new hybrid energy harvesting system for a specific purpose such as powering the base stations in communication networks. The hybrid solar-RF
Get Price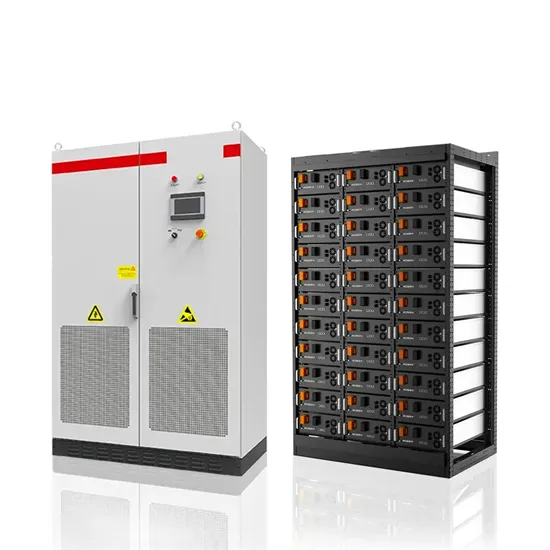
Radio Waves – Networks at ITP
Radio waves, for example, have long wavelengths and low energy levels, making them non-ionizing and generally safe for humans. However, certain
Get Price
The Effect Of Wavelength On Photovoltaic Cells
Any radiation with a longer wavelength, such as microwaves and radio waves, lacks the energy to produce electricity from a solar cell. Any photon with a energy greater than
Get Price
What are Radio Waves?
As radio waves travel at a speed similar to that of light and are slowed down based on that object''s permittivity and permeability while passing through an object. Wavelength is used to
Get Price
Radio Waves: Wavelength, Discovery, Bands & Uses | AESL
Spectrum of radio wave bands is shown in the diagram below: Uses of Radio Waves Radio waves are employed in all of our communications around the world, from the mobile network to
Get Price
Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systems for Telecommunication
Radio link stations are mostly installed on high altitudes so that radio waves transmit a large amount of terrain. Hence, number of required station are reduced and overall costs are
Get Price
Telecom Base Station PV Power Generation System Solution
The communication base station installs solar panels outdoors, and adds MPPT solar controllers and other equipment in the computer room. The power generated by solar energy is used by
Get Price
The Use of Waves for Communication
Terrestrial television signals and radio signals both use radio waves. Radio signals are transmitted at a longer wavelength than terrestrial television signals.
Get Price
13_radio.ppt
Encoding Information on Radio Waves What quantities characterize a radio wave? Two common ways to carry analog information with radio waves Amplitude Modulation (AM) Frequency
Get Price
Workgroup Report: Base Stations and Wireless
Radiofrequency (RF) waves have long been used for different types of information exchange via the airwaves—wireless Morse code, radio, television, and wireless telephony (i.e., construction
Get Price
HF
HF- Communication High frequency (HF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) between 3 and 30 MHz. It is also known as the
Get Price
Management of a base station of a mobile network using a photovoltaic
In this work, we study the best approach to transfer all the useful power from the photovoltaic generator to a telecommunications relay station (BTS or BSC).
Get Price
Microsoft PowerPoint
The primary goal of the communication subsystem is to provide a link to relay data findings and send commands to and from the satellite. Communication subsystem will ensure continuous
Get Price
ken-system: Millimeter-wave Radio on Fiber system using wavelength
A Central Station (CS), witch gathers optical links to a lot of base stations (BSs) in millimeter-wave Radio on Fiber (RoF) system, becomes large and high-cost, because many
Get Price
Management of a base station of a mobile network using a
In this work, we study the best approach to transfer all the useful power from the photovoltaic generator to a telecommunications relay station (BTS or BSC).
Get Price
The Hybrid Solar-RF Energy for Base Transceiver
In this work, we propose a new hybrid energy harvesting system for a specific purpose such as powering the base stations in communication
Get Price
Ground Base Station Antenna Design for Air-to-Ground
Abstract—The sixth generation (6G) of mobile communica-tion networks aims to bring innovations in mobile broadband solutions and airborne communications. This paper proposes an antenna
Get Price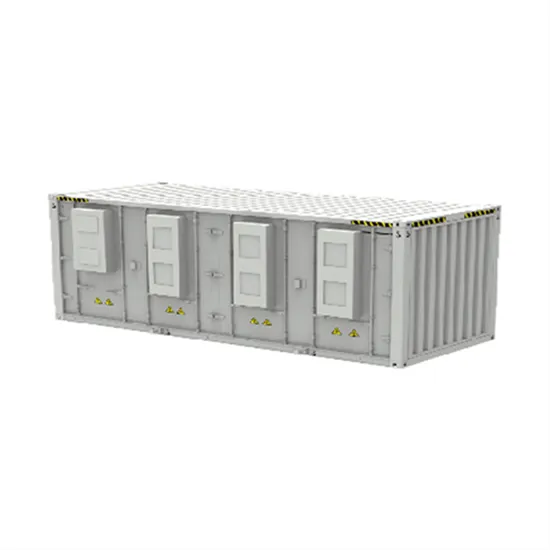
Microsoft Word
C. Beckman† − This paper gives a general overview of the Abstract design of base station antennas for mobile communications. It explains underlying theoretical and practical
Get Price
Basics of Radio Wave Propagation
A basic description of the mechanisms of radio wave propagation. Page includes a comprehensive glossary of solar & propagation terminology.
Get Price
How solar-powered base station signals are transmitted
Radio waves serve as the medium for transmitting signals, which are generated and modulated by base station equipment. The specific frequency used can vary based on the
Get Price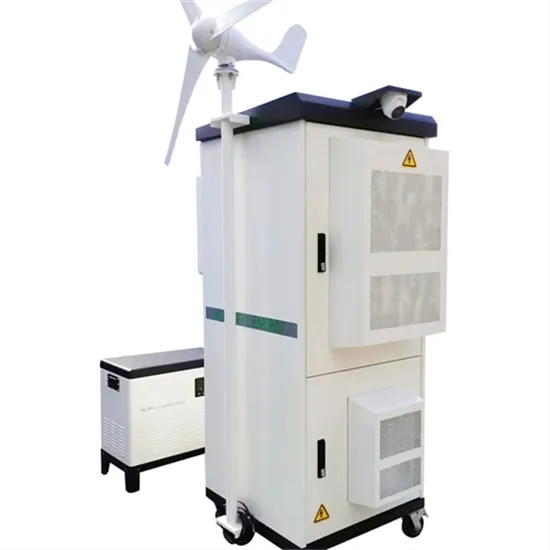
POWERING OF RADIO COMMUNICATION STATIONS IN
Identifying all types of radio sites and radio communication stations in West Bank which need to be powered by PV system, the radio station unit is known as Radio Base Station (RBS).
Get Price
Aviation Radio Communication
It is electromagnetic in nature and part of the electronic spectrum of wave activity that includes gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, infrared waves, and visible
Get Price
Photovoltaic Power Station Monitoring System Using GSM
The purpose of studying radio wave propagation is to predict the field intensity of mobile communication, estimate the loss of radio path, and formulate the networking and optimization
Get Price
Mobile Phone Base Stations and RF Radiation | IMDA
Electromagnetic field ("EMF") radiation refers to the waves of electric and magnetic energy that are transmitted through the air at the speed of light.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Photovoltaic radio wave wavelength of communication base station]
What is the wavelength of a solar cell?
w = h c E = 1, 110 nanometers = 1.11 × 10 6 meters The wavelengths of visible light occur between 400 and 700 nm, so the bandwidth wavelength for silicon solar cells is in the very near infrared range. Any radiation with a longer wavelength, such as microwaves and radio waves, lacks the energy to produce electricity from a solar cell.
What is radio wave propagation?
Radio wave propagation refers to the process by which radio waves travel from their source to a receiver. In some cases, such as during an Aurora, charged particles can affect this propagation by penetrating the Earth's magnetic field near the polar regions.
What is the maximum ordinary mode radiowavefrequency capable of vertical reflection?
The maximum ordinary mode radio wave frequency capable of vertical reflection from the F2 layer of the ionosphere is (See F region for more information).
What is mysterious radio wave propagation?
This is a form of mysterious radio wave propagation that occurs during the spring and fall months during the sunspot minimum. It allows two stations at nearly identical middle latitudes on opposite sides of the geomagnetic equator to communicate at frequencies up to 150 MHz.
What is a transient enhancement of solar radioemission?
A transient enhancement of solar radioemission at 245 MHz consists of an elevated background emission (radiation) and Type I radio bursts. This phenomenon is not related to non-great-circle propagation and describes a degraded condition of radio propagation caused by horizontal gradients in the ionospheric electron density.
What is the difference between short-wavelength radiation and long-wave length radiation?
Short-wavelength radiation occupies the violet end of the spectrum and includes ultraviolet radiation and gamma rays. On the other hand, long-wavelength radiation occupies the red end and includes infrared radiation, microwaves and radio waves.
More related information
-
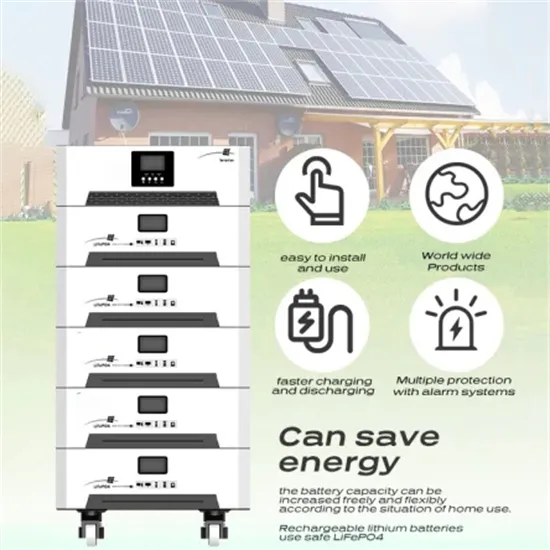
 What are the advantages of photovoltaic communication base station energy storage system
What are the advantages of photovoltaic communication base station energy storage system
-
 Energy efficiency of photovoltaic power generation system of Croatian communication base station
Energy efficiency of photovoltaic power generation system of Croatian communication base station
-
 Eastern European Communication Base Station Photovoltaic Power Generation Specifications
Eastern European Communication Base Station Photovoltaic Power Generation Specifications
-
 Which communication photovoltaic base station is best in the United States
Which communication photovoltaic base station is best in the United States
-
 How large is the scope of Bhutan Communication s 5G base station photovoltaic power generation system
How large is the scope of Bhutan Communication s 5G base station photovoltaic power generation system
-
 Brunei communication base station power supply photovoltaic power generation equipment manufacturer
Brunei communication base station power supply photovoltaic power generation equipment manufacturer
-
 Photovoltaic base station communication principle
Photovoltaic base station communication principle
-
 Kuwait communication base station wind power and photovoltaic power generation manufacturer
Kuwait communication base station wind power and photovoltaic power generation manufacturer
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


