Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid:
Energy storage includes an array of technologies, such as electrochemical batteries, pumped storage hydropower, compressed air and
Get Price
An Introduction to Microgrids and Energy Storage
However, increasingly, microgrids are being based on energy storage systems combined with renewable energy sources (solar, wind, small hydro), usually backed up by a fossil fuel
Get Price
Grid-connected systems | EBSCO Research Starters
Grid-connected systems are integrated electrical networks that link multiple power generation sources to consumers, enhancing the reliability and quality of electricity supply. In contrast to
Get Price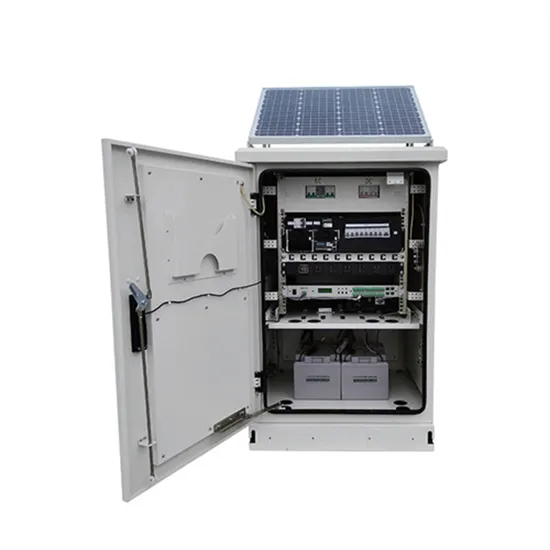
Battery Energy Storage Explained
Battery Energy Storage, Explained Energy storage powers our daily lives. The same technology that charges our phones, laptops, and electric vehicles is
Get Price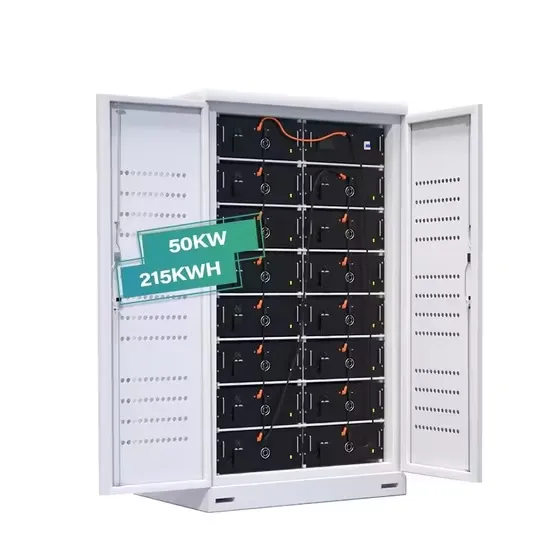
What does grid-connected energy storage mean? | NenPower
Understanding this technology starts with recognizing its significance in current power infrastructure. Traditional power systems primarily relied on fossil fuel generation,
Get Price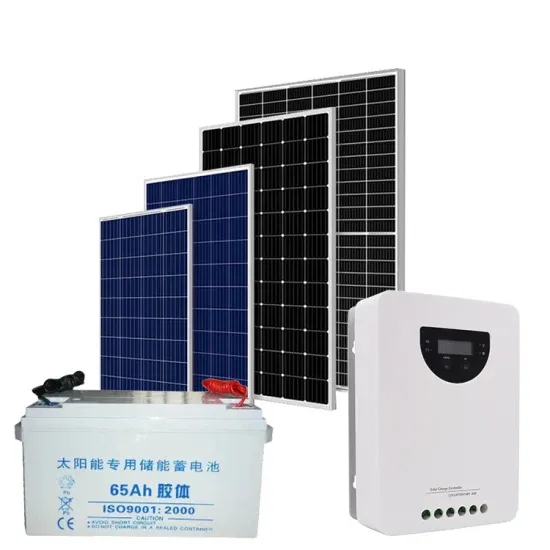
Grid Scale Energy Storage: An In-Depth Look
To overcome this challenge, grid-scale energy storage systems are being connected to the power grid to store excess electricity at times when it''s plentiful and then
Get Price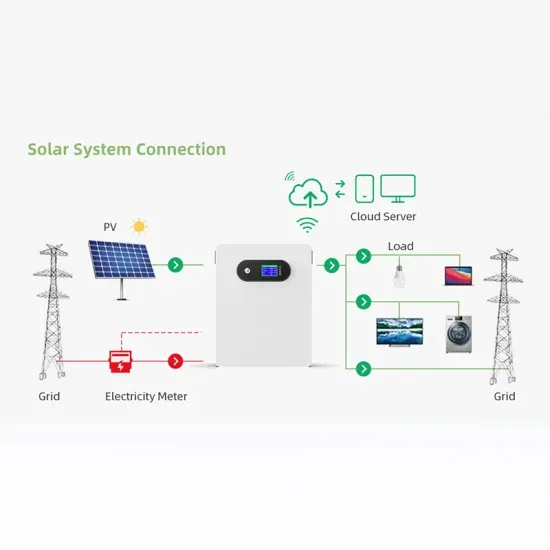
Electric Power Industry Needs for Grid-Scale Storage
Investment in energy storage is essential for keeping pace with the increasing demands for electricity arising from continued growth in U.S. productivity, shifts and continued expansion of
Get Price
How Grid Energy Storage Works: Unlocking the Future of Power
The global shift towards renewable energy sources has spurred a revolution in how we generate, store, and use electricity. Nowadays, we increasingly rely on intermittent energy
Get Price
Grid Scale Energy Storage: An In-Depth Look
To overcome this challenge, grid-scale energy storage systems are being connected to the power grid to store excess electricity at times when
Get Price
Grid-Scale Battery Storage: Frequently Asked Questions
What is grid-scale battery storage? Battery storage is a technology that enables power system operators and utilities to store energy for later use.
Get Price
U.S. Grid Energy Storage Factsheet
Electrical Energy Storage (EES) refers to systems that store electricity in a form that can be converted back into electrical energy when needed. 1 Batteries are one of the most common
Get Price
U.S. Grid Energy Storage Factsheet
Energy storage operation and grid connection refers to the processes and systems designed to store energy generated from various
Get Price
Renewable Energy Storage Facts | ACP
Battery energy storage systems operate by converting electricity from the grid or a power generation source (such as from solar or wind) into stored chemical energy.
Get Price
Energy storage on the electric grid | Deloitte Insights
Energy storage is critical for mitigating the variability of wind and solar resources and positioning them to serve as baseload generation. In fact, the time is ripe for utilities to go "all in" on
Get Price
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or
Get Price
The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Stability and
By examining the fundamental principles of grid stability, exploring the importance of energy storage in grid management, and showcasing real
Get Price
Energy storage
Grid-scale storage refers to technologies connected to the power grid that can store energy and then supply it back to the grid at a more advantageous time
Get Price
How It Works: Electric Transmission
Although most power flowing on the transmission and distribution grid originates at large power generators, power is sometimes also supplied back to the grid by end users via Distributed
Get Price
The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Stability and Management
By examining the fundamental principles of grid stability, exploring the importance of energy storage in grid management, and showcasing real-world examples of its application,
Get Price
Wind Energy Grid Integration: Overcoming Challenges and
Wind energy has become a key player in the global shift towards renewable power. As more wind farms connect to electrical grids, new challenges arise. Grid operators
Get Price
Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid: Technology Trends
Energy storage includes an array of technologies, such as electrochemical batteries, pumped storage hydropower, compressed air and thermal storage.
Get Price
Grid energy storage
Energy from fossil or nuclear power plants and renewable sources is stored for use by customers. Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, is a set of technologies
Get Price
Solar, battery storage to lead new U.S. generating capacity
Battery storage. In 2025, capacity growth from battery storage could set a record as we expect 18.2 GW of utility-scale battery storage to be added to the grid. U.S. battery storage already
Get Price
Electric Grids
A reliable, resilient, and secure electric grid is vital for national security, economic security, and the growing number of services that
Get Price
What is energy storage operation and grid connection?
Energy storage operation and grid connection refers to the processes and systems designed to store energy generated from various sources for later use and the integration of
Get Price
Grid-connected photovoltaic systems with energy storage
There are different interesting ways that can be followed in order to reduce costs of grid-connected photovoltaic systems, i.e., by maximizing their energy production in every operating
Get Price
Role of energy storage technologies in enhancing grid stability
This paper provides an overview of energy storage, explains the various methods used to store energy (focusing on alternative energy forms like heat and electricity), and then
Get Price
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or device, which is
Get Price
Energy storage
Grid-scale storage refers to technologies connected to the power grid that can store energy and then supply it back to the grid at a more advantageous time – for example, at night, when no
Get Price
What is energy storage operation and grid connection?
Energy storage operation and grid connection refers to the processes and systems designed to store energy generated from various
Get Price
6 FAQs about [What is energy storage and grid-connected power generation ]
What is grid energy storage?
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variable renewables such as solar and inflexible sources like nuclear power, releasing it when needed.
What is an energy storage system?
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or device, which is discharged to supply (generate) electricity when needed at desired levels and quality. ESSs provide a variety of services to support electric power grids.
How do grid-scale energy storage systems work?
To overcome this challenge, grid-scale energy storage systems are being connected to the power grid to store excess electricity at times when it’s plentiful and then release it when the grid is under periods of especially high demand.
How does energy storage affect grid management?
One of the primary contributions of energy storage to grid management is its ability to balance supply and demand. Electrical grids must maintain a delicate balance between electricity generation and consumption to ensure stable operation.
How does energy storage improve grid stability?
Another significant advantage of energy storage in grid stability is its ability to improve resilience and reliability. By providing backup power during outages or grid disturbances, energy storage systems can enhance the grid’s ability to withstand and recover from adverse events, such as natural disasters or equipment failures.
Will energy storage change the dynamics of a grid?
With widespread grid failures on this scale, energy storage would have to make up a much larger share of system capacity than it currently does to change the dynamics, although it can respond to sudden system fluctuations by providing ancillary services, like frequency and voltage regulation.
More related information
-
 Estonia s photovoltaic grid-connected energy storage power generation
Estonia s photovoltaic grid-connected energy storage power generation
-
 What energy storage is used for photovoltaic power generation
What energy storage is used for photovoltaic power generation
-
 What kind of energy storage does photovoltaic power station power generation belong to
What kind of energy storage does photovoltaic power station power generation belong to
-
 Grid-connected energy storage power generation project
Grid-connected energy storage power generation project
-
 What is the price of photovoltaic power generation and energy storage in Barbados
What is the price of photovoltaic power generation and energy storage in Barbados
-
 Eritrea Energy Storage Solar Power Generation Project
Eritrea Energy Storage Solar Power Generation Project
-
 What s inside a home energy storage power supply
What s inside a home energy storage power supply
-
 Waste heat power generation and energy storage
Waste heat power generation and energy storage
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


