An optimal dispatch strategy for 5G base stations equipped with
Therefore, this paper proposes an optimal dispatch strategy for 5G BSs equipped with BSCs. Firstly, a joint dispatch framework is established, where the idle capacity of
Get Price
Chapter 3: Basic Architecture — 5G Mobile Networks:
Chapter 3: Basic Architecture ¶ This chapter identifies the main architectural components of cellular access networks. It focuses on the components that
Get Price
Coordination of Macro Base Stations for 5G Network with User
The coordination among the communication equipment and the standard equipment in 5G macro BSs is developed to reduce both the energy consumption and the electricity costs.
Get Price
5G RAN Architecture: Nodes And Components
Base Station Controller (BSC): The BSC manages one or more BTS units. It handles tasks such as handovers, frequency hopping, and power level control.
Get Price
Base Station Subsystem (BSS) in System
In post Introduction to System Architecture of Global System for Mobile communications (GSM), already introduced about component of GSM
Get Price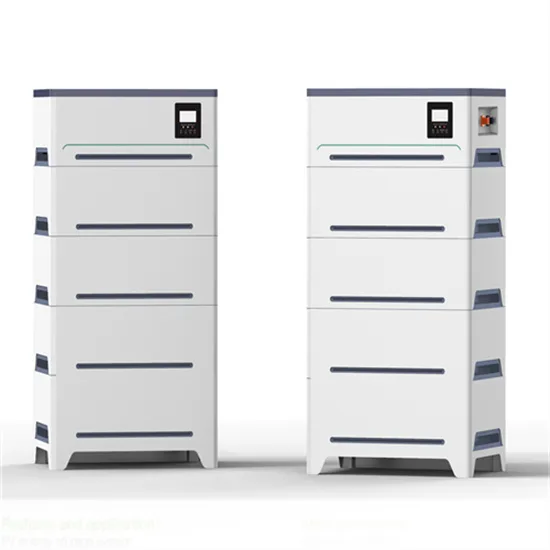
The Future of Hybrid Inverters in 5G Communication Base Stations
Conclusion: As 5G networks expand, hybrid inverters will play a pivotal role in powering next-gen base stations—providing stable, cost-effective, and green energy solutions
Get Price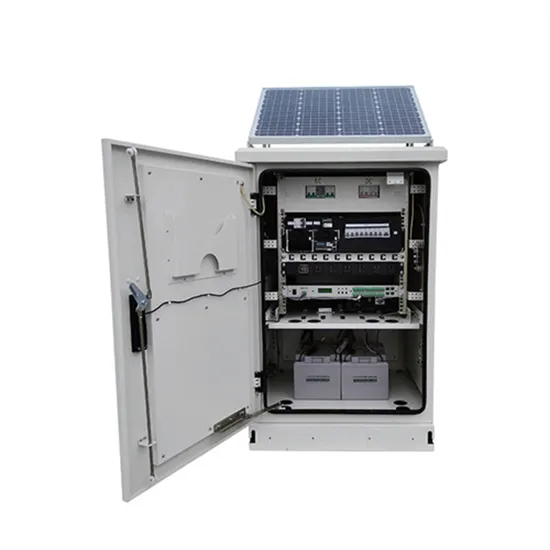
General Architecture and working principle of 2G, 3G, 4G,and 5G
Base Station Subsystem (BSS): This includes the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) that communicates with the mobile phone and the Base Station Controller (BSC) that
Get Price
GSM Base transceiver station
The document provides an extensive overview of Base Transceiver Stations (BTS), detailing their functions, components, operations, and configurations
Get Price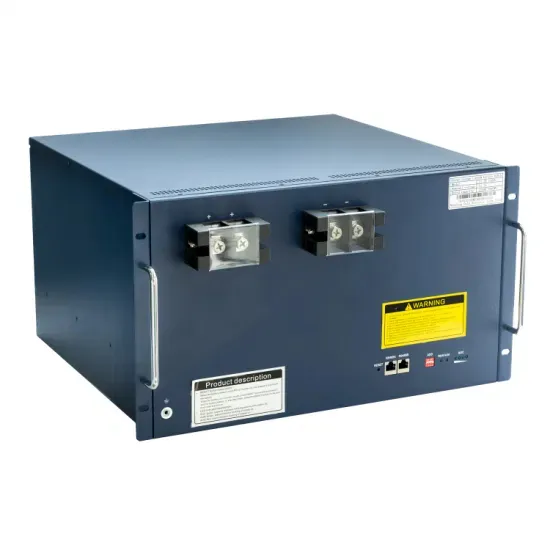
An Introduction to 5G and How MPS Products Can Optimize
This article described the basics of 5G and introduced two MPS parts — the MPQ8645 and MP87190 — that can be used to improve the AAU or BBU architecture within a 5G base cell
Get Price
Base Station Antennas for the 5G Mobile System
The fifth-generation (5G) mobile communication system will require the multi-beam base station. By taking into account millimeter wave use, any antenna types such as an array, reflector and
Get Price
5G Network Architectures and Technologies
In NSA networking, 5G base stations cannot be deployed independently, requiring LTE base stations to be used as anchor points on the control plane for access to the core network. NSA
Get Price
5g Base Station royalty-free images
Find 5g Base Station stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection. Thousands of new, high-quality pictures
Get Price
What is BSC in 5g?
Base Station Controller (BSC): The Base Station Controller was a key component in 2G and 3G Mobile Networks. It Played A Central Role in Managing and Controlling Multiple
Get Price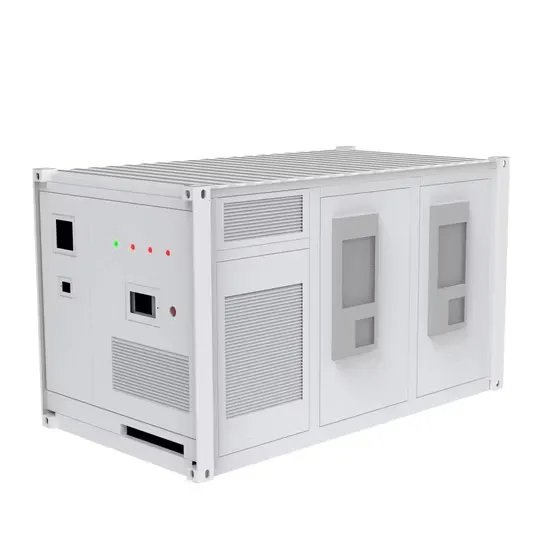
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile
Base stations and cell towers are critical components of cellular communication systems, serving as the infrastructure that supports seamless
Get Price
BS (Base Station)
A base station (BS) is a key component of modern wireless communication networks, providing the interface between wireless devices and the network infrastructure. In
Get Price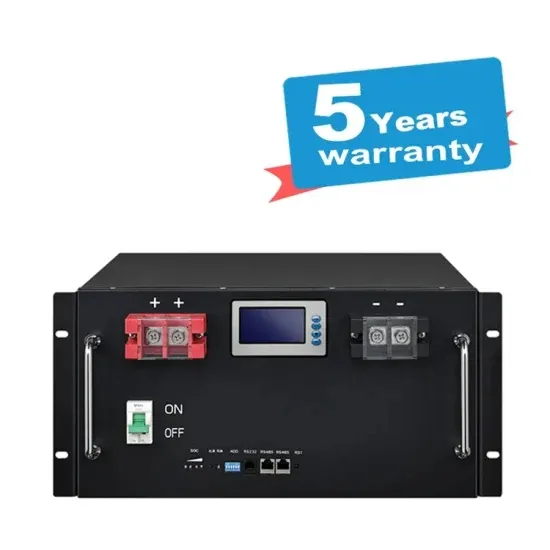
5G RAN Architecture: Nodes And Components
The UE communicates with the network infrastructure through the base station, which serves as the access point for wireless connections. In the context of 5G RAN, UE
Get Price
Base Station Controller
The BSC forms part of the BSS (Base Station Subsystem) and controls a number of BTS (Base Transceiver Stations). In this role, the BSC is responsible for activities such as radio control,
Get Price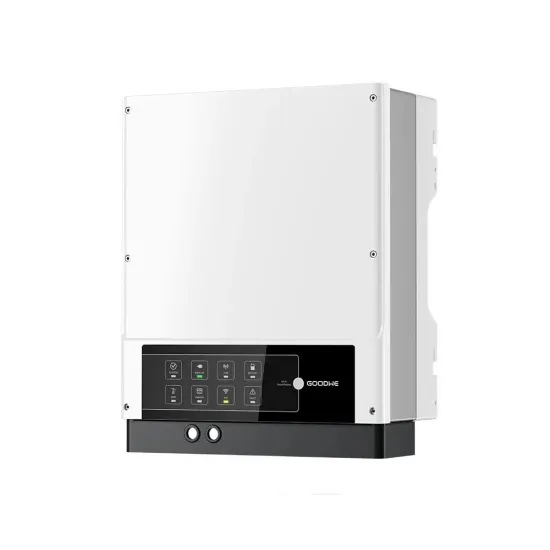
Basic components of a 5G base station
The basic components of a 5G BS, which are illustrated in Figure 1 [20], mainly include communication equipment and power supply equipment.
Get Price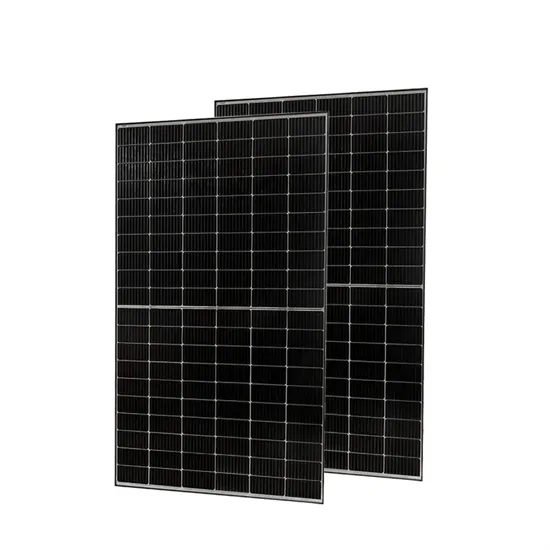
Basestation
A base station (BS) is defined as a fixed communication facility that manages radio resources for one or more base transceiver stations (BTSs), facilitating radio channel setup, frequency
Get Price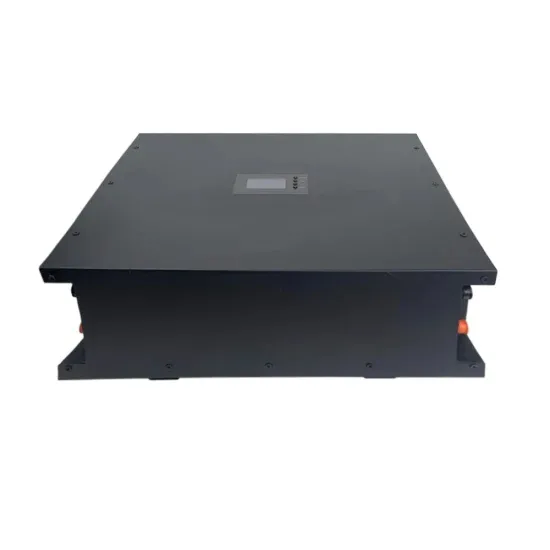
General Architecture and working principle of 2G, 3G,
Base Station Subsystem (BSS): This includes the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) that communicates with the mobile phone and the
Get Price
What Is a gNB in 5G? Next-Gen Base Station Architecture
It represents the base station in a 5G network architecture, facilitating communication between the user equipment (UE) and the core network. Unlike its
Get Price
2g 3g 4g 5g architecture
A technical overview of the architectures of 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G mobile networks. 2G (Second Generation): 1. Architecture: Network
Get Price
The Applicability of Macro and Micro Base Stations for 5G Base Station
The construction of the 5G network in the communication system can potentially change future life and is one of the most cutting-edge engineering fields today. The 5G base
Get Price
bss 5g
Base Station Controller (BSC): The BSC manages one or more BTS units. It handles tasks such as handovers, frequency hopping, and power level control.
Get Price
What is BSC (base station controller)
A BSC is a critical component in mobile networks that manages one or more Base Transceiver Stations (BTS), also known as base stations or cell sites. Its primary functions include: Radio
Get Price
5G Base Station Architecture
Uncover the intricate world of 5G Base Station Architecture, from gNode B to NGAP signaling. Dive into flexible network deployment options.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [5g communication base station inverter equipment bsc introduction]
What is a 5G base station controller (BSC)?
In 5G, the network architecture is based on the 5G Core (5GC) and the New Radio (NR). That said, let’s provide information about the historical context of BSC: Base Station Controller (BSC): The Base Station Controller was a key component in 2G and 3G mobile networks.
What is a 5G base station?
Base Station Base Station (BS) is a key component of the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) architecture that serves as an access point for wireless connections between user equipment (UE) and the network. It consists of a radio unit and an antenna system that transmits and receives signals to and from the UE.
What is a BSc in 5G?
In summary, while the traditional concept of the BSC is not directly applicable in 5G, the evolution of network architecture in 5G involves the distributed and flexible roles of the Central Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit (DU). These components collectively contribute to the efficient management and coordination of radio resources in 5G networks.
What is BS in 5G ran?
The BS is responsible for establishing, maintaining, and releasing wireless connections to the network, enabling seamless connectivity for the UE. In 5G RAN, BS nodes can also support multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) antennas, increasing the network capacity and data throughput for improved performance.
What is 5G ran architecture?
One of the key components of 5G is the Radio Access Network (RAN) architecture, which is responsible for managing the wireless connections between devices and the network. This article will provide a technical overview of the 5G RAN architecture, including its various nodes and components.
What is a 5G ran control unit?
Control Unit (CU) The Central Unit (CU) efficiently orchestrates network resources and manages base stations, playing a critical role in enhancing 5G RAN performance and adaptability. One of the key functions of the CU is to establish and release connections between user equipment and the network.
More related information
-
 Communication base station inverter equipment sales ranking
Communication base station inverter equipment sales ranking
-
 Yaounde 5G communication base station inverter grid-connected project
Yaounde 5G communication base station inverter grid-connected project
-
 5g communication base station inverter process
5g communication base station inverter process
-
 Liberia 5G communication base station inverter space layout planning
Liberia 5G communication base station inverter space layout planning
-
 Communication 5G base station equipment energy method
Communication 5G base station equipment energy method
-
 5g communication base station battery energy storage cabinet equipment
5g communication base station battery energy storage cabinet equipment
-
 China s 5G communication base station inverter grid connection construction
China s 5G communication base station inverter grid connection construction
-
 Communication base station inverter grid-connected power equipment
Communication base station inverter grid-connected power equipment
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


