Microgrids: Role, Types, Challenges, and Future
Small residential systems, often powered by solar panels and battery storage, can cost between $10,000 to $50,000, while larger commercial or industrial
Get Price
A critical review of energy storage technologies for microgrids
Microgrids are small-scale energy systems with distributed energy resources, such as generators and storage systems, and controllable loads forming an electrical entity within defined
Get Price
Microgrid Energy Storage Methods: Comparison
At the heart of an efficient microgrid lies a robust energy storage system that can handle varying loads and supply demands. This article delves
Get Price
What are the small energy storage devices in microgrids
Microgrids are small-scale energy systems with distributed energy resources,such as generators and storage systems,and controllable loads forming an electrical entity within defined electrical
Get Price
Microgrid: Advantages, Structure, & Applications
The article discusses the structure, advantages, and applications of microgrids, which are small, autonomous energy systems capable of operating
Get Price
What are small energy storage devices? | NenPower
These systems utilize small energy storage devices to balance supply and demand, ensuring a consistent energy supply even during outages
Get Price
Zero-carbon microgrid: Real-world cases, trends, challenges, and
Then, three development trends of the zero-carbon microgrid are discussed, including an extremely high ratio of clean energy, large-scale energy storage, and an
Get Price
Microgrids are small-scale energy systems with distributed energy resources,such as generators and storage systems,and controllable loads forming an electrical entity within defined electrical
Get Price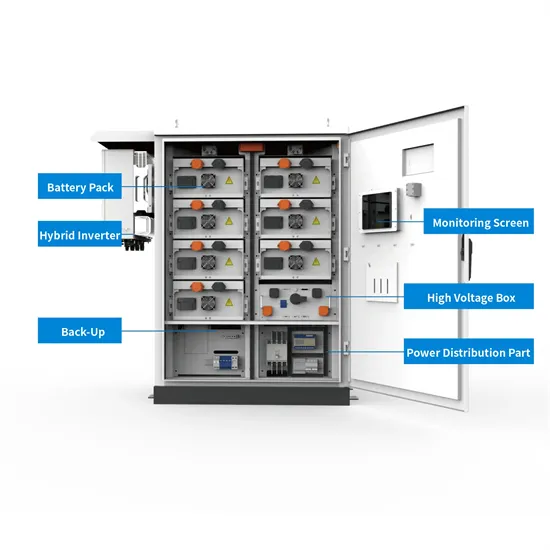
Microgrid Energy Storage Methods: Comparison & Benefits
At the heart of an efficient microgrid lies a robust energy storage system that can handle varying loads and supply demands. This article delves into the different energy storage
Get Price
Review on the Microgrid Concept, Structures, Components
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the microgrid (MG) concept, including its definitions, challenges, advantages, components, structures, communication
Get Price
An Introduction to Microgrids: Benefits
[2] Energy Storage: Energy storage systems, such as batteries, are an important component of microgrids, allowing energy to be stored for times when it is not
Get Price
MICROGRIDS FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATION IN CHINA
The term "microgrid" refers to a small power generation and distribution system composed of distributed generators, energy storage devices, energy conversion devices, related loads,
Get Price
What is a Micro-Grid?
What is a microgrid? Microgrids are considered to be locally confined and independently controlled electric power grids in which a distribution architecture integrates
Get Price
What are small energy storage devices? | NenPower
These systems utilize small energy storage devices to balance supply and demand, ensuring a consistent energy supply even during outages or disruptions in the main grid.
Get Price
Microgrid Controls | Grid Modernization | NREL
Microgrids can include distributed energy resources such as generators, storage devices, and controllable loads. Microgrids generally must also include a control strategy to
Get Price
An Introduction to Microgrids and Energy Storage
However, increasingly, microgrids are being based on energy storage systems combined with renewable energy sources (solar, wind, small hydro), usually backed up by a fossil fuel
Get Price
What are the energy storage devices in microgrids
From microgrids to transportation networks and large-scale power grids, HESSs emerge as a robust solution, leveraging the synergies between energy storage devices to create a resilient
Get Price
Comparative analysis of selected energy storage technologies for
To achieve the best results such devices should be located as close to the micro source as possible – behind the meter. Small, distributed energy storage devices could be
Get Price
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
Energy storage for electricity generation An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an
Get Price
Comprehensive discussions on energy storage devices:
Therefore in this chapter, the roles of ESSs in microgrids are analyzed and a one real-time application is provided in which battery energy storage system is demonstrated,
Get Price
What is a microgrid?
Energy storage devices such as batteries or flywheels store excess power generated by the microgrid. This stored energy can be used when demand exceeds production, or during
Get Price
Microgrids: Role, Types, Challenges, and Future | Diversegy
Small residential systems, often powered by solar panels and battery storage, can cost between $10,000 to $50,000, while larger commercial or industrial designs that integrate multiple
Get Price
Microgrid: Advantages, Structure, & Applications
The article discusses the structure, advantages, and applications of microgrids, which are small, autonomous energy systems capable of operating independently or in
Get Price
An Introduction to Microgrids, Concepts, Definition, and
In a widely accepted definition "Microgrids are electricity distribution systems containing loads and distributed energy resources, (such as distributed generators, storage
Get Price
An Introduction to Microgrids: Benefits
[2] Energy Storage: Energy storage systems, such as batteries, are an important component of microgrids, allowing energy to be stored for times when it is not being generated. This helps to
Get Price
A critical review of energy storage technologies for microgrids
Renewable energy intermittency requires flexibility ancillary services to smooth the variability in power production, both on a large and small-scale, e.g., interconnected bulk power systems
Get Price
What is a microgrid?
Energy storage devices such as batteries or flywheels store excess power generated by the microgrid. This stored energy can be used when demand
Get Price
Energy storage devices in microgrids
Microgrids are small-scale energy systems with distributed energy resources,such as generators and storage systems,and controllable loads forming an electrical entity within defined electrical
Get Price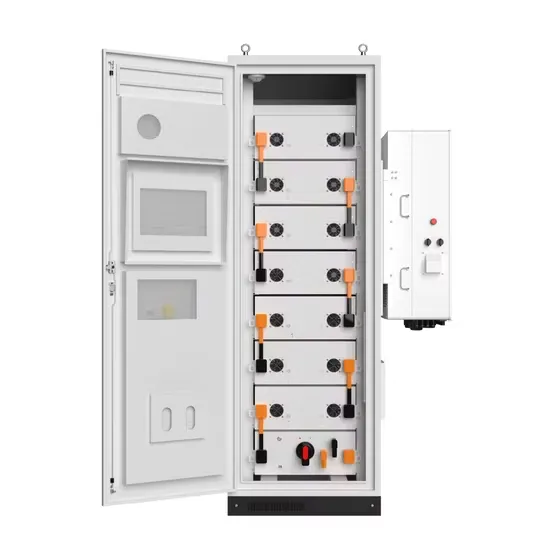
6 FAQs about [What are the small energy storage devices in microgrids ]
Why is energy storage important in a microgrid?
Energy Storage: Energy storage systems, such as batteries, are an important component of microgrids, allowing energy to be stored for times when it is not being generated. This helps to ensure a stable and reliable source of energy, even when renewable energy sources are not available.
Which features are preferred when deploying energy storage systems in microgrids?
As discussed in the earlier sections, some features are preferred when deploying energy storage systems in microgrids. These include energy density, power density, lifespan, safety, commercial availabil-ity, and financial/ technical feasibility. Lead-acid batteries have lower energy and power densities than other electro-chemical devices.
What is an energy microgrid?
A microgrid is a small electricity generation and distribution system containing distributed generation, energy storage systems, loads and monitoring and protection devices. It is an autonomous system that is self-controlled and self-managed. An energy microgrid provides users thermal energy for heating and cooling in addition to electricity.
What are the components of a microgrid?
They can be used to power individual homes, small communities, or entire neighborhoods, and can be customized to meet specific energy requirements. Microgrids typically consist of four main components: energy generation, energy storage, loads and energy management. The architecture of microgrid is given in Figure 1.
What are the advantages of a microgrid?
However, increasingly, microgrids are being based on energy storage systems combined with renewable energy sources (solar, wind, small hydro), usually backed up by a fossil fuel-powered generator. The main advantage of a microgrid: higher reliability.
Are microgrids a viable alternative to traditional power distribution?
As the central energy grid continues to face both infrastructure and energy security challenges, microgrids are becoming a popular alternative to traditional power distribution. Microgrids are small, self-sufficient energy systems and are playing an increasingly important role in grid modernization and distributed energy systems.
More related information
-
 What are the energy storage devices of the space station
What are the energy storage devices of the space station
-
 What are the solar energy storage devices
What are the solar energy storage devices
-
 What are the grid energy storage devices
What are the grid energy storage devices
-
 What are the wind and solar energy storage devices
What are the wind and solar energy storage devices
-
 What is a Small Energy Storage Project
What is a Small Energy Storage Project
-
 What are the outdoor energy storage devices
What are the outdoor energy storage devices
-
 What are the small energy storage power stations in New Zealand
What are the small energy storage power stations in New Zealand
-
 What are Huawei s super energy storage devices
What are Huawei s super energy storage devices
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


