
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
Inverter is the device which converts DC into AC is known as Inverter. Most of the commercial, industrial, and residential loads require Alternating Current (AC) sources. One of the main
Get Price
Single Phase vs Split Phase Inverter: Key Differences
Compare single phase and split phase inverters to find the right fit for your energy needs. Learn their pros, cons, uses, and benefits for home
Get Price
Inverter Generator vs Generator: What''s the Difference?
Generators and inverter generators are two popular options that provide power when we need it most. But what is the difference between
Get Price
Invertor vs. Inverter — What''s the Difference?
What''s the difference between an inverter and a converter? An inverter converts DC power to AC power, while a converter does the opposite,
Get Price
Pure Sine Wave vs. Modified Sine Wave Inverters:
Learn the difference between pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters. Discover which one is right for your electronics, appliances,
Get Price
Inverter vs Transformer Welder: Power, Efficiency
Choosing between inverter vs transformer welder options? Our guide breaks down performance differences, efficiency ratings, and true cost
Get Price
Inverters Guide
What is the difference between a Modified/Quasi Sinewave Inverter and a Pure Sinewave Inverter? An inverter will create an output frequency (i.e.
Get Price
What''s the Difference Between 110v and 220v?
At first, discussing the difference between 110v and 220v power can seem complicated, but remember that they are really two sides of the same coin.
Get Price
Key differences between three-phase 220V and three
In this paper, we will discuss the nine core differences between three-phase 220V and three-phase 380V inverters, to help readers more fully
Get Price
Difference Between 220V & 380V 3-Phase Power
Understanding the difference between 220V and 380V three-phase power supplies, including how inverters handle these voltage levels. Learn
Get Price
220 Volt Inverter: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right One
What is the difference between modified and pure sine wave inverters? Modified sine wave inverters are more affordable and suitable for basic devices, while pure sine wave
Get Price
Types of Power Inverters And How To Choose
Discover the different types of power inverters and learn how to choose the right one for your needs. Expert advice from Junchipower.
Get Price
120v vs 240v Mini Split Efficiency
In terms of efficiency the only difference may be how efficient the "inverter " or variable frequency drive is. Where none of the answers below touch on is balancing your
Get Price
Power Play: Unveiling the Efficiency Battle: 110v vs.
The primary difference between 110v and 220v AC systems lies in the magnitude of this potential difference. While 110v AC delivers a lower
Get Price
Installation Tips: 110v vs 220v Mini Split Considerations
Choosing between a 110V and 220V mini-split can seem daunting, but by understanding the key differences and considering one''s specific needs, one can make an
Get Price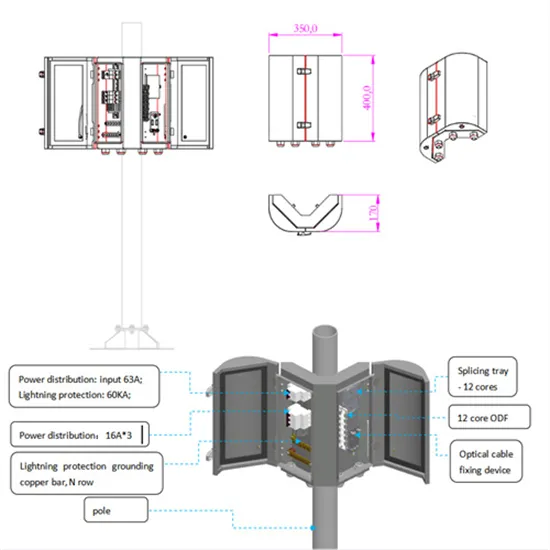
voltage
I would assume 220V loads would be more energy expensive to run, as the voltage converter adds another step in energy conversion and every step results in some energy loss.
Get Price
Understanding Inverters and How-to Select one that is right for you
Voltage is essentially the difference in electrical charge between two points. The greater the voltage difference, the greater the flow of electrical current if all other factors remain the same
Get Price
Invertor vs. Inverter — What''s the Difference?
What''s the difference between an inverter and a converter? An inverter converts DC power to AC power, while a converter does the opposite, changing AC power to DC power.
Get Price
Difference Between 220V & 380V 3-Phase Power Supplies:
Understanding the difference between 220V and 380V three-phase power supplies, including how inverters handle these voltage levels. Learn about voltage between
Get Price
Key differences between three-phase 220V and three-phase 380V inverters
In this paper, we will discuss the nine core differences between three-phase 220V and three-phase 380V inverters, to help readers more fully understand the application
Get Price
Understanding Inverters and How-to Select one that is
Voltage is essentially the difference in electrical charge between two points. The greater the voltage difference, the greater the flow of electrical current if all
Get Price
12V vs 24V Inverter: What''s The Difference & Which is Better
Torn between 12V and 24V inverters? Discover the key differences in efficiency, cost, and power capacity to determine which is better for your energy needs.
Get Price
Pros and Cons of Inverter Generators
Consumer Reports'' expert, independent tests find that inverter generators run longer, quieter, and more efficiently than other generators. But they cost more.
Get Price
What is the Difference Between Single-Phase and
Understanding the differences between single-phase and three-phase inverters is crucial when designing or upgrading your solar system. These two types of
Get Price
The difference between inverter output three-phase 220v and
In short, there are certain differences between three-phase 220V and three-phase 380V inverters in terms of voltage level, power capacity, motor drive, energy consumption,
Get Price
The Only Inverter Size Chart You''ll Ever Need
FAQs What is the difference between a modified sine wave inverter and a pure sine wave inverter? A pure sine wave inverter replicates
Get Price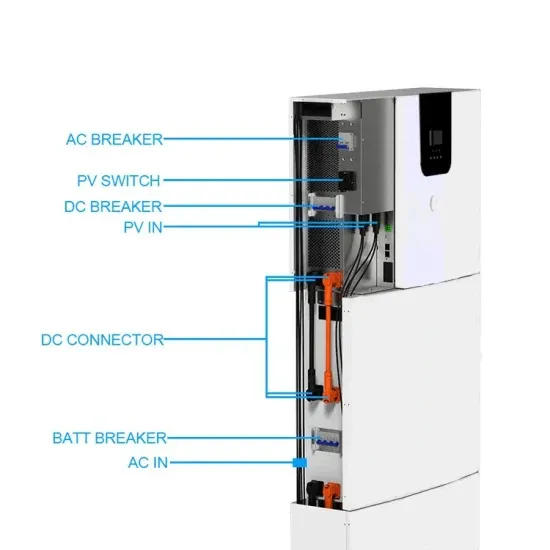
220 Volts vs 110 Volts AC. Which one is better and
220v and 110v are the most common type of AC mains supply we use. But the question is why do we have two options and as we have two options then
Get Price
Single Phase vs Split Phase Inverter: Key Differences Explained
Compare single phase and split phase inverters to find the right fit for your energy needs. Learn their pros, cons, uses, and benefits for home and solar setups.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Difference between inverter and 220v]
What is the difference between 220V and 380V?
It is clarified that 220V is typically the phase-to-neutral voltage, while 380V is the phase-to-phase voltage in a three-phase system. Inverters can be designed for single-phase (230V) or three-phase (400V) outputs, with configurations such as star (Y) and delta (Δ) affecting the voltage levels.
What are the different types of inverters?
Inverters are classified into many different categories based on the applied input source, connection wise, output voltage wise etc. In this article, we will see some of the categories. The inverter can be defined as the device which converts DC input supply into AC output where input may be a voltage source or current source.
Are all inverters the same?
That’s where inverters come into play. They’re the quiet heroes turning DC (direct current) power from your solar panels or batteries into AC (alternating current) power that your home can actually use. But here’s where things get tricky: not all inverters are the same.
What is a single phase inverter?
A single phase inverter is like the basic workhorse of inverters. It takes direct current (DC) power from a source, like solar panels or batteries, and converts it into alternating current (AC) power. AC is the kind of electricity your home uses for running appliances, so this conversion is very important.
Are split phase solar inverters the same as two phase inverter?
" Split phase Solar Inverter is the same as two phase inverter": Nope, they’re not the same! Split phase inverters use a single power source to deliver two 120V outputs that are 180 degrees out of phase. Two-phase, on the other hand, is a totally different system with separate power sources, and it’s rarely used today.
What is a voltage source inverter?
The inverter is known as voltage source inverter when the input of the inverter is a constant DC voltage source. The input to the voltage source inverter has a stiff DC voltage source. Stiff DC voltage source means that the impedance of DC voltage source is zero. Practically, DC sources have some negligible impedance.
More related information
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.



 The difference between 12v and 220v inverter
The difference between 12v and 220v inverter
 Combined inverter 220v
Combined inverter 220v
 220v to 7kw inverter
220v to 7kw inverter
 37v to 220v inverter production
37v to 220v inverter production
 Universal home inverter 12v to 220v
Universal home inverter 12v to 220v
 12kw output 220V inverter
12kw output 220V inverter
 How many watts does a 24V to 220V inverter have
How many watts does a 24V to 220V inverter have
 Slovakia 96v to 220v inverter power supply
Slovakia 96v to 220v inverter power supply