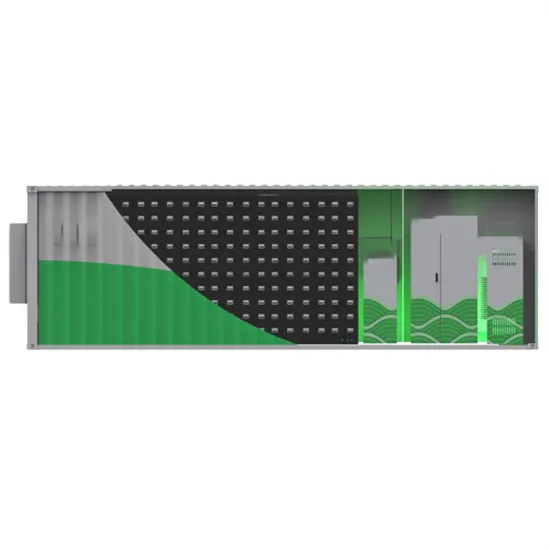
Accelerating energy transition through battery energy storage systems
Abstract This paper examines the present status and challenges associated with Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) as a promising solution for accelerating energy
Get Price
Thermal Design for the Passive Cooling System of Radio Base Station
As communication systems are gradually transferred to 5G, the system''s heat dissipation is getting larger, and thermal design becomes an important issue. This paper
Get Price
Optimization of 5G communication base station cabinet based on heat
This is done byfocusing on the problems of poor heat dissipation performance, high energy consumption, high overheating risk, and low cooling efficiency of 5G communication base
Get Price
STUDY ON AN ENERGY-SAVING THERMAL
Through the previous analysis of the energy-saving integrated thermal management system for the communication base station, the indoor temperature control of the base station throughout
Get Price
(PDF) A Review on Thermal Management and Heat
A literature review is presented on energy consumption and heat transfer in recent fifth-generation (5G) antennas in network base stations.
Get Price
Communication base station
In summary, the tower energy storage battery plays a key role in improving the reliability of the power supply of the communication base station, energy saving and consumption reduction,
Get Price
5G base stations and the challenge of thermal
Right now, one of the major challenges of 5G is the fact that form factors limit heat management systems for base stations. Remember, the
Get Price
The cooling challenges of 5G base stations
More encrypted base stations mean higher energy consumption, which is a major cost challenge facing 5G networks. From the energy
Get Price
Cooling for Mobile Base Stations and Cell Towers
Heat is absorbed and dissipated through custom designed heat exchangers with high aspect ratio, air ducted shrouds and high-performance fans. The heat pumping action occurs from custom
Get Price
Modeling and aggregated control of large-scale 5G base stations
A significant number of 5G base stations (gNBs) and their backup energy storage systems (BESSs) are redundantly configured, possessing surplus capacity during non-peak
Get Price
Cooling for Mobile Base Stations and Cell Towers
Heat is absorbed and dissipated through custom designed heat exchangers with high aspect ratio, air ducted shrouds and high-performance fans. The heat
Get Price
Coordinated scheduling of 5G base station energy
College of Electrical and Information Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, China With the rapid development of 5G base station
Get Price
Energy Efficient Thermal Management of 5G Base Station Site
The rapid development of Fifth Generation (5G) mobile communication system has resulted in a significant increase in energy consumption. Even with all the effor.
Get Price
Cooling technologies for data centres and telecommunication
This article represents the first review that provides a comprehensive comparison of energy efficiency between different energy-saving cooling technologies for both the DCs and
Get Price
5G base stations and the challenge of thermal management
Right now, one of the major challenges of 5G is the fact that form factors limit heat management systems for base stations. Remember, the solutions developed must work together.
Get Price
Cooling technologies for data centres and telecommunication base
This article represents the first review that provides a comprehensive comparison of energy efficiency between different energy-saving cooling technologies for both the DCs and
Get Price
Numerical simulation of flow and heat transfer characteristics of
In response to the current high demand for communication, additional communication base stations are being constructed, leading to more stringent heat dissipation
Get Price
What is a base station energy storage power station
A base station energy storage power station refers to a facility designed to store energy generated from various renewable sources and
Get Price
Telecom Battery Backup System | Sunwoda Energy
A telecom battery backup system is a comprehensive portfolio of energy storage batteries used as backup power for base stations to ensure a reliable and stable power supply.
Get Price
Thermal Design for the Passive Cooling System of Radio
Compared with active heat dissipation, passive cooling scheme is the optimal choice for reducing temperature of RBS. The purpose of thermal design is to achieve the lowest average
Get Price
Improved Model of Base Station Power System for the Optimal
The widespread installation of 5G base stations has caused a notable surge in energy consumption, and a situation that conflicts with the aim of attaining carbon neutrality.
Get Price
7.0 Thermal Control
A phase change material used as a thermal storage unit is made up of a material (e.g., wax) within a metal housing with a heat source attached so
Get Price
The cooling challenges of 5G base stations
More encrypted base stations mean higher energy consumption, which is a major cost challenge facing 5G networks. From the energy structure, power consumption means
Get Price
Energy performance analysis on telecommunication base station
Telecommunication base station (TBS) has high indoor IT heat dissipation rate, and cooling load exists almost all year around. Energy consumption of air-conditioning system is
Get Price
A Review on Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation
This review of the scientific literature is developed and presented in order to explore various aspects of energy consumption and thermal management strategies in last
Get Price
Flexible, Highly Thermally Conductive and Electrically Insulating
However, with the significant growth in energy consumption of 5G base stations, existing heat dissipation technologies can hardly fulfill the operation requirements of 5G
Get Price
(PDF) A Review on Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation
A literature review is presented on energy consumption and heat transfer in recent fifth-generation (5G) antennas in network base stations.
Get Price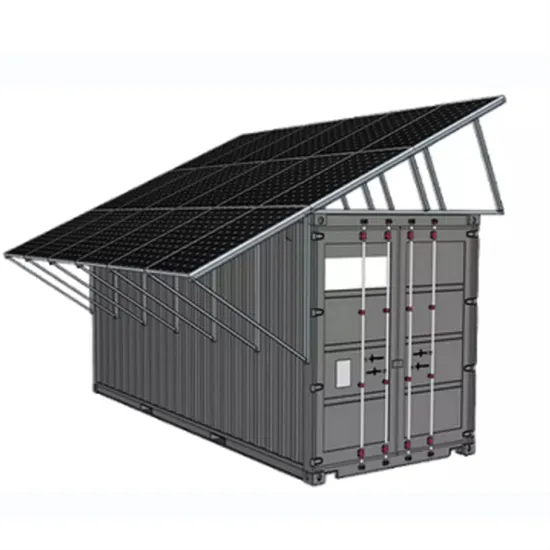
Base Station Energy Storage Thermal Management
Recent data from GSMA reveals that 23% of base station failures in tropical regions directly correlate with thermal management issues, costing operators up to $18,000 per incident in
Get Price
Application of the integrated technology of heat pipe and air
The research on communication base station cooling systems primarily focuses on temperature control effectiveness and energy efficiency, this is crucial for achieving energy
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Current status of heat dissipation in communication base station energy storage systems]
Are data centres and telecommunication base stations energy-saving?
Data centres (DCs) and telecommunication base stations (TBSs) are energy intensive with ∼40% of the energy consumption for cooling. Here, we provide a comprehensive review on recent research on energy-saving technologies for cooling DCs and TBSs, covering free-cooling, liquid-cooling, two-phase cooling and thermal energy storage based cooling.
Does a 5G base station have heat dissipation?
Currently, the majority of research concerning heat dissipation in 5G base stations is primarily focusing on passive cooling methods. Today, there is a clear gap in the literature in terms of research investigations that tend to quantify the temperature performances in 5G electronic devices.
How does 5G heat dissipation affect data handling performance?
Heat dissipation impacts a device’s maximum receiving rate. If the device is unable to manage heat, its data handling performance is compromised. Any solution that addresses 5G heat dissipation in base stations will need to be compatible with the requirements of device form factors while working seamlessly with core functionality.
Why is heat-dissipation important?
Innovative heat-dissipation solutions are necessary in preventing overheating and ensuring the reliable operation of future antennas and equipment. Energy consumption reduction should be developed in combination with a reduction in operational costs, all while retaining respect for the environment.
Can solid adsorption Heat pipe reduce heat transfer rate limitations?
The solid adsorption heat pipe can effectively resolve the problem of heat transfer rate limitations of traditional heat pipes. Their computational study showed that the system could reduce the peak temperature of the server from 75.8 °C to 68.8 °C and enhance the PUE from 2.0 to 1.7 (Yu et al., 2019).
Can phase-change materials improve the thermal performance of electronic devices?
Phase-change materials (PCMs) are recognized for their ability to handle superior temperature control within a well-defined time period. Thus, their integration with heat sinks can be a promising approach for enhancing the thermal performance of electronic devices .
More related information
-
 Heat dissipation of energy storage system in communication base station
Heat dissipation of energy storage system in communication base station
-
 Reliable communication base station energy storage system heat dissipation
Reliable communication base station energy storage system heat dissipation
-
 Guinea-Bissau has several communication base station energy storage systems
Guinea-Bissau has several communication base station energy storage systems
-
 Construction status of energy storage systems for communication base stations in the Marshall Islands
Construction status of energy storage systems for communication base stations in the Marshall Islands
-
 Energy storage ESS principle of wind power energy storage cabinet in communication base station
Energy storage ESS principle of wind power energy storage cabinet in communication base station
-
 Somalia Communication Base Station Wind and Solar Hybrid Energy Storage Cabinet Company
Somalia Communication Base Station Wind and Solar Hybrid Energy Storage Cabinet Company
-
 Communication base station energy storage system technical transformation project application
Communication base station energy storage system technical transformation project application
-
 Orchard Photovoltaic Communication Base Station Energy Storage System
Orchard Photovoltaic Communication Base Station Energy Storage System
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.