Photovoltaic Efficiency: The Temperature Effect
This article examines how the efficiency of a solar photovoltaic (PV) panel is affected by the ambient temperature. You''ll learn how to predict the power output of a PV panel at different
Get Price
Do solar panels work better on hot days?
Solar panels work by using incoming photons to excite electrons in a semiconductor to a higher energy level. But the hotter the panel is, the greater the number of electrons that are already in
Get Price
Solar Panel Efficiency vs. Temperature (2025) | 8MSolar
One of the most significant yet often misunderstood factors is temperature. In this guide, we''ll explore the relationship between solar panel efficiency and temperature, diving into
Get Price
The Impact of Temperature on Solar Panel Performance: What
In this article, we delve deeper into the effects of temperature on solar panel efficiency and explore how temperature fluctuations can affect their overall performance. We
Get Price
How Does Temperature Affect Solar Panels?
High and low temperatures affect solar panel efficiency, but solar panels work just fine in places with extreme heat and cold.
Get Price
How Temperature Impacts Solar Cell Efficiency
At higher temperatures, the increased thermal energy in the semiconductor material causes more electrons to become excited and move randomly, leading to higher electrical
Get Price
Solar energy is quickly becoming a popular choice for
The Anker SOLIX PS400 Portable Solar Panel, for instance, is a monocrystalline solar panel boasting 23% efficiency. This makes them the
Get Price
How Much Electricity Do Solar Panels Generate?
The Concept of Solar Panel Wattage and Its Significance Wattage Explained: Definition: Wattage is the measure of electrical power output,
Get Price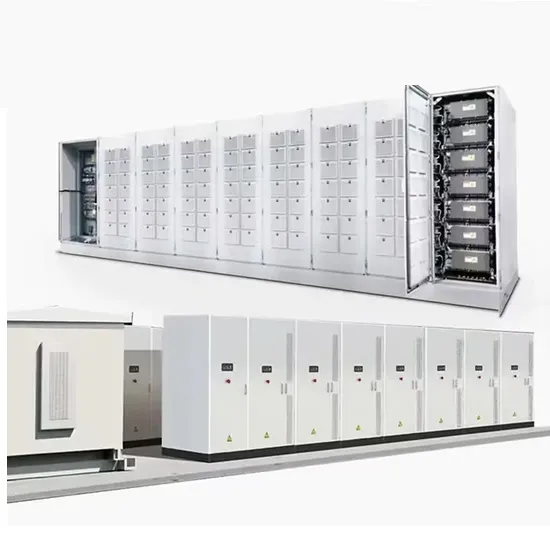
Thermal effects in photovoltaic systems
Semiconductor Properties: Most photovoltaic cells are made from silicon, a semiconductor whose electrical properties change with temperature.
Get Price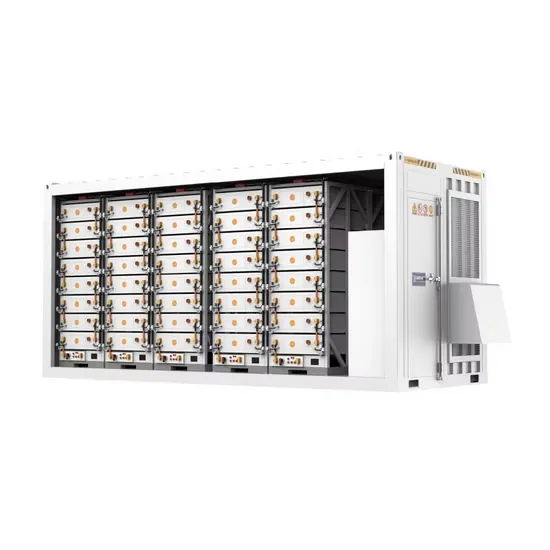
Do Solar Panels Work Less Efficiently at Certain Temperatures?
When a solar panel is hot, the difference between the rest state and the excited energy state is smaller, so less energy is created. The opposite happens when a solar panel is
Get Price
Effect of Temperature on Solar Panel Efficiency |Greentumble
Most of us would assume that the stronger and hotter the sun is, the more electricity our solar panels will produce. But that''s not the case. One of the key factors
Get Price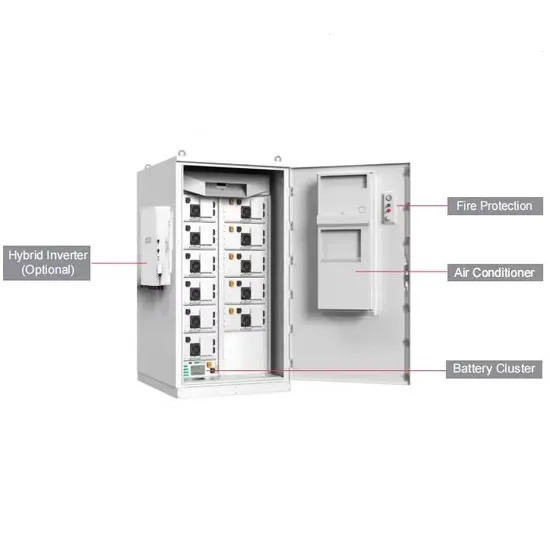
Temperature Dependent Photovoltaic (PV) Efficiency and Its Effect on PV
Solar cell performance decreases with increasing temperature, fundamentally owing to increased internal carrier recombination rates, caused by increased carrier concentrations.
Get Price
Understanding Solar Panel Performance Metrics
Solar energy is a rapidly growing industry, and with the increasing number of solar installations, it''s important for people to understand how solar panels
Get Price
What Are the Effects of Temperature on Solar Panel
Temperature, humidity, and solar panel efficiency are interconnected factors that impact the overall performance of a photovoltaic system. In general, research
Get Price
how do solar panels generate electricity
The Science Behind Solar Energy The Photovoltaic Effect: Definition: The photovoltaic (PV) effect is the process by which solar panels
Get Price
How Does Temperature Affect Solar Panels: A Deep Dive
For every degree Celsius increase above their optimal operating temperature (usually around 25°C), solar panels'' efficiency declines by about 0.3% to 0.5%. So, while
Get Price
How Does Temperature Affect Solar Panels: A Deep
For every degree Celsius increase above their optimal operating temperature (usually around 25°C), solar panels'' efficiency declines by about
Get Price
What is the Maximum Temperature a Solar Panel Can
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity. The maximum temperature a solar panel can withstand depends on the type of
Get Price
The Impact of Temperature on Solar Panel
In this article, we delve deeper into the effects of temperature on solar panel efficiency and explore how temperature fluctuations can affect their
Get Price
How Temperature Impacts Solar Cell Efficiency
At higher temperatures, the increased thermal energy in the semiconductor material causes more electrons to become excited and move
Get Price
The Science Behind Solar Panels: How They Convert Sunlight into Electricity
The cost of solar panels has decreased significantly over the past decade, making solar energy more accessible to homeowners and businesses. The economic benefits of solar panels
Get Price
Thermal effects in photovoltaic systems
Learn how temperature impacts photovoltaic system efficiency, the consequences of thermal effects on solar panels, and strategies to
Get Price
The Effects of Specific Weather Conditions on Solar
The Effects of the Environment and Different Seasons on Solar Panels and Mitigation Strategies Solar energy is a pivotal component of the
Get Price
Solar Panel Efficiency vs. Temperature (2025) | 8MSolar
One of the most significant yet often misunderstood factors is temperature. In this guide, we''ll explore the relationship between solar panel
Get Price
How Physics Powers Solar Panels and Renewable Energy
If they do, and if their energy is high enough, they can knock electrons free, forming current. The freed electrons flow through the external circuit—lighting a bulb, charging
Get Price
Temperature Coefficient''s Impact on Solar Panel Efficiency
Discover the crucial relationship between temperature coefficient and solar panel efficiency. Learn how environmental factors affect solar power generation now!
Get Price
Does Temperature Affect Solar Panels? Unveiling the
Overview of Solar Panels and Temperature Yes, temperature does affect solar panels. High temperatures can reduce the efficiency of solar
Get Price
Thermal effects in photovoltaic systems
Semiconductor Properties: Most photovoltaic cells are made from silicon, a semiconductor whose electrical properties change with temperature. As temperature
Get Price
How Temperature Affects Solar Panels: A
A change as small as 1-degree Celsius can make a solar panel up to 0.5% less efficient. This shows how important temperature is for solar
Get Price
What Are the Effects of Temperature on Solar Panel Efficiency?
Temperature, humidity, and solar panel efficiency are interconnected factors that impact the overall performance of a photovoltaic system. In general, research has found that higher
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Does the higher the temperature of photovoltaic panels the more electricity they generate ]
Do solar panels work less at certain temperatures?
This is because of the unique characteristics of a solar panel. This difference plays a major role in answering the question of whether or not solar panels work less at certain temperatures. The number one (often forgotten) rule of solar electricity is that solar panels generate electricity with light from the sun, not heat.
How does temperature affect solar panels?
In a nutshell: Hotter solar panels produce less energy from the same amount of sunlight. Luckily, the effect of temperature on solar panel output can be calculated and this can help us determine how our solar system will perform on summer days. The resulting number is known as the temperature coefficient.
Do solar panels produce electricity if it's Hot?
High temperatures can cause a decrease in panel efficiency due to the temperature coefficient. However, it’s worth noting that solar panels still produce electricity even on hot days. They are designed to dissipate excess heat to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Why do solar panels produce more power than rated capacity?
With ambient temperatures often below freezing and panel temperatures around 10°C (50°F), the system regularly produced 10-15% more power than its rated capacity. The combination of high solar irradiance and low temperatures led to efficiency gains of up to 10% above rated values.
How does temperature affect the efficiency of a photovoltaic (PV) cell?
Several factors can influence how temperature affects the efficiency of a photovoltaic (PV) cell. One of the most significant factors is the ambient temperature, which refers to the temperature of the surrounding environment. PV cells are exposed to varying ambient temperatures throughout the day and across different seasons.
Do solar panels produce more power?
For example, at 0°C (32°F), a panel might produce 5-7% more power than its rated output. It’s worth noting that while efficiency decreases with temperature, the total energy output might still be higher on a hot, sunny day compared to a cool, cloudy day, simply due to the increased solar irradiance.
More related information
-
 Suitable temperature for photovoltaic panels to generate electricity
Suitable temperature for photovoltaic panels to generate electricity
-
 545 Photovoltaic panels generate electricity in one day
545 Photovoltaic panels generate electricity in one day
-
 Is it cost-effective to generate electricity from photovoltaic panels in factories
Is it cost-effective to generate electricity from photovoltaic panels in factories
-
 Photovoltaic panels generate electricity for home use at 220V
Photovoltaic panels generate electricity for home use at 220V
-
 Can solar photovoltaic panels generate enough electricity for home use
Can solar photovoltaic panels generate enough electricity for home use
-
 How much electricity can forty photovoltaic panels generate
How much electricity can forty photovoltaic panels generate
-
 Which photovoltaic panels generate the best electricity in Saudi Arabia
Which photovoltaic panels generate the best electricity in Saudi Arabia
-
 Photovoltaic panels that can generate electricity during the day
Photovoltaic panels that can generate electricity during the day
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


