Voltage Source Inverter : Construction, Phases & Its
3 Phase Full Bridge Voltage Source Inverter Working of Single-Phase Voltage Source Inverter A voltage source inverter can operate in any of 2 conduction
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter Circuit Diagram
So here we will discuss the working of an ideal three-phase converter circuit, neglecting all the issues related to a practical 3 phase inverter. A 3 phase inverter circuit
Get Price
[Solved] A three-phase voltage source inverter with ideal devices
A three-phase voltage source inverter with ideal devices operating in 180° conduction mode is feeding a balanced star-connected resistive load. The DC voltage input is V dc.
Get Price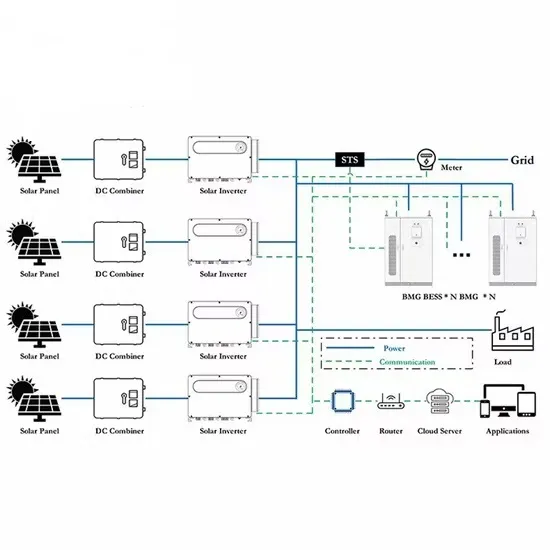
Three Phase Bridge Inverter Explained
This article outlines the definition and working principle of three phase bridge inverter. 180 degree conduction mode of operation, formula for phase & line voltages of three
Get Price
Derivation of a Stationary-Frame Single-Loop Controller for Three-Phase
In this paper, a stationary-frame, single loop controller for three-phase standalone inverter supplying nonlinear loads has been derived from synchronous reference frame proportional
Get Price
Three-Phase Inverter Design | Tutorials on Electronics | Next
The most common three-phase inverter topology is the Voltage Source Inverter (VSI), where a fixed DC voltage is converted into a variable AC output. The VSI employs six power switches
Get Price
How does a Three Phase Inverter Work? | inverter
Three-phase inverters play a crucial role in converting direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) in various applications, from industrial machinery to renewable
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter : Circuit, Working and Its
What is Three Phase Inverter? Definition: We know that an inverter converts DC to AC. We have already discussed different types of inverters. A three-phase
Get Price
How to calculate the loss of a three-phase inverter
How to calculate the switching loss and conduction loss of each IGBT in a three-phase inverter bridge circuit composed of IGBTs? Is there a
Get Price
Review, Comprehensive Analysis and Derivation of
Moreover, the literature lacks a detailed summarizing description of these analytical equations and their derivation, starting from the standard
Get Price
How does a Three Phase Inverter Work? | inverter
Three-phase inverters play a crucial role in converting direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) in various applications, from
Get Price
Three-Phase Inverters
The primary features and benefits of three-phase inverters over single-phase inverters are highlighted in this section. We will go through numerous three-phase inverter types, their
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter | DC-TO-AC INVERTER
The input dc voltage to the inverter is often derived from an ac source after rectification and filtering. A simple diode bridge rectifier followed by a filter
Get Price
CHAPTER4
4.1 Introduction In this chapter the three-phase inverter and its functional operation are discussed. In order to realize the three-phase output from a circuit employing dc as the input voltage a
Get Price
What is Three Phase Inverter and How Does It Work
Learn about what a three-phase inverter is, how it functions in a solar system, and its application areas.
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter Circuit Diagram
A three-phase inverter is a type of power electronic device that converts DC (Direct Current) power into AC (Alternating Current) power with three phases.
Get Price
Derivation of a Stationary-Frame Single-Loop Controller for Three-Phase
In this paper, a stationary-frame, single-loop controller for three-phase standalone inverter supplying nonlinear loads has been derived from synchronous reference frame
Get Price
Lecture 23: Three-Phase Inverters
One might think that to realize a balanced 3-phase inverter could require as many as twelve devices to synthesize the desired output patterns. However, most 3-phase loads are
Get Price
3-Phase Inverter
The Hybrid Multilevel Inverter is a three-phase inverter specially designed for industrial applications with medium voltage and high power demands. It uniquely combines
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter : Circuit, Working, Types & Its
This Article Discusses an Overview of What is a Three Phase Inverter, Circuit, Working, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages & Its Applications.
Get Price
CHAPTER 2
three-phase or multiphase topologies. Some industrial applications of inverters are for adjustable-speed ac drives, induction heating, standby aircraft power supplies, UPS (uninterruptible
Get Price
Analytic Calculation of The DC Link PDF | PDF
This document analytically calculates the DC-link capacitor current for pulsed three-phase inverters with symmetrical loads. It describes the pulse control
Get Price
Space Vector PWM Intro — Switchcraft
The above schematic is the well-known and well-used inverter topology. From left to right the following is shown: A three phase supply and a three-phased diode rectifier A DC-link
Get Price
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
Types of Inverters: Inverters are categorized by their output waveforms (square wave, modified sine wave, and sine wave) and by their load type (single-phase and three-phase).
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter | DC-TO-AC INVERTER
The input dc voltage to the inverter is often derived from an ac source after rectification and filtering. A simple diode bridge rectifier followed by a filter capacitor is often the most cost
Get Price
Three Phase VSI with 120° and 180° Conduction Mode
A three-phase inverter is a type of power electronic device that converts DC (Direct Current) power into AC (Alternating Current) power with three phases. It is widely used in various
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Derivation of three-phase inverter]
What is a 3 phase inverter circuit diagram?
A 3 phase inverter circuit diagram converts DC voltage into balanced three-phase AC supply using six switching devices. What is a Three Phase Inverter? A three phase inverter is an electronic power conversion device that transforms DC input voltage into a balanced three-phase AC output.
What is a three phase bridge inverter?
A three phase bridge inverter is a device which converts DC power input into three phase AC output. Like single phase inverter, it draws DC supply from a battery or more commonly from a rectifier. A basic three phase inverter is a six step bridge inverter. It uses a minimum of 6 thyristors.
What is a three-phase inverter?
Modern electronic systems cannot function without three-phase inverters, which transform DC power into three-phase AC power with adjustable amplitude, frequency, and phase difference. They are essential in several applications, including as power distribution networks, renewable energy systems, and industrial motor drives.
How many switches are in a three phase inverter?
The three-phase inverter consists of six switches, typically arranged in a bridge configuration, and each phase is connected to a load as shown in Figure 1. The switching patterns and timing of the switches determine the shape, magnitude, and frequency of the output voltage. 1. Three Phase 180° Mode Voltage Source Inverter
How does a DC power source work in a three-phase inverter?
The DC power source of the three-phase current-type inverter, i.e., the DC current source, is achieved through a variable voltage source using current feedback control. However, employing only current feedback cannot reduce the power ripple in the inverter input voltage caused by switch actions, resulting in current fluctuations.
What is 180 degree conduction mode in a 3 phase inverter?
In the 180-degree conduction mode, the driven conduction time of each three phase inverter circuit is precisely 180° of the fundamental period. Hence, better voltage utilisation is offered under a three-phase inverter output voltage. Maximum voltage utilisation from a DC source. Maximum fundamental voltage output. High power transfer capability.
More related information
-
 Three-phase inverter derivation
Three-phase inverter derivation
-
 Off-grid 30kw three-phase 380v inverter
Off-grid 30kw three-phase 380v inverter
-
 Namibia three-phase low voltage inverter
Namibia three-phase low voltage inverter
-
 DC component of three-phase inverter
DC component of three-phase inverter
-
 Three-phase electric water pump inverter can use inverter
Three-phase electric water pump inverter can use inverter
-
 Three-phase inverter square wave
Three-phase inverter square wave
-
 Mongolia three-phase inverter price
Mongolia three-phase inverter price
-
 Vanuatu three-phase inverter manufacturer
Vanuatu three-phase inverter manufacturer
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.