Design and Implementation of a Highly Eficient Three-Level
In this paper, the alternative of using three-level converters for low-voltage applications is addressed. The performance and the com-petitiveness of the three-level T-type converter
Get Price
T-Type Multilevel Converter Topologies: A Comprehensive Review
Three-phase T-type qZ source inverter with control current associated to a vectorial modulator for photovoltaic applications. In: 2017 11th IEEE International Conference
Get Price
Improved Model Predictive Control for Asymmetric T-Type NPC 3
In this paper, a model predictive control for an asymmetric T-type NPC 3-level inverter is presented. The mathematical model and characteristics of the reduced switching
Get Price
Balancing control of neutral-point voltage for three
A three-level T-type inverter has higher efficiency and lower output voltage harmonics compared with the traditional two-level inverter. However,
Get Price
Full SiC Three‐Level T‐Type Quasi‐Z Source Inverter as
As a relatively recent advanced inverter topology, the three-level T-type quasi-impedance source inverter (3L T-Type qZSI) offers the improved harmonic distortion and lower
Get Price
Midpoint Potential Control of T-type Three-Level Inverter Based
T-type three-level inverter has been widely used in medium-voltage and high-power situations, but its own topological characteristics make it have the problem of midpoint
Get Price
SVPWM Strategies for Three-level T-type Neutral-point
Abstract In this paper, the three-level T-type neutral-point-clamped indirect matrix converter topology and the relative space vector modulation methods are introduced to improve the
Get Price
Three-Phase T-Type Inverter
This demonstration presents a three-phase T-type inverter for grid-tie applications that deploys Wolf-speed SiC MOSFETs. Fig. 1 shows the electrical circuit of the T-type inverter.
Get Price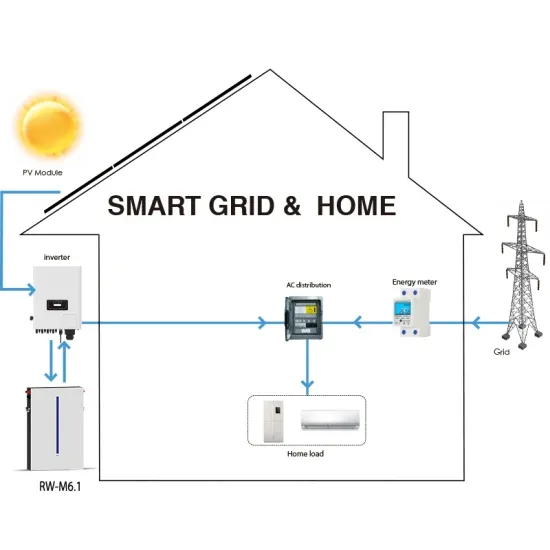
Balancing control of neutral-point voltage for three-level T-type
A three-level T-type inverter has higher efficiency and lower output voltage harmonics compared with the traditional two-level inverter. However, neutral-point voltage
Get Price
Three-phase three-level T-type rectifier.
A sliding mode control (SMC) strategy with dc capacitor voltage balancing is proposed for three-phase three-level T-type rectifiers. The proposed SMC
Get Price
Three-phase three-level boost inverter with self-balanced
Conventional multi-level inverters such as neutral point clamped and flying capacitor inverters do not have boosting capability and self-balanced capacitor voltage. Thus,
Get Price
Voltage Balancing of the DC-Link Capacitors in Three-Level T
This article illustrates an algorithm to balance the voltages across the dc-link capacitors of a three-level multiphase inverter feeding a star-connected load with an odd
Get Price
Mid-point potential balancing in three-level inverters
r is discussed, and the problem and causes of the uneven neutral potential of the T-type three-level inverter are investigated. Based on this, the research develops the processing
Get Price
Comprehensive Analysis of Three-phase Three-level T-type
This paper comprehensively evaluates three spacevector-modulation (SVM) schemes on a novel three-phase hybridswitch-based 3-level T-type neutral-point-clamped (3L
Get Price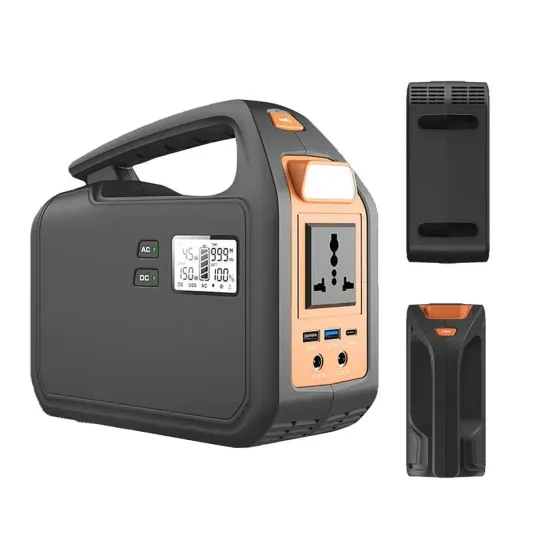
Voltage Balancing of the DC-Link Capacitors in Three-Level T-Type
This article illustrates an algorithm to balance the voltages across the dc-link capacitors of a three-level multiphase inverter feeding a star-connected load with an odd
Get Price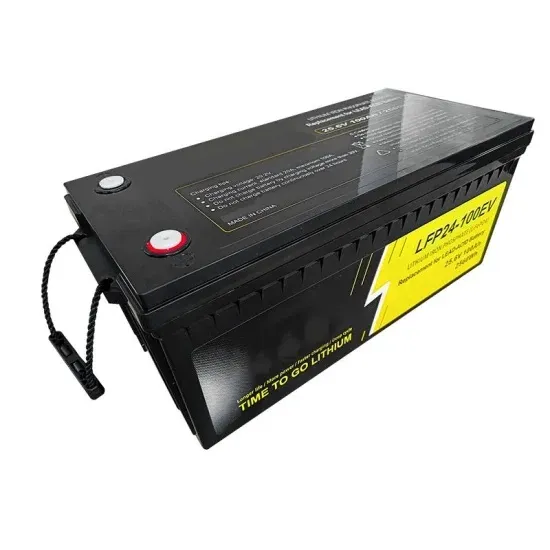
Research on Control Method of Neutral Point Potential Balance of
This article combines constant power inverter, independent control of active and reactive power output, Analyzed and studied the neutral point potential balance control of the
Get Price
Optimized balance factor assisted neutral-point voltage balance
A neutral-point voltage control method based on optimized balance factor is proposed by analyzing the role of basic vectors. This method utilizes the phase current
Get Price
Research and Simulation of a T-Type Three-Level Inverter
The analysis begins with a detailed examination of the operational modes of the T-type three-level inverter to identify the causes of midpoint voltage imbalance.
Get Price
Fault-Tolerant Methods for Three-Level T-Type Inverter to
This paper proposes new fault-tolerant (FT) space-vector modulation (SVM) techniques for three-level T-type inverter (3L-T 2 I) to balance neutral-point voltage (NPV)
Get Price
Mitigation of the low-frequency neutral-point current
Large electrolytic capacitors are normally applied to maintain a stiff DC-bus in uninterrupted power supply systems. However, the low-frequency
Get Price
Fault-Tolerant Methods for Three-Level T-Type Inverter to Balance
This paper proposes new fault-tolerant (FT) space-vector modulation (SVM) techniques for three-level T-type inverter (3L-T 2 I) to balance neutral-point voltage (NPV)
Get Price
Mid-point potential balancing in three-level inverters
As a result, this paper analyzes the remedies for NPC-type three-level inverters'' fluctuating neutral potential and offers hardware and software solutions to regulate the
Get Price
Simplified model predictive control of a three-phase T-type NPC inverter
Abstract This study presents a simplified model predictive control (SMPC) strategy for three-phase T-type neutral-point-clamped (NPC) inverters to reduce the computational
Get Price
Research on Control Method of Neutral Point Potential Balance of T-Type
This article combines constant power inverter, independent control of active and reactive power output, Analyzed and studied the neutral point potential balance control of the
Get Price
A Modified SVPWM Strategy for Reducing PWM
This paper focuses on the three-phase T-type three-level inverter as the research object and addresses existing PWM voltage noise and
Get Price
Comprehensive Analysis of Three-phase Three-level
This paper comprehensively evaluates three spacevector-modulation (SVM) schemes on a novel three-phase hybridswitch-based 3
Get Price
A Proposed Neutral-Point Voltage Balancing Method for Three-Phase Three
As a typical topology of power conversion system (PCS), three-phase three-level T-type inverter (3LT2I) may have the problem of neutral-point (NP) voltage unbalance under non-unity power
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Three-phase T-type inverter balance]
What is a three-level T-type inverter?
A three-level T-type inverter has higher efficiency and lower output voltage harmonics compared with the traditional two-level inverter. However, neutral-point voltage fluctuation and common-mode voltage (CMV) can negatively affect the performance of the three-level T-type inverter.
What is a T type inverter?
Extended T-type construction is used in boost converter to improve the efficiency of the inverter circuit, in general, T-type inverters have stepdown voltage performance, the output of T-type inverter is connected to boost converter to improve grid peak to peak voltage, and diodes are replaced with SiC MOSFET to get bidirectional output.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a three-level inverter?
The reason for this attention is its advantages of high efficiency, low harmonic output voltage, and low filter inductance [1 - 6]. However, the T-type three-level inverter also has a few drawbacks, such as neutral-point voltage imbalance and common-mode voltage (CMV) [7 - 9], which limit its applications.
What is neutral point potential balance control of T-Type 3 -level inverter topology?
the neutral point potential balance control of the T-type three -level inverter topology. Through is controlled within ±0.23%. This method can effectively avoid the influence of the difference capacitor voltage equalization. 1. Introduction voltage change rate, and low EMI. At present, it has very impor tant applications in medium and high
Does CMV affect the performance of a three-level T-type inverter?
However, neutral-point voltage fluctuation and common-mode voltage (CMV) can negatively affect the performance of the three-level T-type inverter. This study proposes a novel hybrid variable virtual space vector (HV 2 SV) strategy to mitigate this problem.
What are the advantages of T-type three-level inverter topology?
The T-type three-level inverter topology has the advantages of low electromagnetic interference, high efficiency, and low output harmonic content.
More related information
-
 Japanese industrial frequency three-phase inverter
Japanese industrial frequency three-phase inverter
-
 The role of three-phase grid-connected inverter
The role of three-phase grid-connected inverter
-
 DC component of three-phase inverter
DC component of three-phase inverter
-
 Three-phase electric water pump inverter can use inverter
Three-phase electric water pump inverter can use inverter
-
 Three-phase inverter 400hz
Three-phase inverter 400hz
-
 Vanuatu three-phase inverter manufacturer
Vanuatu three-phase inverter manufacturer
-
 Off-grid 30kw three-phase 380v inverter
Off-grid 30kw three-phase 380v inverter
-
 Costa Rica three-phase 100kw off-grid inverter
Costa Rica three-phase 100kw off-grid inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


