
Working Principle of Inverter and Its Application in Power System
Inverters can be divided into several types according to the form of the output waveform, such as square wave inverters, modified sine wave inverters, and pure sine wave
Get Price
Inverter Generator Basics: Classification and Working
Classification of Inverter Generator Classification by Control Mode Inverter generator can be divided into open-loop control inverter generator and
Get Price
Inverter Classification|Home Energy Storage
Inverters can be divided into single-phase inverters and three-phase inverters according to the number of phases of their output AC voltage.
Get Price
Solar inverters: Principle and Classification | DSBsolar
2. Classification of inverters Inverter classification methods are many, according to the nature of the source can be divided into active inverters and passive inverters, according to the inverter
Get Price
Introduction to 17 types of inverter – TYCORUN
The input of the inverter can be a voltage source or a current source, so these types of inverter are divided into voltage source inverter (VSI)
Get Price
Working Principle of Inverter and Its Application in
Inverters can be divided into several types according to the form of the output waveform, such as square wave inverters, modified sine wave
Get Price
Introduction different types of inverters
Classification by installed use (1)Off-grid inverter An off-grid inverter is an inverter that converts DC power generated by distributed power sources such
Get Price
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC
Get Price
How Do Inverters Convert DC to AC?
Wind power: Inverters are also used in wind power systems to convert DC power generated by wind turbines into AC power for use by the grid or loads. Grid and Emergency
Get Price
Classification of inverters
4. According to power level Divided into high-power inverter, medium-power inverter, low-power inverter. 5. According to the nature of the wave string
Get Price
Inverter Basics: Classification and Applications
Inverters are classified into different types based on input, output, application and power rating. These are constant input voltage inverters.
Get Price
An overall introduction to working principle of inverter
This article introduces the working principle of inverter in the main parts of the inverters, including the inverter PWM, the communication protocols, and the DC-DC circuit.
Get Price
DC-to-AC Converters (Inverters): Design, Working &
The electrical circuits that transform Direct current (DC) input into Alternating current (AC) output are known as DC-to-AC Converters or
Get Price
Different Types of Inverters and Their Applications
Power inverters are fundamental devices for power electronics that convert DC (Direct Current) into AC (Alternating Current). There are many
Get Price
How inverters are classified ?
Voltage source inverter (VSI) and current source inverter (CSI): classified according to the characteristics of the DC power supply, the former has a constant DC voltage
Get Price
VFD vs inverter
This article will introduce the working principles, functions and characteristics of VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) and inverters respectively,
Get Price
Different Types of Inverters and Their Applications
Power inverters are fundamental devices for power electronics that convert DC (Direct Current) into AC (Alternating Current). There are many types of power inverters
Get Price
DC-AC Inverter Circuit
High-side power supplies can be divided into two types: 1) a bootstrap power supply that uses the switching of the main inverter and 2) a charge pump that uses the switching of a driver or a
Get Price
Which type of transformer is used in DC to AC
An inverter converts DC into AC, while a transformer is an electrical device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to convert
Get Price
Types of Inverters
In the dynamic world of strength electronics, inverters play an important position in changing direct Current (DC) into alternating Current (AC). These devices are instrumental in
Get Price
Introduction to 17 types of inverter – TYCORUN
The input of the inverter can be a voltage source or a current source, so these types of inverter are divided into voltage source inverter (VSI) and current source inverter (CSI).
Get Price
Off Grid Inverter Basics: Classification and Working
Off-grid inverters, as a core component of modern energy solutions, are gaining increasing attention. The role of off-grid inverters is to separate the
Get Price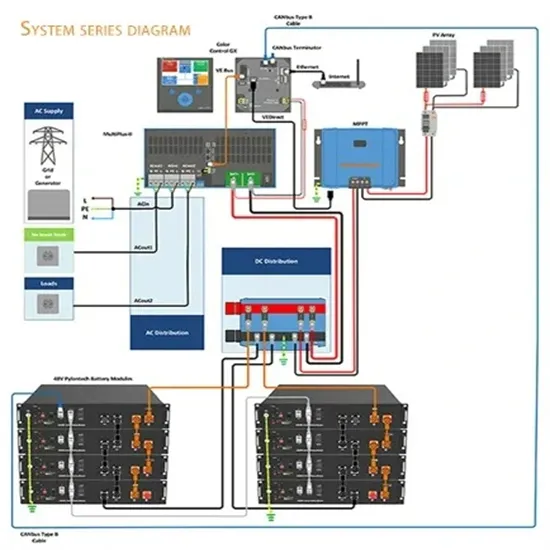
Inverter Types | AC DC Power Converters | Circuits
Companies and households that require a constant power supply need inverters. We''ll cover the different types of inverters and their wide range of applications.
Get Price
Inverter Basics: Classification and Applications
Inverters are classified into different types based on input, output, application and power rating. These are constant input voltage inverters. Current varies according to load
Get Price
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
The inverter can be defined as the device which converts DC input supply into AC output where input may be a voltage source or current source. Inverters are mainly classified into two main
Get Price
INSTALLATION GUIDE AND USER MANUAL
On parallel inverter installations, the emergency stop button must be wired to the designated "1aster" inverter. 9nlike the 1aster, the "slave" inverters won''t lose their 12:dc
Get Price
Inverter types and classification | AE 868: Commercial Solar
Now that we understand why we need an inverter for PV systems, it is time to introduce the different types of inverters that exist in the market and discover the advantages and
Get Price
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
In the dynamic world of strength electronics, inverters play an important position in changing direct Current (DC) into alternating Current (AC). These devices are instrumental in
Get Price
6 FAQs about [According to the inverter DC power supply can be divided into]
How many types of power inverters are there?
According to the output characteristic of an inverter, there can be three different types of inverters. These power inverter types differ in their output quality, cost, and suitable applications.
What is a power inverter?
Unlike rectifiers which convert AC into DC; Inverter is a type of converter that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) of desired voltage and frequency with the help of control signals and electronic switches. Here in this post, we are going to discuss inverter basics, classification and application of power inverters.
Which type of inverter system is best for continuous power supply?
Advantage This type of inverter system is one the best for providing continuous power supply. These inverters provide stable frequency to the load. Off-grid or standalone inverters are much cheaper. Energy self-sufficient and power failure on the utility grid will don’t affect the off-grid system.
How do power inverters convert DC to AC?
For this reason, AC power must first be converted to DC and then stored in batteries and ultra-capacitors.. Once you want to use AC power, power inverters will convert the stored DC back to AC to supply power to operate AC-based appliances and equipment. So, the device which converts DC into AC is called an Inverter.
What are the different types of inverter circuits?
Inverters can be classified into many types based on output, source, type of load, etc. Below is the complete classification of the inverter circuits: (I) According to the Output Characteristic (II) According to the Source of Inverter (III) According to the Type of Load (IV) According to different PWM Techniques
What is inverter output?
The inverter output is neither of the two kinds we’ve covered above. Instead, it is a sum of two square waves with a shape closely resembling a sine wave. Inverter Classification According to the Source of the Inverter. Under this tier, there are two inverter types. The CSI’s input is a current source.
More related information
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


 DC Power Supply and Inverter
DC Power Supply and Inverter
 Inverter home power supply
Inverter home power supply
 Grenada Base Station DC Power Supply System
Grenada Base Station DC Power Supply System
 Latvian portable AC DC power supply
Latvian portable AC DC power supply
 Oman portable AC DC power supply
Oman portable AC DC power supply
 Nepal portable DC power supply manufacturer
Nepal portable DC power supply manufacturer
 Price of portable DC power supply in South Ossetia
Price of portable DC power supply in South Ossetia