Understanding Inverter Power Ratings: kW vs kVA Explained
Conclusion Knowing the difference between kW and kVA prevents common inverter sizing mistakes. For solar or hybrid applications, always ask about the power factor and real kW
Get Price
Inverter Current Calculator, Formula, Inverter Calculation
Inverter Current Formula: Inverter current is the electric current drawn by an inverter to supply power to connected loads. The current depends on the power output required by the load, the
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Input and Output: What is the Relationship
What is an Inverter Output? The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input source into alternating current (AC).
Get Price
Power Inverter Troubleshooting – Common Problems
Understanding Your Power Inverter Before diving into troubleshooting, it''s important to understand the basics of how a power
Get Price
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
An inverter is a static device that converts one form of electrical power into another but cannot generate electrical power. This makes it a converter, not a generator. It can be
Get Price
Inverter: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) | inverter
Inverter size is typically measured in terms of its power output capacity, which is expressed in watts. To determine the ideal size, you need to consider the total power consumption of the
Get Price
Power Inverter Basics
High input voltages like 100000V DC or higher are used for inverters used in high voltage DC power transmission stations / lines. What is the power inverter typical outputs?
Get Price
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To Power Conversion
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and expert insights.
Get Price
Inverter Power Calculator, Formula,Inverter Calculation
Inverter power (Pi) refers to the power output provided by an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources such as batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) used
Get Price
Configure Powerwall 3 Maximum Power / Current
The maximum power / current output for Powerwall 3 is . Beginning with software version 24.20, the power / current output can be configured to one of the
Get Price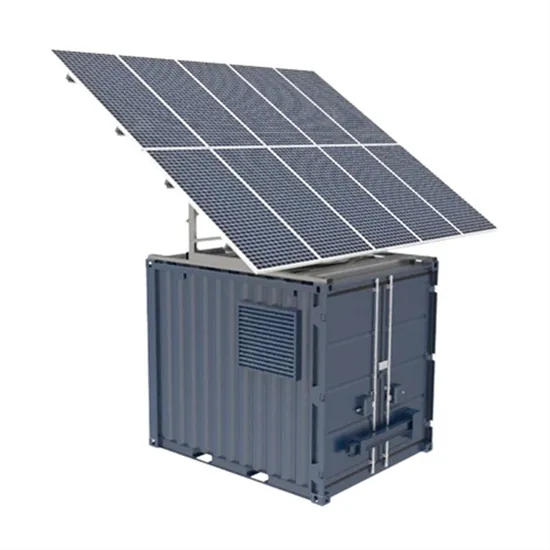
Power Inverter
A power inverter, or inverter, is an electronic device or circuitry that converts DC to AC. The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the
Get Price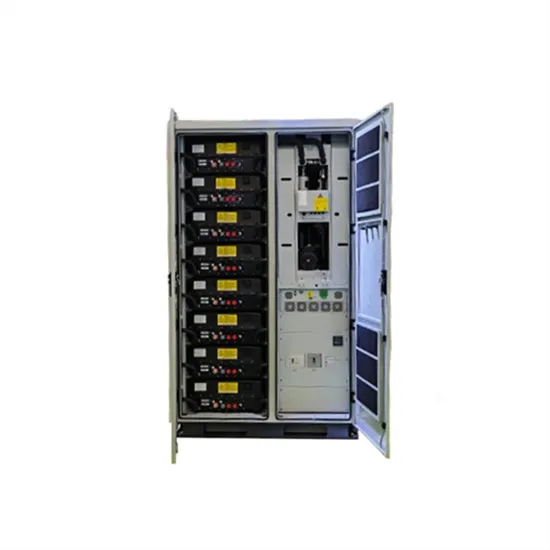
Power inverter
OverviewInput and outputBatteriesApplicationsCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
A typical power inverter device or circuit requires a stable DC power source capable of supplying enough current for the intended power demands of the system. The input voltage depends on the design and purpose of the inverter. Examples include: • 12 V DC, for smaller consumer and commercial inverters that typically run fro
Get Price
What is the difference between continuous power and
Continuous output power is the long term normal operation. It offers continuous power for your load normal working. If your electric devices draw a combined
Get Price
Inverter | Efficiency & Output Waveform
A power inverter controls voltage and current between the source (PV array, wind turbine, or other types of DC source) and the electrical loads
Get Price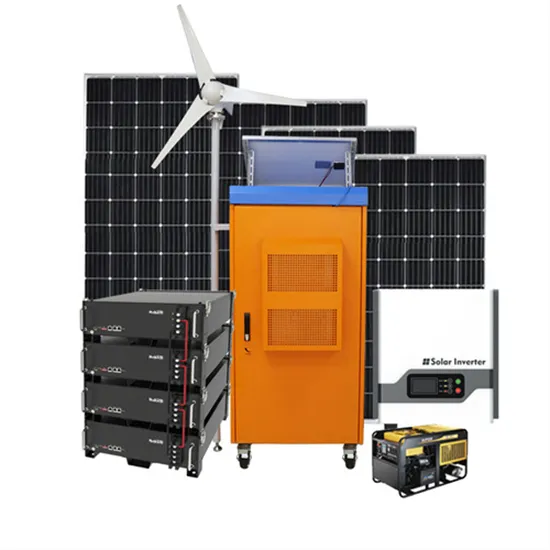
Power Inverter vs. Frequency Inverter | inverter
Applications: solar power systems, backup power supplies, mobile power sources (e.g., in vehicles or boats). Frequency inverter The frequency
Get Price
What Is An Inverter
What Is An Inverter, And How Does It Work? In simple terms, an inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into
Get Price
10 Best Inverter Power Stations of 2025
Key Takeaways Power Capacity: Look for inverter power stations with capacities ranging from 1,000Wh to over 5,000Wh to meet various energy needs. Output Rating: Ensure
Get Price
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
An inverter is a static device that converts one form of electrical power into another but cannot generate electrical power. This makes it a converter, not a generator. It can be
Get Price
Power inverter
The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source. A power inverter can be entirely electronic or maybe a combination of mechanical effects (such as a
Get Price
What Is an Inverter: Inverter Ratings, Efficiency & More
AC is used for grid service because it is more practical for long distance transmission. An inverter converts DC to AC, and also changes the voltage. In other words, it is a power adapter. It
Get Price
What Is An Inverter? | Definition, Types, Uses, How It Works
An inverter is a vital electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is used to power many household appliances and industrial
Get Price
What is a Power Inverter, and How Does It Work?
Power inverters mimic an alternating power source to convert the unidirectional DC output to AC output. By rapidly switching the polarity of the
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Input and Output: What is the
What is an Inverter Output? The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input
Get Price
Power Inverter
A power inverter is defined as an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) using power electronics, facilitating the generation of electrical power from DC
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power calculations and inverter
Get Price
What is a Power Inverter, and How Does It Work?
Power inverters mimic an alternating power source to convert the unidirectional DC output to AC output. By rapidly switching the polarity of the DC power source, these power
Get Price
What is an Inverter? Working Principle, Types, and
Pure Sine Wave Inverter: Produces a smooth, continuous sine wave output, closely resembling the AC power supplied by the utility grid. This type is ideal
Get Price
How to Calculate the Power Requirements for an Inverter | ehow
While most plug-in electrical appliances are designed to run on alternating current (AC) power, batteries and emergency generators produce direct current (DC) power. To convert the DC
Get Price
More related information
-
 PV inverter output power quality
PV inverter output power quality
-
 How much voltage does the inverter of a photovoltaic power station output
How much voltage does the inverter of a photovoltaic power station output
-
 PV inverter adjusts power output time
PV inverter adjusts power output time
-
 Affects the inverter output power
Affects the inverter output power
-
 Liechtenstein power frequency off-grid inverter price
Liechtenstein power frequency off-grid inverter price
-
 Inverter output 700V DC
Inverter output 700V DC
-
 How much power can We inverter exceed
How much power can We inverter exceed
-
 Brunei photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
Brunei photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


