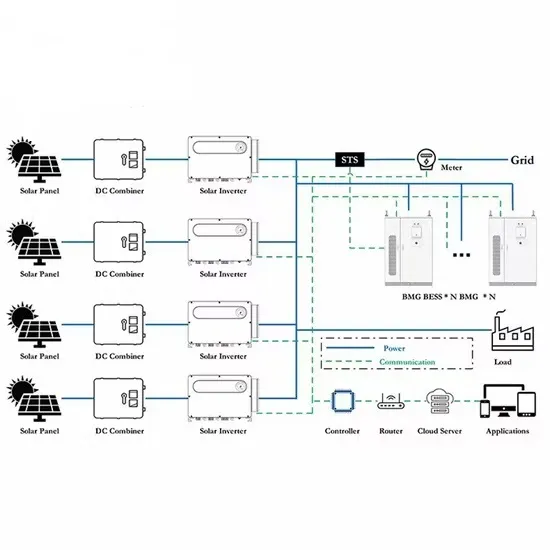
Renewable Energy Generation and Storage Models
Renewable Energy Generation and Storage Models Renewable energy generation and storage models enable researchers to study the impact of integrating large-scale
Get Price
Energy Storage Systems: Types, Pros & Cons, and
Energy storage systems (ESS) are vital for balancing supply and demand, enhancing energy security, and increasing power system efficiency.
Get Price
What is power generation and energy storage? | NenPower
Power generation refers to the process of converting various forms of energy into electrical power, essential for meeting the demands of modern society, while energy storage
Get Price
Hybrid Energy Solutions: Advantages & Challenges
Hybrid energy solutions are emerging as the answer, combining renewable sources like solar and wind with traditional power generation and
Get Price
A comprehensive review of wind power integration and energy storage
Integrating wind power with energy storage technologies is crucial for frequency regulation in modern power systems, ensuring the reliable and cost-effective operation of
Get Price
Green Hydrogen vs Traditional Energy Sources in
Conventional sources, like fossil fuels and nuclear power, have dominated for decades. In contrast, green hydrogen offers a cleaner energy
Get Price
Energy Storage
Storage is particularly useful in supporting the wide-scale integration of renewable resources, like wind and solar, because it can help smooth out changes in
Get Price
Energy Generation: Sources, Challenges, and Solutions
Energy: It refers to power derived from some resources to help in undertaking some work or to provide heat or to operate some machine. The source of energy may be renewable
Get Price
Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid:
Storage technologies can help meet peak demand when power prices are high, provide backup power during power outages, or help the grid
Get Price
Supercapacitors: Overcoming current limitations and charting the
The growing adoption of eco-friendly renewable energy has driven the need for sophisticated energy storage solutions [1], [2]. This shift aims to address the economic and
Get Price
Microgrids vs. Traditional Grids: Advanced Energy Storage Systems
Traditional large power grids adopt a centralized power generation and transmission model to send power from power plants to users through transmission lines, while microgrids
Get Price
Electrical Power Systems: Evolution from Traditional Configuration
Electric power system begins in last two decades of nineteenth century. At that time, it only provided energy to street lamps. Energy was generated in low DC machines of
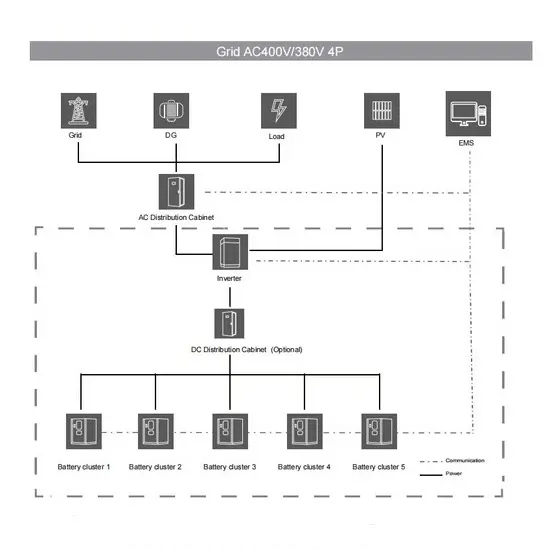
Get Price
Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid: Technology Trends
Storage technologies can help meet peak demand when power prices are high, provide backup power during power outages, or help the grid adapt to sudden power
Get Price
Electrical Power Systems: Evolution from Traditional
Electric power system begins in last two decades of nineteenth century. At that time, it only provided energy to street lamps. Energy was generated in low DC machines of
Get Price
Microgrid Energy Storage Solutions vs. Traditional Energy Storage
Discover the benefits of microgrid energy storage solutions compared to traditional systems.
Get Price
Energy storage for electricity generation and related processes
This paper presents an up to date comprehensive overview of energy storage technologies. It incorporates characteristics and functionalities of each storage technology, as
Get Price
Power Generation Methods: An Overview of Traditional and
Explore the various methods of power generation and their impact on modern society. This comprehensive guide covers traditional energy sources like coal and natural gas,
Get Price
Hybrid Energy Solutions: Advantages & Challenges | Diversegy
Hybrid energy solutions are emerging as the answer, combining renewable sources like solar and wind with traditional power generation and energy storage. This
Get Price
Integrating Energy Storage Technologies with Renewable Energy
Modern energy storage technologies play a pivotal role in the storage of energy produced through unconventional methods. This review paper discusses technical details and
Get Price
The Power Shift: How Energy Storage Solutions are Rewriting
As the world shifts toward a more sustainable energy future, two essential innovations are emerging as key drivers of the energy transition: energy storage solutions and
Get Price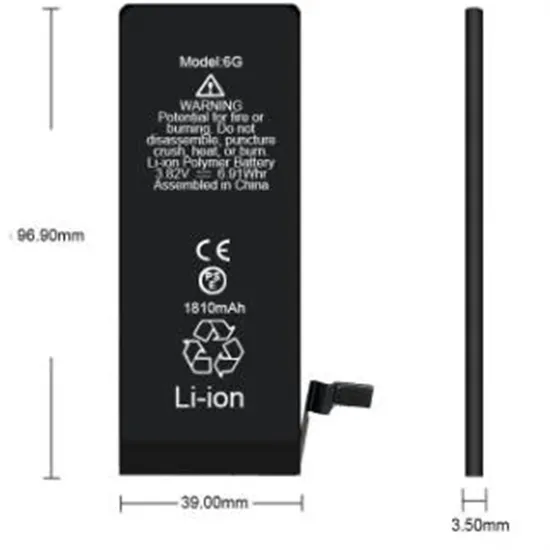
Technology
An evolution on traditional geothermal, leveraging breakthroughs in sub-surface technologies to create power generation & energy storage systems
Get Price
Conventional Power Plant
Conventional power plants are defined as facilities that generate electricity using turbines driven by conventional energy sources such as petroleum, coal, natural gas, and hydropower. These
Get Price
Green Hydrogen vs Traditional Energy Sources in Power Generation
Conventional sources, like fossil fuels and nuclear power, have dominated for decades. In contrast, green hydrogen offers a cleaner energy solution. This new fuel reduces
Get Price
Decentralized Energy Grids: The Future of Local Power
Unlike traditional electric grids that depend on centralized power plants, decentralized systems harness local resources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and
Get Price
Energy Storage: Traditional Methods Meet Renewable Solutions
Grid stability presents the primary challenge between conventional and renewable power sources. Solar and wind generation fluctuates naturally, requiring robust storage
Get Price
Traditional Power Grid
The Traditional Power Grid refers to an interconnected network of power plants, transmission lines, substations, distribution lines, and users, designed to deliver power from generation
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Traditional power generation and energy storage]
How are energy storage systems different from traditional power systems?
Table 1.1 Comparison among energy storage systems The traditional electrical power system structure is centrally operated. In such a way, the flow of energy and communication is unidirectional. There is no interaction between utilities and consumers. Conventional meters can perform only one-way communications.
What are the characteristics of all energy storage methods?
Table 1 and Table 2 contain the characteristics of all storage methods. A comparison of all energy storage technologies by their power rating, autonomy at rated power, energy and power density, lifetime in cycles and years, energy efficiency, maximum DoD (permitted), response time, capital cost, self-discharge rate and maturity is presented.
How to choose a storage method for a grid electricity system?
All storage technologies can reinforce the quality, stability and reliability of the grid electricity systems. However, the proper storage method should be selected based on several parameters, such as the capital and operational cost, the power density, the energy density, the lifetime and cycle life and the efficiency.
What makes energy storage unique?
One attribute that makes energy storage unique is its scalability. It can be implemented as a large utility-scale project to help meet peak energy demand and stabilize the grid, or as a small system sited in a residence or commercial facility to manage electricity costs and provide backup power.
What is a long-term energy storage system?
In the most usual designs the air from the atmosphere is used . CAES is classified as a long-term energy storage method because it can reserve or supply power for days. It is not an independent system and has to be associated to a gas turbine plant.
How do energy storage technologies compare?
Furthermore, Section 3 compares all energy storage technologies by their energy and power density, lifetime in cycles and years, energy efficiency, response time, capital cost, self-discharge rate and maturity. A brief comparison is given by the form of tables. In Section 4, a discussion of the grid scale energy storage applications is presented.
More related information
-
 Huawei Norway Energy Storage Power Generation Project
Huawei Norway Energy Storage Power Generation Project
-
 Design standards for wind solar and energy storage combined power generation
Design standards for wind solar and energy storage combined power generation
-
 Central Asia Hybrid Energy Storage Power Generation
Central Asia Hybrid Energy Storage Power Generation
-
 Vietnam Photovoltaic Power Generation and Energy Storage
Vietnam Photovoltaic Power Generation and Energy Storage
-
 Energy storage power station power generation time
Energy storage power station power generation time
-
 Nanya Photovoltaic Power Generation and Energy Storage Benefits
Nanya Photovoltaic Power Generation and Energy Storage Benefits
-
 Greek energy storage solar power generation
Greek energy storage solar power generation
-
 Energy storage solar thermal power generation industry
Energy storage solar thermal power generation industry
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.