String vs Centralized Photovoltaic Inverter System Selection
1. Introduction The selection of an appropriate photovoltaic (PV) inverter system is a crucial decision in the design and installation of solar power generation systems. Among the various
Get Price
What are central and string solar inverters and how do
What is the difference between a central and a string inverter? The primary difference between central and string inverters is that a string inverter
Get Price
What Is a Central Inverter System? Understanding Its Role in
A central inverter system is frequently the preferred choice for larger installations, as it effectively consolidates the conversion of power from multiple panels into one unit,
Get Price
Choosing Between Central, String, and Micro Solar
Main Types of Solar Panel Inverters Selecting the appropriate solar power inverter might appear challenging, but fear not – we''ll guide you
Get Price
What Is a Central Inverter System? Understanding Its
A central inverter system is frequently the preferred choice for larger installations, as it effectively consolidates the conversion of power from
Get Price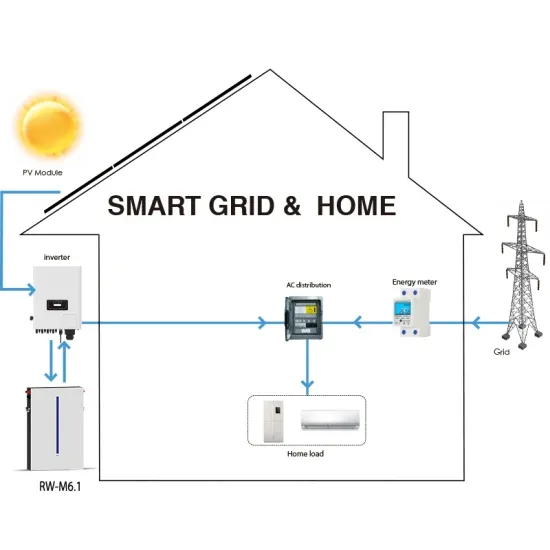
Central Inverter Key Benefits, Features, and Applications Explained
Central inverters are typically used in industrial, commercial, and utility-scale solar power installations due to their ability to handle high power output efficiently. Unlike smaller inverters,
Get Price
Solutions for PV transformation cabines
Connection from Centralized inverter to Power transformer done by Busbar duct (IP54 protection degree) and according to Inverter manufacturer designed solution (see
Get Price
What is a Central Inverter?
The single inverter in a residential installation is sometimes referred to as the central inverter, although the correct term is a string inverter. It is a particular kind of inverter
Get Price
Comparing Central vs String Inverters for Utility-Scale PV Projects
There are three primary tiers of PV inverters: microinverters, string inverters, and central inverters. Since microinverters are not rated for utility-scale voltages, we will largely
Get Price
Review on novel single-phase grid-connected solar inverters:
An ever-increasing interest on integrating solar power to utility grid exists due to wide use of renewable energy sources and distributed generation. The grid-connected solar
Get Price
Differences between Central Inverter and String Inverter
Narrow MPPT voltage scope of the central inverter, generally 500-820V, inflexible component configuration, short power generation time in rainy or misty days. Difficult inverter
Get Price
Central Inverters in Solar PV Systems: Advantages
There are two main types of inverters: central inverters and micro-inverters. Central inverters (also called string inverters) connect a string of PV
Get Price
What are central and string solar inverters and how do they
What is the difference between a central and a string inverter? The primary difference between central and string inverters is that a string inverter will typically sit at the
Get Price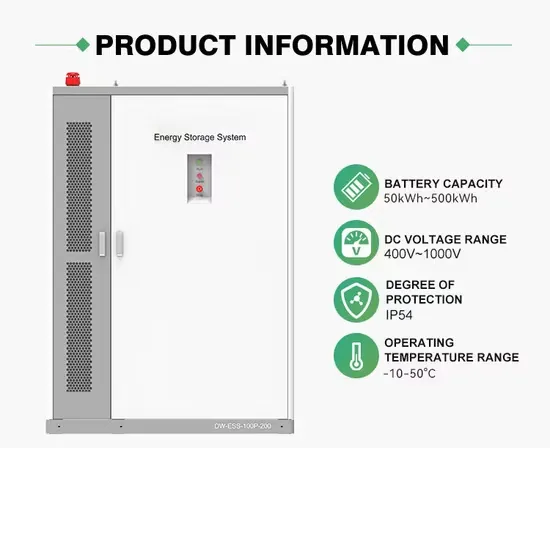
Inverter Topologies for Grid Connected Photovoltaic
Inverter constitutes the most significant component of the grid connected photo-voltaic system. The power electronics based device, inverter inverts DC quantity from array in AC quantity as
Get Price
Centralized inverter detailed introduction
The MPPT voltage range of the centralized inverter is narrow, generally 450-820V, and the component configuration is not flexible. On rainy days and foggy areas, the power generation
Get Price
Analysis of Local and Centralized Control of PV Inverters for
This study aims at evaluating performance of a sensitivity based method and an optimal power flow (OPF) based centralized method of reactive power control (in coordination with APC) from
Get Price
Central inverter introduction and functional analysis – TYCORUN
Generally, three-phase IGBT power modules are used for large power, and field-effect transistors are used for small power. At the same time, a DSP conversion controller is
Get Price
Central Inverters in Solar PV Systems: Advantages and
There are two main types of inverters: central inverters and micro-inverters. Central inverters (also called string inverters) connect a string of PV panels and convert the DC electricity into AC.
Get Price
Optimizers vs Microinverters, Which is Better for you?
The DC energy''s voltage is fixed during the conditioning process, allowing the centralized inverter to transform the DC energy into AC energy more effectively. Warranty
Get Price
Centralized inverter detailed introduction
The MPPT voltage range of the centralized inverter is narrow, generally 450-820V, and the component configuration is not flexible. On rainy days and
Get Price
What is a Central Inverter?
The single inverter in a residential installation is sometimes referred to as the central inverter, although the correct term is a string inverter.
Get Price
Central inverter introduction and functional analysis –
Generally, three-phase IGBT power modules are used for large power, and field-effect transistors are used for small power. At the same time,
Get Price
Photovoltaic Inverters: Key Parameters and
Composition of Inverter Inversion is the opposite process to rectification, which is the process of converting DC power into AC power.
Get Price
Central inverter solutions
Central inverters typically rely on single-stage power conversion, and most inverter designs are transformer-based or isolated. In the DC-AC stage, variable DC is converted to grid
Get Price
Solar Inverter Guide: Definition, Types, Costs, and
A complete guide on what is a solar inverter, types of solar inverters, costs, and buying to help you choose the right solar inverter for you!
Get Price
MV CENTRAL INVERTER
R7500 TL FIMER Centralized inverters with MV connection to the electricity distribution are completely innovative machines. The MPS technology (Modular Power System), owned and
Get Price
A review on microgrid decentralized energy/voltage control
This method does not use a voltage gradient in its structure and an inverter to control the output voltage. In Xin et al. (2015), self-optimized control that uses power
Get Price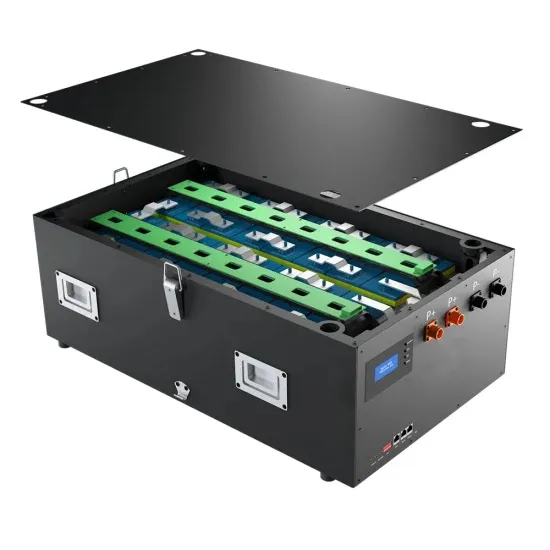
What are central and string solar inverters and how do
What is a solar inverter? A solar inverter is a device within a photovoltaic (PV) system that converts the direct current (DC) electricity
Get Price
central inverters
Effective connectivity ''s transformerless central inverter series enables system integrators to design the solar power plant using a combination of different power rating inverters, which are
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Centralized inverter voltage]
What is the power of a central inverter?
Inverter scheme comparison Central inverter: The power is between 100kW and 2500kW. With the development of power electronics technology, the string inverter is having an increasingly bigger market, and the central inverters below 500KW have already basically been eliminated from the market. The power device adopts high-current IGBT.
How many panels can a central inverter have?
Central inverters could have approximately 2000-3000 panels operating from a single multi power point tracker (MPPT), leading to efficiency losses caused by module mismatch. The cost of cables is usually 33% higher with central inverters than with string with power losses that are 1% greater.
What is the difference between a central and string inverter?
The primary difference between central and string inverters is that a string inverter will typically sit at the end of each PV string, is distributed throughout the array, and receives fewer strings than a central inverter. In contrast, a central inverter aggregates multiple PV strings and is situated in the middle of all these strings.
What are the disadvantages of a central inverter?
Narrow MPPT voltage scope of the central inverter, generally 500-820V, inflexible component configuration, short power generation time in rainy or misty days. Difficult inverter machine room installation and deployment, require the dedicated machine room and equipment.
How many kilowatts can a central inverter handle?
Pad-mounted central inverter co-located with a medium-voltage transformer. The first PV inverters were developed in the 1980s as a spinoff of drive system technologies. At the time, all models could be considered central inverters rated to handle no more than a few kilowatts.
Do central inverters take up a lot of land?
Central inverters take up more land area as they need to be housed, and possible shading losses from this need to be considered. Central inverters have more perceived reliability, with more historical data on central inverters being used successfully. As mentioned above, string inverters tend to sit at the end of each PV string.
More related information
-
 Inverter voltage 630v
Inverter voltage 630v
-
 High voltage inverter outdoor amorphous
High voltage inverter outdoor amorphous
-
 Is the 220v voltage converted by the inverter stable
Is the 220v voltage converted by the inverter stable
-
 Inverter voltage per channel
Inverter voltage per channel
-
 Inverter outputs high voltage and low current
Inverter outputs high voltage and low current
-
 What is the appropriate current and voltage of the inverter
What is the appropriate current and voltage of the inverter
-
 Variable frequency inverter adjusts voltage
Variable frequency inverter adjusts voltage
-
 What is the module inverter voltage
What is the module inverter voltage
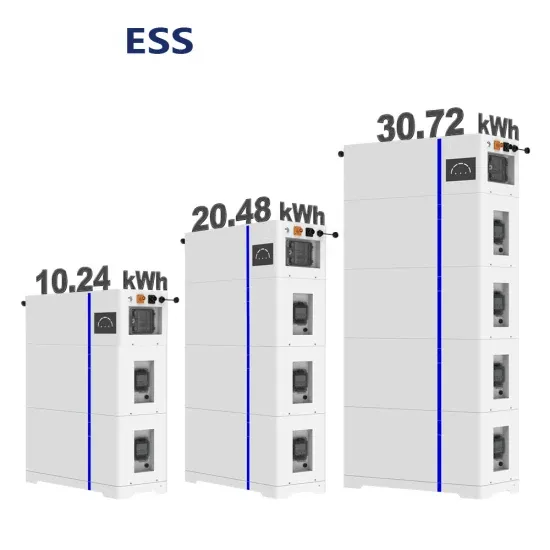
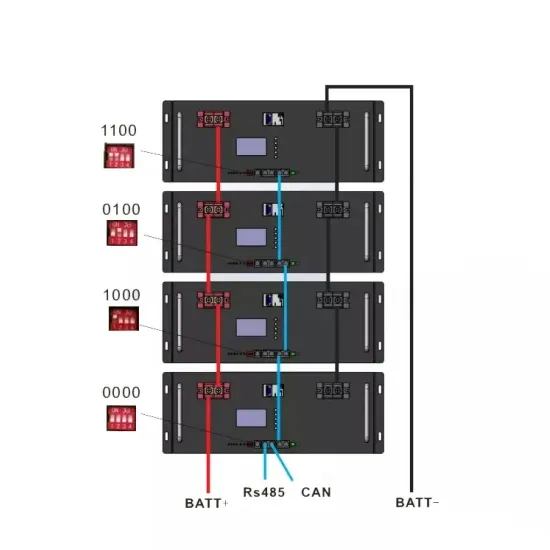
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


