Converter vs Inverter: Which is Better for Your Needs?
Both devices have specific roles: converters adjust voltage levels to match what your devices need, while inverters change the direct current (DC) from solar panels or
Get Price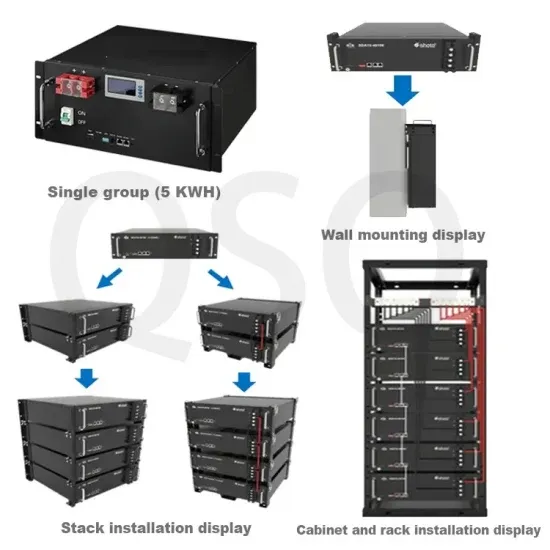
The Differences Between Converters vs Inverters
Today''s blog dives into the essential functions, types, and applications of converters and inverters, shedding light on their distinct roles in energy
Get Price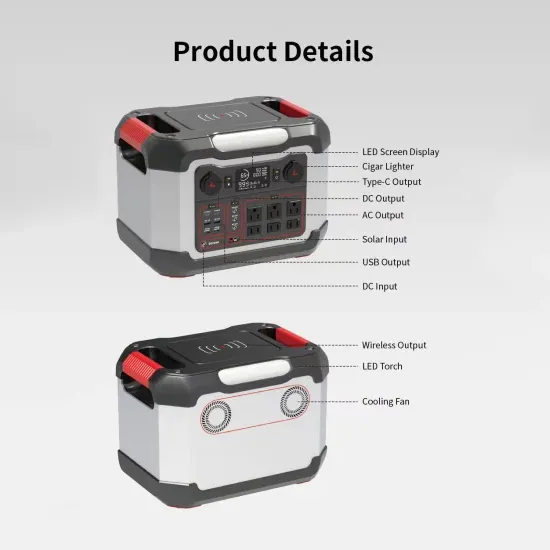
Inverter vs Converter
While both devices'' functions are closely connected, their features differ drastically. The converter turns AC power into DC and can change the voltage level for further usage. On
Get Price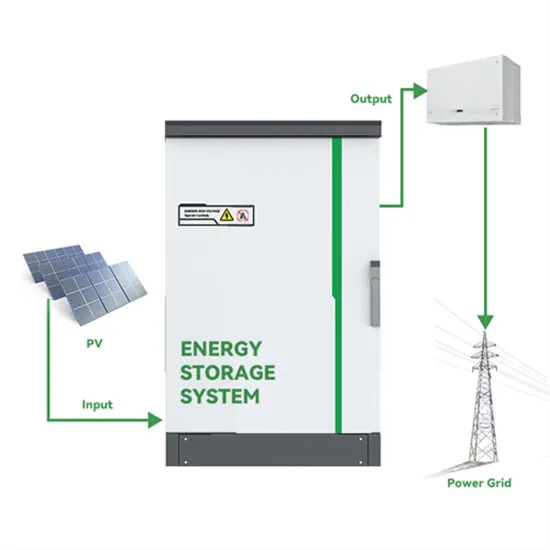
What is the difference between photovoltaic inverter and energy storage
Photovoltaic inverters convert DC power into AC, while energy storage inverters convert DC power from batteries, handling charge and discharge protection, reducing power
Get Price
Difference Between Inverter and Converter –
Understanding the difference between them can ensure your devices run efficiently. In this article, we''ll explain how inverters and
Get Price
AC vs. DC Coupling Energy Storage Systems —
ESS (s) can include but is not limited to batteries, capacitors, and kinetic energy devices (e.g., flywheels and compressed air). These systems
Get Price
What''s the Difference Between Inverter and Converter? Here''s
In choosing an inverter, keep in mind your energy objectives, the size of your system, and any possible future expansions (such as adding batteries). Converters play a key
Get Price
Difference Between Inverter and Converter – Explained Clearly
Understanding the difference between them can ensure your devices run efficiently. In this article, we''ll explain how inverters and converters work, their unique roles,
Get Price
Understanding the Differences: Inverter vs Converter
Q: What''s the difference between an inverter and a converter in terms of electrical devices? A: An inverter is an electronic device that changes DC to AC power, while a
Get Price
In the energy storage industry, what are the similarities and
In the energy storage industry, what are the similarities and differences between energy storage converters and photovoltaic inverters in terms of technology and
Get Price
Inverter vs converter: What''s the difference?
Converters change the voltage of an electrical power source and can convert AC to DC (rectification) or DC to AC (inversion). Inverters specifically convert DC into AC. There''s
Get Price
Difference Between Inverter and Converter –
In this article, we''ll explain how inverters and converters work, their unique roles, and how to choose the right one for your home, vehicle, or
Get Price
The Differences Between Converters and Inverters – Hinen
In this article, we will explore the inverter and converter comparison, their functions, and practical applications to help you determine which one best suits your energy
Get Price
Introduction to Grid Forming Inverters
Why do we need Grid-forming (GFM) Inverters in the Bulk Power System? There is a rapid increase in the amount of inverter-based resources (IBRs) on the grid from Solar PV, Wind,
Get Price
Difference Between PV Inverters and Energy Storage Inverters
The energy storage converter, also known as a Power Conversion System (PCS), or bidirectional energy storage inverter, is a critical component that enables bidirectional energy flow between
Get Price
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PCS AND ENERGY STORAGE INVERTER
PCS converter for battery energy storage in commercial and industrial application. PCS power conversion system energy storage is a multi-functional AC-DC converter by offering both basic
Get Price
What is a Solar Inverter? Full Guide and Generator
So the core difference between inverter and generator is this: inverters are energy optimizers that rely on clean solar input, while generators
Get Price
Inverters Vs. Converters | What''s The Difference?
Discover the key differences between inverters and converters, their functions, types, and applications in modern power systems.
Get Price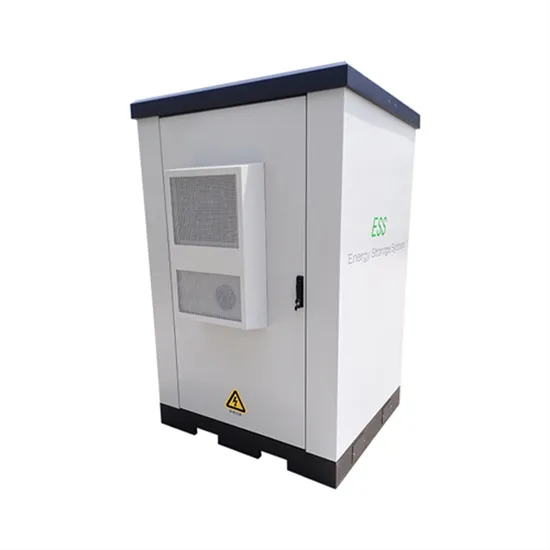
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ENERGY STORAGE CONVERTER AND GRID CONNECTED INVERTER
What is the difference between energy storage inverter and PCs? Energy Storage Inverters typically focus on the conversion of DC to AC for grid integration, often with a focus on
Get Price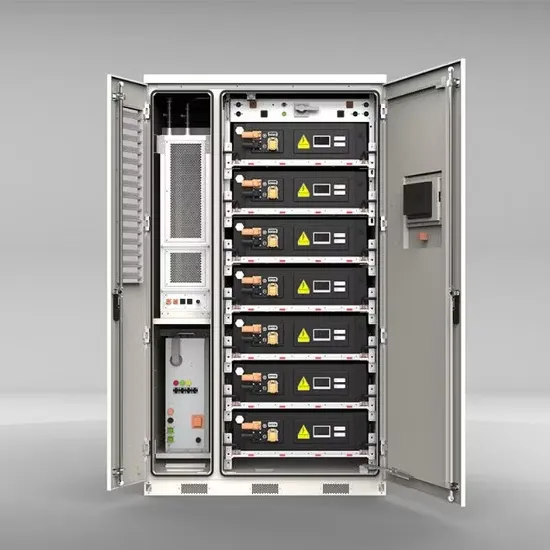
Understanding the Differences: Inverter vs Converter
Q: What''s the difference between an inverter and a converter in terms of electrical devices? A: An inverter is an electronic device that changes
Get Price
Solar Converter vs Inverter: What''s the Difference
String Inverters: Connect multiple solar panels wired in series and convert combined DC to AC power. Microinverters: Installed on individual solar panels for optimized,
Get Price
The Differences Between Converters vs Inverters
Today''s blog dives into the essential functions, types, and applications of converters and inverters, shedding light on their distinct roles in energy management. We''ll explore their advantages
Get Price
Differences between Energy Storage Inverter and Photovoltaic Inverter
Energy storage inverters and photovoltaic inverters are two types of power electronic devices that play an important role in energy conversion and management. Both inverters are converse DC
Get Price
The Main Differences Between Inverters and Converters
This table provides a clear overview of the primary differences between inverters and converters, making understanding their roles in electrical systems easier.
Get Price
What is PCS? -Bidirectional energy storage converter
It is the voltage of the battery pack and the input voltage of the energy storage converter. The energy storage inverters of different technologies have a large
Get Price
Converter vs Inverter: Which is Better for Your Needs?
Both devices have specific roles: converters adjust voltage levels to match what your devices need, while inverters change the direct current
Get Price
Power converters for battery energy storage systems
Recent works have highlighted the growth of battery energy storage system (BESS) in the electrical system. In the scenario of high penetration
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Differences between energy storage inverters and converters]
What is the difference between inverter and converter?
Difference between inverter and converter? An inverter changes DC power to AC power, while a converter does the opposite, turning AC power into DC. Inverters are used for solar systems, while converters are more common in electrical devices.
What is the difference between AC converter and DC inverter?
Below are the main differences: Functionality Inverters: Convert DC (direct current) into AC (alternating current). Converters: Convert either AC to DC (rectification) or adjust the DC voltage from one level to another (DC-DC conversion). They can also change AC voltages (AC to AC converters). Applications
What are converters & inverters?
Converters and inverters are essential electrical devices used to manage and transform electrical power. The fundamental distinction lies in the types of conversion they perform. Below is a detailed comparison of their functions, applications, efficiency, complexity, and cost.
What is an inverter & how does it work?
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling the use of DC power sources, such as batteries or solar panels, to power AC appliances.
Why should you choose a converter or inverter?
Each type of converter and inverter serves a specific purpose. Selecting the right converter or inverter ensures the efficiency, compatibility, and longevity of your electronic devices. Converters and inverters have applications in a broad range of scenarios. Both are essential for everyday use and specialized settings.
How does an inverter convert DC to AC?
An inverter converts Direct Current (DC) to Alternating Current (AC) electricity (and vice-versa). It plays a critical role in on-grid and solar power. Electricity is transmitted over power lines and also stored in batteries as DC. For most consumer applications, an inverter must convert the DC into AC (household) electricity.
More related information
-
 What are the grid-connected inverters for 4G mobile energy storage sites
What are the grid-connected inverters for 4G mobile energy storage sites
-
 How to match energy storage inverters with battery cabinets
How to match energy storage inverters with battery cabinets
-
 Installation of energy storage cabinets for communication base station inverters
Installation of energy storage cabinets for communication base station inverters
-
 Huawei s future layout of energy storage inverters
Huawei s future layout of energy storage inverters
-
 There are several types of energy storage inverters
There are several types of energy storage inverters
-
 Differences between energy storage cabinets and complete sets of electrical equipment
Differences between energy storage cabinets and complete sets of electrical equipment
-
 Differences between outdoor battery energy storage batteries
Differences between outdoor battery energy storage batteries
-
 Differences between two-in-one energy storage batteries
Differences between two-in-one energy storage batteries
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


