Introduction to Inverters
It can be compared to sinusoidal wave. The main advantage of using AC current over DC current is that it helps to supply current to long
Get Price
9 Best RV Inverters – Pure Sine Wave Power Converter
Modified sine wave inverters produce an AC output that is a close approximation of a true sine wave but with some distortion. Pure sine wave
Get Price
An overall introduction of inverter waveform and the comparisons
This article will give you a detailed introduction and comparison of inverter waveform, including the principles of generating different waveforms, and comparison between
Get Price
800VA Pure Sine Wave Inverter''s Reference Design
An Inverter not only converts the DC Voltage of battery to 220-V/120-V AC Signals but also charge the Battery when the AC mains is present. The block diagram shown above is a simple
Get Price
AC Circuit Theory (Part 2): AC Waveforms and their
Alternating current or voltage is generically represented by the Sine wave to the extent that in the development of inverters, they distinguish
Get Price
AC Circuit Theory (Part 2): AC Waveforms and their Properties
Alternating current or voltage is generically represented by the Sine wave to the extent that in the development of inverters, they distinguish between inverters by describing
Get Price
DC-AC Inverter Circuit
The inverter generates a waveform composed of many narrow pulses in each cycle and converts 240 VDC into AC. The width of switching pulses (i.e., the duty cycle) is varied in
Get Price
H-Bridge Sine Wave Inverter Circuit using Arduino
In this article I will explain how we can build an Arduino-controlled H-Bridge sine wave inverter circuit using some easy parts. So this thing will basically convert DC into AC but
Get Price
3 types of inverters with different wave types
These inverters have a square wave-like waveform with an additional step or two. They may work well with most equipment, but compromises the equipment''s power or efficiency.
Get Price
Inverter | Efficiency & Output Waveform
The article provides an overview of inverters in renewable energy systems, focusing on their role in converting DC to AC, their efficiency, and
Get Price
An Overview of Inverter Waveforms and Comparative Analysis
The output waveform of an inverter when supplied with AC power is determined by its operational principle. This article provides a comprehensive introduction and comparison of
Get Price
Modified vs. Pure Sine Wave Inverter: What''s the Difference?
The three most common types of inverters made for powering AC loads include: (1) pure sine wave inverter (for general applications), (2) modified square
Get Price
Inverter Types & Working Principle | Sine Wave,
The article provides an overview of inverter technology, explaining how inverters convert DC to AC power and detailing the different types of inverters—sine
Get Price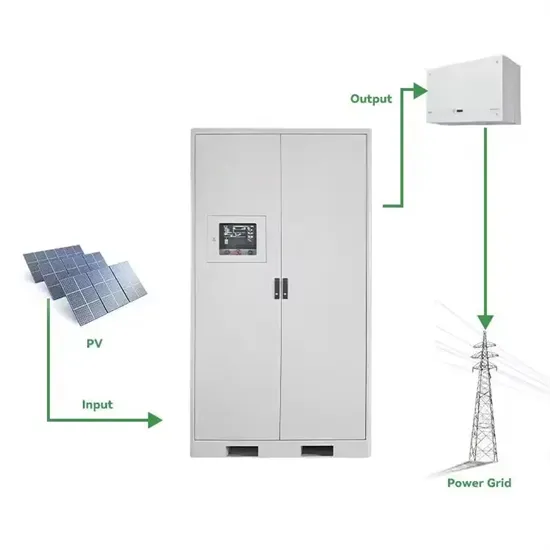
The Only Inverter Size Chart You''ll Ever Need
A pure sine wave inverter replicates the clean and smooth flow of power you get from your utility company, suitable for sensitive electronics and
Get Price
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
The three most common types of inverters made for powering AC loads include: (1) pure sine wave inverter (for general applications), (2) modified square wave inverter (for resistive,
Get Price
Best Inverter Modified Sine Wave Power Converters for Vehicles
2 days ago· Inverter modified sine wave power converters are essential for converting DC power from vehicles or batteries into usable AC power for a range of devices. These inverters are
Get Price
Pure Sine Wave Inverter: All You Need to Know
This is where pure sine wave inverter, also known as true sine wave inverter, comes into play. They are advanced power conversion devices that produce a high-quality AC
Get Price
DC/AC Pure Sine Wave Inverter
Introduction This report focuses on DC to AC power inverters, which aim to efficiently transform a DC power source to a high voltage AC source, similar to power that would be available at an
Get Price
Global LF Series Pure Sine Wave Inverter Charger User''s
2-1. General Information The Global LF Series Pure Sine Wave Inverter Charger product line is a combination of an inverter, battery charger and auto AC transfer switch in one unit and has a
Get Price
An Overview of Inverter Waveforms and Comparative
The output waveform of an inverter when supplied with AC power is determined by its operational principle. This article provides a
Get Price
Lecture 17: Inverters, Part 1 | Power Electronics
This lecture starts with a review of the Fourier series and waveform characteristics in the time and frequency domains, including the
Get Price
Inverter Types & Working Principle | Sine Wave, Square Wave,
The article provides an overview of inverter technology, explaining how inverters convert DC to AC power and detailing the different types of inverters—sine wave, square wave, and modified
Get Price
DC to AC Conversion (INVERTER)
• Output of the inverter is "chopped AC voltage with zero DC component" some applications such as UPS, " high purity " sine wave output is required.
Get Price
Inverter | Efficiency & Output Waveform
The article provides an overview of inverter in renewable energy systems, focusing on their role in converting DC to AC, their efficiency, and
Get Price
Pure Sine Wave Inverter (12v/24v/48v) | inverter
Factory price 12V 200W pure sine wave inverter for sale online. This pure sine wave 200 watt inverter adopts aluminum shell, anti-oxidation and high
Get Price
Modified vs. Pure Sine Wave Inverter: What''s the
Here''s your sine.Modified Sine Inverters Simulate AC Power A modified sine wave inverter produces an approximation of a real AC sine
Get Price
1500 Watt Pure Sine Wave Power Inverter DC 12V to 110V/120V AC
Buy Jecatiy 1500 Watt Pure Sine Wave Power Inverter DC 12V to 110V/120V AC Converter with 2 AC,18W USB, and 30W Type-C Charging Ports, Car Solar Power Inverters with LCD Display
Get Price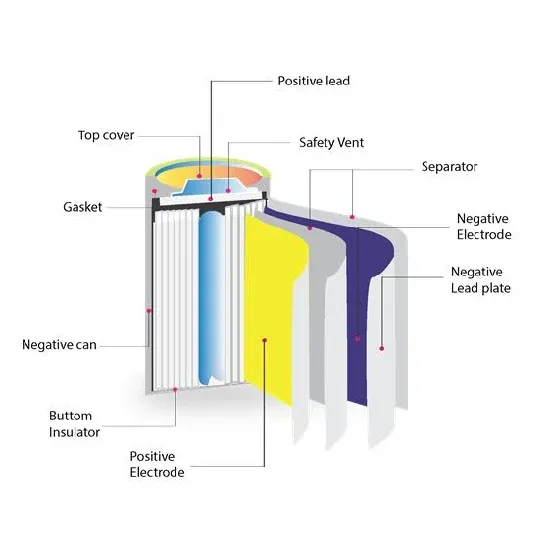
Inverter | Efficiency & Output Waveform
The article provides an overview of inverters in renewable energy systems, focusing on their role in converting DC to AC, their efficiency, and output waveforms.
Get Price
Powering Your Circular Saw: Is A 2000-Watt Inverter Enough?
If you''re wondering if a 2000-watt inverter is enough to power your circular saw, read this article for a detailed analysis and helpful tips.
Get Price
Diablo-10-circular-saw-blade in Modified Sine Wave Inverter
Availability Show Only Available Products VEVOR Modified Sine Wave Inverter, 3000Watt, DC 12V to AC 230V LCD Display Power Inverter with 3 AC Outlets 2 USB Port 1 Type-C Port 10
Get Price
Design your own Sine Wave Inverter Circuit from the
In this article I have explained comprehensively regarding how to design a sine wave inverter without any form of coding or complex circuit
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Inverter AC circular wave]
What are the different types of AC inverters?
The three most common types of inverters made for powering AC loads include: (1) pure sine wave inverter (for general applications), (2) modified square wave inverter (for resistive, capacitive, and inductive loads), and (3) square wave inverter (for some resistive loads) (MPP Solar, 2015).
Can a square wave inverter be used for alternating current?
While square wave output is highly efficient, it might not be compatible with certain appliances. For applications needing smoother AC power, inverters producing pure sine wave alternating current are essential. By adjusting the duty cycle of PWM according to sinusoidal law, inverters generate a waveform resembling a sine wave.
How does a sine wave inverter work?
As you can see in this diagram, when you plot out AC and DC current polarity, AC power forms a smooth wave. This is known as an AC sinusoidal or "sine" wave. An inverter's job is to reproduce that wave from a DC power source, and there are two answers to this problem. A modified sine wave inverter produces an approximation of a real AC sine wave.
What does a modified sine wave inverter look like?
A modified sine wave inverter produces an approximation of a real AC sine wave. If you chart it out, it looks like a sine wave at first, but if you look closely, there are jagged stair steps in the waveform as the inverter crudely flips between polarities rather than the smooth wave seen above.
How does a PWM inverter work?
In the inverter, a low-power reference 60 Hz sine wave and a higher-frequency triangular wave are used to produce the PWM waveform. The sine wave amplitude values are sampled by the triangular wave to produce the PWM waveform.
What is an inverter bridge?
The inverter bridge (H-bridge) is a method of producing a square wave from a DC voltage. The operation of a basic H-bridge is enhanced to produce the misnamed modified sine wave, which is shown in Figure 5. (Perhaps modified square wave would be a better name.)
More related information
-
 Bulgarian DC to AC inverter
Bulgarian DC to AC inverter
-
 Togo sine wave inverter merchants
Togo sine wave inverter merchants
-
 Samoa pure sine wave inverter manufacturer
Samoa pure sine wave inverter manufacturer
-
 What battery is suitable for a sine wave inverter
What battery is suitable for a sine wave inverter
-
 High frequency inverter is also a sine wave
High frequency inverter is also a sine wave
-
 Uzbekistan sine wave inverter
Uzbekistan sine wave inverter
-
 Inverter three-phase AC modulation control
Inverter three-phase AC modulation control
-
 Pure sine wave inverter structure
Pure sine wave inverter structure
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


