Installation of solar power generation facilities in North Korea
Bid for tender to Installation of solar power generation facilities in North Korea by Incheon International Airport Corporation in Korea. Access documents, deadlines, and CPV
Get Price
N. Korea expands renewable energy focus in revised
The updated legislation represents Pyongyang''s ambitious attempt to stabilize the country''s chronically unreliable electricity grid through
Get Price
Exploring solar and wind energy resources in North Korea with
Although the region''s mountainous terrain may be an obstacle for future development of renewable energy infrastructure, these initial annual mean solar and wind
Get Price
SOUTH KOREA''S SOLAR POWER INDUSTRY: STATUS
South Korea''s National Assembly has recently passed legislation to encourage further solar PV deployment. Under the Special Act on the Promotion of Distributed Energy, the national
Get Price
Renewable Energy in North Korea
Prioritizing the development of off-grid renewable energy in North Korea, such as solar panels and wind turbines, near under-electrified rural areas will provide a more
Get Price
North Korea Electricity Generation Mix 2022 | Low
History North Korea''s history of low-carbon electricity generation, predominantly through hydropower, has seen periods of expansion and decline over the
Get Price
Power-starved North Korea turns to solar energy to keep the
North Korea is increasingly turning to solar power to help meet its energy needs, as the isolated regime seeks to reduce its dependence on imported fossil fuels amid chronic
Get Price
South Korea''s 2024 solar additions surpassed 3.1 GW
South Korea deployed over 3.1 GW of solar last year, according to provisional figures published by the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO). The utility''s figures are
Get Price
N. Korea expands renewable energy focus in revised power
The updated legislation represents Pyongyang''s ambitious attempt to stabilize the country''s chronically unreliable electricity grid through enhanced energy management
Get Price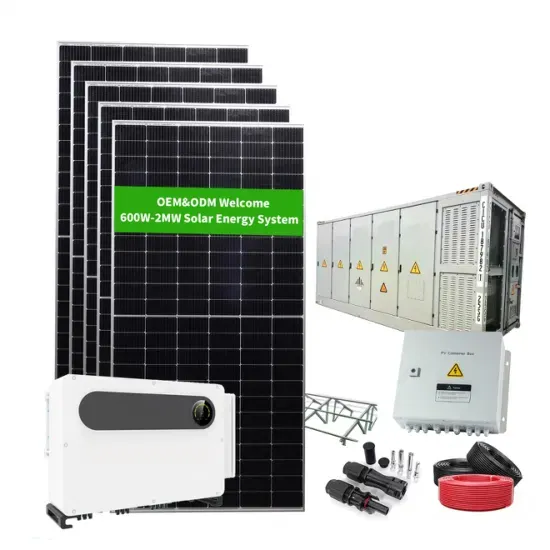
North Korea''s Energy Sector: Civilian Solar Power
In this installment of our series on North Korea''s energy sector, we move away from official and commercial uses of solar and seek to understand
Get Price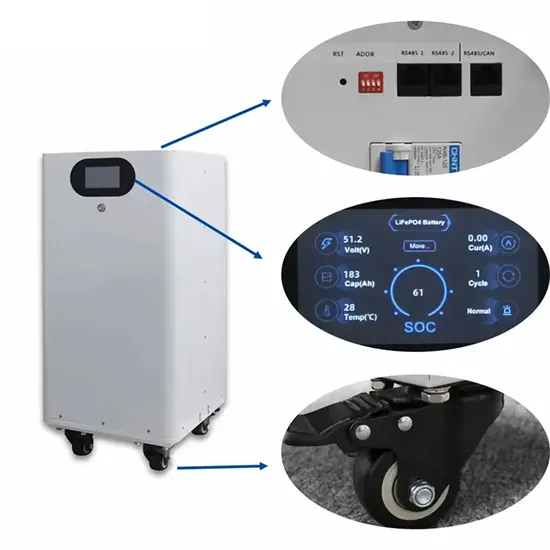
North Korea''s Energy Sector: Notable Solar Installations
In the last installment of our series on North Korea''s energy sector, we looked at state development of solar power and panels and discussed how solar was beginning to
Get Price
How many solar panels does North Korea have? | NenPower
Solar energy in North Korea operates primarily through the use of photovoltaic solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity. The country has started to adopt various solar
Get Price
North Korea solar cell power
Does North Korea have solar energy? In this second installment of our series on North Korea''s energy sector,we will examine the evolution of solar energy in the state''s energy plans and
Get Price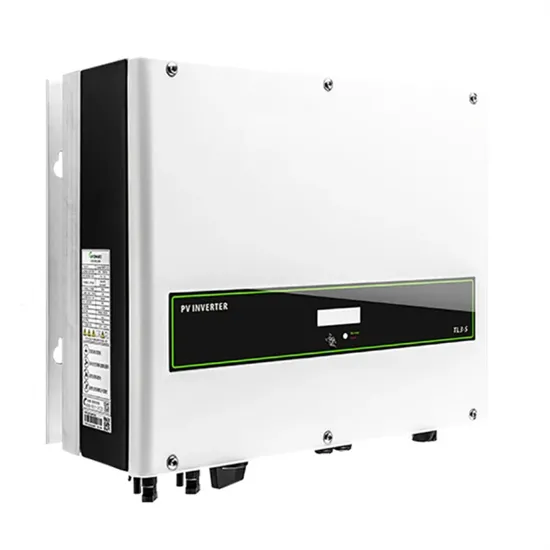
North Korea solar city system
Jeong-hyeon,a North Korean escapee,told the Financial Times that many residents in Hamhung,the second-most populous city,"relied on a solar panel,a battery and a power
Get Price
Bottlenecks to renewable energy integration in South
Renewable energy capacity in South Korea increased sixfold from 2013 to 2023. However, renewable electricity generation rose only threefold
Get Price
North Korea''s Energy Sector: State Solar Electricity
In this second installment of our series on North Korea''s energy sector, we will examine the evolution of solar energy in the state''s energy
Get Price
Energy in South Korea
Yongpyeong wind farm South Korea is a major energy importer, importing nearly all of its oil needs and ranking as the second-largest importer of liquefied
Get Price
South Korea plans 120 GW space solar project
Two Korean research institutes are designing the 2.2 km × 2.7 km Korean Space Solar Power Satellite project with the aim of providing
Get Price
Solar power station near me North Korea
In this installment of our series on North Korea''s energy sector, we move away from official and commercial uses of solar and seek to understand the growing use of solar power for personal
Get Price
Power-starved North Korea turns to solar energy to
North Korea is increasingly turning to solar power to help meet its energy needs, as the isolated regime seeks to reduce its dependence on
Get Price
Smart grid inverter North Korea
Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL): A Review to Advance Smart Inverter Over the past decade, the world''''s electrical grid infrastructure has experienced rapid growth in the integration of grid
Get Price
Energy Cooperation With North Korea: Conditions Making
For instance, the Korea East–West Power Company proposed solar and wind power plants as a short-term solution to North Korean energy shortage, as building them would require a much
Get Price
North Korea Solar electricity generation
North Korea: Solar electricity generation, billion kilowatthours: The latest value from 2023 is 0.15 billion kilowatthours, unchanged from 0.15 billion kilowatthours in 2022. In comparison, the
Get Price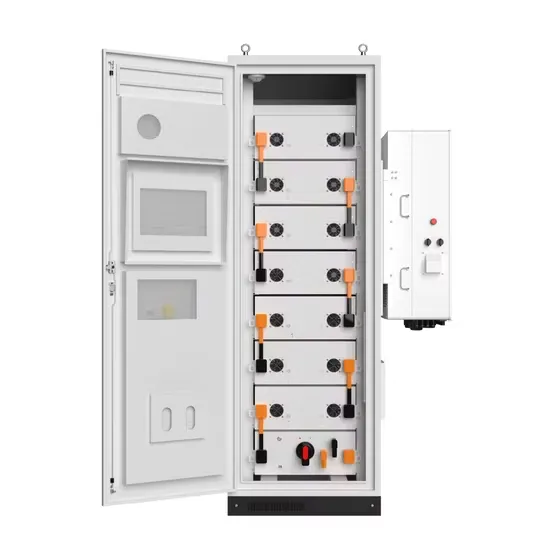
North Korea''s Energy Sector: State Solar Electricity Research and
In this second installment of our series on North Korea''s energy sector, we will examine the evolution of solar energy in the state''s energy plans and policies.
Get Price
<Inside N. Korea>Solar and Biomass Power Facilities Being
2 days ago· The introduction of renewable energy is being promoted on North Korean farms. According to central government directives, the installation of solar power generation and
Get Price
Power grid solar North Korea
North Korea is increasingly turning to solar power to help meet its energy needs,as the isolated regime seeks to reduce its dependence on imported fossil fuels amid chronic power shortages.
Get Price
NORTH MACEDONIA PUTS ITS BIGGEST SOLAR POWER
North Korea solar power plant setup cost The reactor design that would be used in North Korea is estimated to cost $6 billion and likely take five years or longer for construction, delaying power
Get Price
6 FAQs about [North Korea s solar power generation system]
Does North Korea have solar energy?
In this second installment of our series on North Korea’s energy sector, we will examine the evolution of solar energy in the state’s energy plans and policies. Hydropower still makes up the bulk of the country’s renewable energy generation, but solar has become increasingly important over the past decade.
How many solar panels are there in North Korea?
The Korea Energy Economics Institute in Seoul estimates that 2.88mn solar panels, mostly small units used to power electronic devices and LED lamps, are now in use across North Korea, accounting for an estimated 7 per cent of household power demand.
Can solar power solve North Korea's energy problems?
Jeong-hyeon, a North Korean escapee, told the Financial Times that many residents in Hamhung, the second-most populous city, “relied on a solar panel, a battery and a power generator to light their houses and power their television”. But solar power is still only a partial solution to the country’s energy woes.
Is solar a good idea for North Korea?
Introduction of Solar to North Korea’s Energy Mix The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK or North Korea) appears to have identified the benefits of harnessing renewable energy in the mid-2000s.
What is the average solar energy potential in North Korea?
The mean solar energy potential in North Korea during the three-year period was 3.36 kWh m −2 d −1 (Table 4), which is lower than South Korea's average of 3.65 kWh m −2 d −1. Table 4. Evaluation of solar energy potential in the nine administrative provinces and North Korea as a whole for three years (2013, 2014, and 2015).
Does North Korea have a good energy sector?
North Korea’s energy sector requires a lot of attention. North Korea struggles to meet energy demands as domestic energy production and consumption have been generally declining for years. As of 2020, 48% of the North Korean population did not have access to electricity, and in 2016, only 10.8% had access to clean fuel for cooking.
More related information
-
 Photovoltaic power station power generation in North Korea
Photovoltaic power station power generation in North Korea
-
 Can solar power generation be used in the north
Can solar power generation be used in the north
-
 North Asia solar power generation for household electric
North Asia solar power generation for household electric
-
 North Macedonia solar power generation for home use
North Macedonia solar power generation for home use
-
 Is there any solar power generation for home use in North Macedonia
Is there any solar power generation for home use in North Macedonia
-
 North Asia Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation System for Home Use
North Asia Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation System for Home Use
-
 Black Mountain Photovoltaic Power Generation Curved Solar Panels
Black Mountain Photovoltaic Power Generation Curved Solar Panels
-
 Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation Forecast System
Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation Forecast System
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


