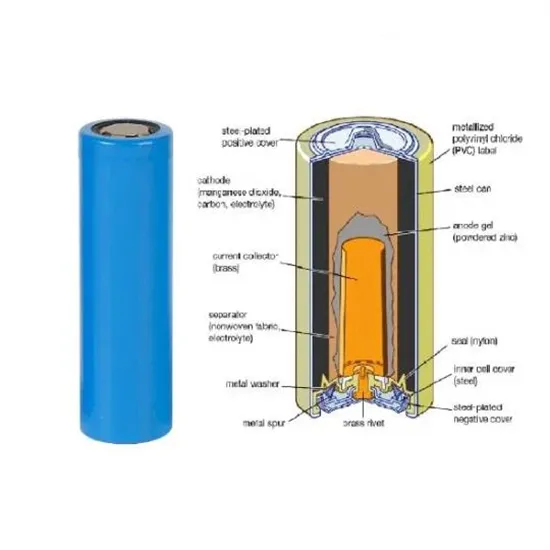
What is a centralized inverter?
Centralized inverters are mainly used in large-capacity photovoltaic power generation systems such as ground power stations and
Get Price
Inverter clipping: How to maximize solar project value
Balancing inverter clipping ratios to tune cash flows Pushing the limits of DC loading on an inverter could be detrimental to its long-term service
Get Price
Differences between Central Inverter and String Inverter
The National grid has the following requirements to the distributed photovoltaic power station: The single grid connection point is less than 6MW, the annual self-use power
Get Price
Inverter vs Generator: Which One Is Right for You?
If you prioritize clean, quiet, and portable power, a portable power station (inverter) is your best bet. On the other hand, if you need higher power output and longer runtimes, a
Get Price
Oversizing a PV system for more solar energy
Oversizing means that we have the capacity to produce more DC power in a system than the inverter can effectively turn into AC energy. On the surface,
Get Price
Generator vs. Inverter: Which is Better for Your Power
Discover the differences between generators and inverters in this comprehensive guide. Learn which is better for your power needs, their pros
Get Price
Which Is Best: Generator or Inverter? A Complete Guide to
Choosing between a generator and an inverter depends on your specific power needs, lifestyle, and priorities. Generators offer robust power for heavy-duty appliances and extended outages,
Get Price
Generator vs. Inverter: Which is Better for Your Power Needs?
Discover the differences between generators and inverters in this comprehensive guide. Learn which is better for your power needs, their pros and cons, and how to choose the
Get Price
Inverter vs Generator: Which One Is Right for You?
If you prioritize clean, quiet, and portable power, a portable power station (inverter) is your best bet. On the other hand, if you need higher power
Get Price
Inverter vs. Generator: What Is the Difference?
Generators can provide more power for longer periods of time, but may require frequent charging or refueling. Inverters offer a more limited runtime, but can
Get Price
power engineering
This answer skips over many real world details, such as reactive power, which play a role in the power sharing between the grid and a grid-tie
Get Price
Generator vs. Inverter Generator: Which Is Best for You? | Angi
Traditional generators offer high power output at a lower price than inverter generators. Inverter generators run more quietly and use fuel more efficiently than traditional
Get Price
Inverter system up to 30kVA
To allow residents of such sites to take advantage of solar power an exemption is available to the land-owners or their representative e.g. the strata management company, of multi-residential
Get Price
Inverter Generator Vs. Generator: Which Is Best for
Inverter generators and traditional generators serve different needs. Explore the key differences, advantages, and disadvantages to
Get Price
Inverter Generator vs Regular Generator: Understanding the
Traditional generators offer high power output at a lower price than inverter generators. Inverter generators run more quietly and use fuel more efficiently than traditional
Get Price
Inverter vs. Generator: What Is the Difference?
Generators can provide more power for longer periods of time, but may require frequent charging or refueling. Inverters offer a more limited runtime, but can easily be recharged. Portability and
Get Price
Impact of inverter loading ratio on solar photovoltaic system
Higher ILRs increase the utilization of the inverter, thereby decreasing the inverter costs per kW h of AC output. The drawback to increasing a project''s ILR occurs when the
Get Price
Inverter Vs Generator: Which Power Source is Right
This guide will explore the key features, advantages, and potential drawbacks of both inverters and generators, helping you choose the best
Get Price
Inverter vs. Generator: Which One Is Better?
In the ongoing debate of Inverter vs. Generator, determining which is better depends heavily on individual needs and circumstances. Both inverters and generators serve
Get Price
Understanding DC/AC Ratio – HelioScope
Clipping Losses and DC/AC Ratio When the DC/AC ratio of a solar system is too high, the likelihood of the PV array producing more power than the inverter
Get Price
electric circuits
What happens if the load on the electrical generator exceeds its power generation? and why? To be more precise, suppose we have a standard induction generator operating at
Get Price
Inverter Vs. Generator: Which One Is More Powerful?
This article delves into the specifics of inverters and generators, exploring their power capabilities, advantages, and disadvantages to help you determine which is the more
Get Price
Inverter Generator Vs. Generator: Which Is Best for Home Use?
Inverter generators and traditional generators serve different needs. Explore the key differences, advantages, and disadvantages to determine which is best for your home.
Get Price
Inverter Generator vs Generator: What''s the Difference?
While both generators and inverter generators produce electrical power, there are significant differences in the way they operate, their power output, and their fuel efficiency. In
Get Price
7 Reasons Why You Should Oversize Your PV Array
Oversizing a PV array, also referred to as undersizing a PV inverter, involves installing a PV array with a rated DC power (measured @ Standard Test Conditions) which is
Get Price
Solar inverters and clipping: What DC/AC inverter
The key driver here is the "clipping loss": when the DC power feeding an inverter is more than the inverter can handle, the resulting power is
Get Price
Inverter Vs Generator: Which Power Source is Right for You?
This guide will explore the key features, advantages, and potential drawbacks of both inverters and generators, helping you choose the best power backup solution for your
Get Price
What size inverter is best for solar panels?
Conclusion You need to consider the solar panel power, conversion efficiency, battery voltage and future expansion needs when
Get Price
Reactive Power Capability and Interconnection
Inverters would be able to produce or absorb reactive power when it operates at a power levels lower than P1 (e.g., P2). However, in response to recent grid
Get Price
Inverter Generator vs Regular Generator: Understanding the
One of the main differences between regular generators and inverter generators is the power output. Regular generators typically produce more power than inverter generators.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Generation power is greater than inverter power]
What is the difference between a generator and an inverter generator?
Generator vs. Inverter Generator: Key Differences Traditional generators produce power at a constant rate while inverter generators produce power based on demand. Although typically more expensive, inverter generators are the more efficient, stable, quiet, and lightweight of the two options.
Are traditional generators better than Inverter generators?
Lower cost: Traditional generators are generally less expensive than inverter generators of the same power output. This makes them a more cost-effective option for people who need a power source but have a limited budget. Durability and ruggedness: Traditional generators are typically built to withstand harsh environments and rough handling.
Are regular generators more fuel-efficient than Inverter generators?
Regular generators are typically less fuel-efficient than inverter generators. This is because regular generators use more fuel to generate the same amount of power as an inverter generator. Inverter generators are more fuel-efficient because they use a smaller engine and have a more efficient power generation system.
Are regular generators Louder Than Inverter generators?
Regular generators tend to be louder than inverter generators. This is because regular generators have a larger engine and generator head, which makes them noisier. Inverter generators, on the other hand, are typically quieter because they use a smaller engine and have a more efficient power generation system.
How much power does an inverter generator produce?
Regular generators can produce power ranging from 3,000 watts to over 15,000 watts, whereas inverter generators typically produce power ranging from 1,000 watts to 4,000 watts. Another significant difference between regular generators and inverter generators is the power quality.
What is an inverter generator?
An inverter generator is a type of generator that converts DC power produced by the generator into AC power. This is done by using a device called an inverter. The inverter allows the generator to produce a stable and consistent flow of power, making it suitable for sensitive electronic equipment such as laptops, smartphones, and televisions.
More related information
-
 The photovoltaic inverter with the highest power generation
The photovoltaic inverter with the highest power generation
-
 Bhutan photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
Bhutan photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
-
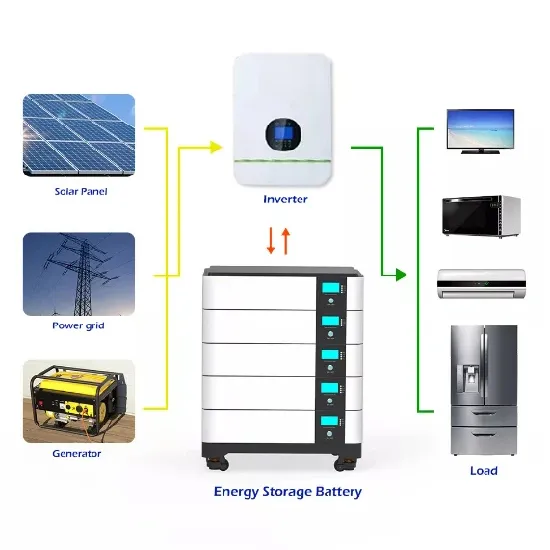 Photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
Photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
-
 Photovoltaic power generation small home inverter
Photovoltaic power generation small home inverter
-
 Solar 48v power generation water pump inverter
Solar 48v power generation water pump inverter
-
 Nordic photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
Nordic photovoltaic power generation equipment inverter
-
 Which inverter has greater power
Which inverter has greater power
-
 Photovoltaic power generation inverter power generation
Photovoltaic power generation inverter power generation
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.