Understanding the Difference Between Frequency Inverters and High
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power efficiency, space saving, or suitability for...
Get Price
DC-AC inverter question: why square wave can have such high frequency
This is common in PV inverters which use some sort of maximum power point tracking where input voltage might vary in order to maintain the maximum power point (or a controlled lower
Get Price
Which is Better Low Frequency or High-frequency
Introduction Inverters convert DC power into AC power to operate AC equipment and devices. They utilize power electronic switching at different frequencies to
Get Price
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
An inverter (or power inverter) is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage. While DC power is common in small gadgets, most
Get Price
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
Get Price
Understanding harmonics in inverters
For GTR high-power inverter components, the carrier frequency of PWM is 2-3kHz, while the highest carrier frequency of PWM of IGBT high
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency,
Get Price
How to Distinguish High Frequency Inverter and Low Frequency Inverter
High frequency inverters produce AC power of a higher frequency and voltage level, while low frequency inverters produce AC power of a lower frequency and voltage. How high frequency
Get Price
Inverter Basics | inverter
Unless you have a basic system that offers a low-voltage DC power source, the inclusion of an inverter becomes essential. An inverter
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters are usually designed for small to medium power loads and are difficult to support the operation of high-power equipment
Get Price
How to Distinguish High Frequency Inverter and Low Frequency
High frequency inverters produce AC power of a higher frequency and voltage level, while low frequency inverters produce AC power of a lower frequency and voltage. How high frequency
Get Price
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of inverter frequency, exploring its significance, factors affecting it, and its practical implications.
Get Price
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
There are two distinct types of industrial grade power inverters distinguished by the size of their transformers, and the switching speed of their transistors.
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power
Get Price
The difference between high frequency inverter and
On the other hand, low frequency inverters are known for their durability and reliability, making them a preferred choice for heavy-duty or
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Low-frequency inverter: heavy and capable of surge power, lower efficiency, more reliable, expensive. High-frequency inverter: lightweight, not
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverters: From Photovoltaic, Wind, and
(3) efficiency, and (4) power density. Conventional approach to inverter design is typically based on the architecture illustrated in Fig. 29.1a. A problematic feature of such an approach is the
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Low-frequency inverter: heavy and capable of surge power, lower efficiency, more reliable, expensive. High-frequency inverter: lightweight, not capable of surges, more efficient,
Get Price
Introduction to Grid Forming Inverters: A Key to Transforming
Why do we need Grid-forming (GFM) Inverters in the Bulk Power System? There is a rapid increase in the amount of inverter-based resources (IBRs) on the grid from Solar PV, Wind,
Get Price
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
High frequency inverters excel in energy efficiency, converting DC to AC power with minimal loss, which can lead to long-term cost savings. Low frequency inverters are better for off-grid
Get Price
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
Inverters are essential components of many electrical systems, converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to power various devices and
Get Price
A Guide to Solar Inverters: How They Work & How to
Learn what a solar inverter is, how it works, how different types stack up, and how to choose which kind of inverter for your solar project.
Get Price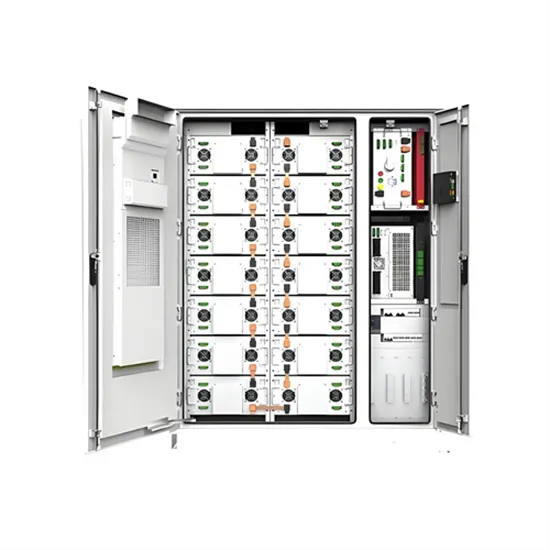
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Low-frequency power inverters have much better peak power capability to manage large loads with power spikes than high-frequency inverters. In fact, low-frequency inverters
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency, typically above 20 kHz (Kilohertz), to achieve
Get Price
HIGH VS LOW FREQUENCY INVERTERS
The second main difference is reliability: low-frequency inverters operate using powerful transformers, which are more reliable and sturdy than the high-frequency inverter''s
Get Price
The 3 Most Common Faults on Inverters and how to Fix Them
At IDS we have a wealth of inverter experience. We have been an ABB Partner for over 20 years and are used to supporting clients with a variety of inverter-controlled applications. In this
Get Price
How does a high
High - frequency inverters, however, are more efficient in terms of power conversion. Since they use smaller transformers, there are fewer losses in the form of heat.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Does a high inverter frequency mean high power ]
What is the difference between a low frequency and high frequency inverter?
Low-frequency inverter: heavy and capable of surge power, lower efficiency, more reliable, expensive. High-frequency inverter: lightweight, not capable of surges, more efficient, less reliable, cheaper. I’m an off-grid enthusiast.
What is a high frequency inverter?
The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency. They are typically less expensive, have smaller footprints, and have a lower tolerance for industrial loads. HF inverters have over twice the number of components and use multiple, smaller transformers.
What is inverter frequency?
In today's world, inverters play a vital role in various applications, such as home solar power system, inverter for office use, inverter for van, etc. Central to their operation is the concept of an inverter frequency, which determines the rate at which the current alternates direction.
Does victron use a high frequency inverter?
Victron combines both inverters, which they call Hybrid HF or Combined high frequency and line frequency technologies. What frequency inverter does growatt use? Growatt uses a high-frequency inverter. Which one is best? Low or high frequency? The best inverter is the low-frequency inverter.
What is AC inverter frequency?
1. What is the frequency of AC inverter? An AC inverter frequency refers to the number of power signal fluctuations, typically measured in Hertz (Hz). In most regions, the standard inverter frequency for AC power systems is 50 or 60 Hz, representing the number of complete cycles per second.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Efficiency: Low-frequency inverters are known for their robustness and ability to handle high surge currents, making them suitable for powering heavy-duty appliances or equipment with high starting currents, such as motors and compressors.
More related information
-
 Austria high frequency power inverter
Austria high frequency power inverter
-
 Energy storage inverter high power
Energy storage inverter high power
-
 Power frequency inverter connected to solar energy
Power frequency inverter connected to solar energy
-
 New Zealand single-phase 110v power frequency inverter
New Zealand single-phase 110v power frequency inverter
-
 Solar power replacement for industrial frequency inverter
Solar power replacement for industrial frequency inverter
-
 Pure rotary inverter high power
Pure rotary inverter high power
-
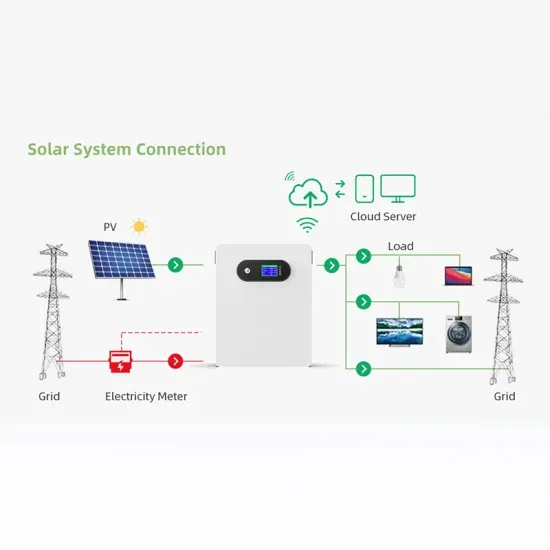 Inverter transformation from industrial frequency to high frequency
Inverter transformation from industrial frequency to high frequency
-
 12v water pump inverter high power solar
12v water pump inverter high power solar
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


