high frequency inverter pcb board
What is high frequency inverter board? This guide covers its basics, how it works, function and application and differences from low-frequency ones through this blog.
Get Price
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
High-Frequency Inverter: Utilizes high-frequency switching technology and miniaturized transformers, resulting in more compact and lightweight designs. However, high
Get Price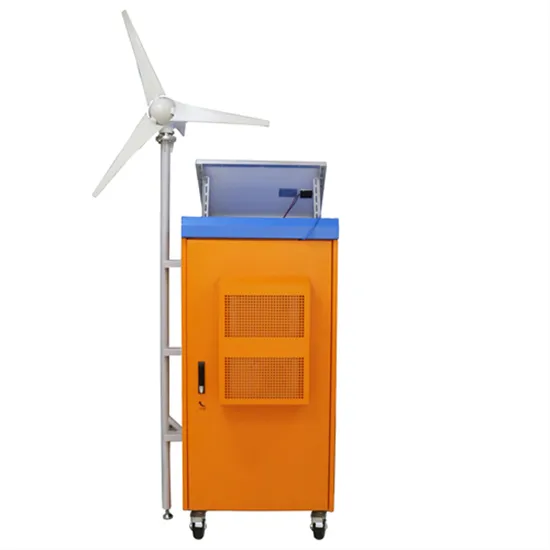
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
The low frequency inverters typically operate at ~60 Hz frequency. To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used. These inverters use the
Get Price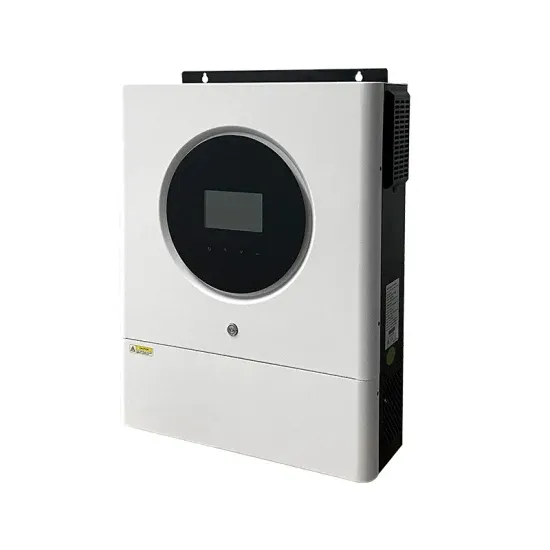
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key
Explore the key differences in low frequency vs high frequency inverters including their applications, advantages, and which is best for your needs.
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High
High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency inverters - typically 20 kHz to 100
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
High-frequency inverters deploy high-frequency switching systems to chop direct current power at high frequency with high-frequency tubes like MOSFETs. They then shift the
Get Price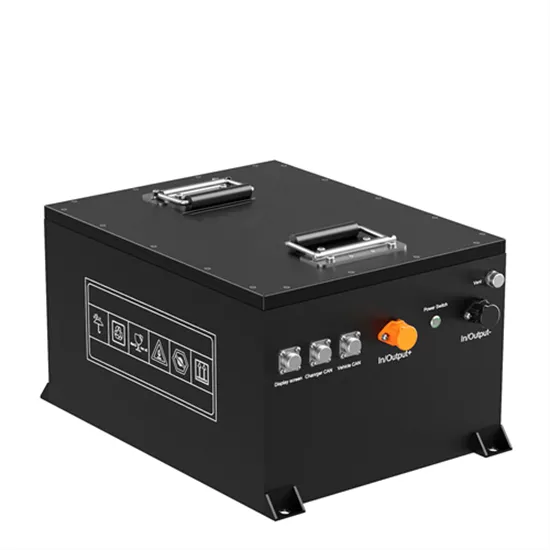
Frequency inverter
Frequency inverter A frequency inverter is an electronic device which enables the conversion of an electrical variable ''current''. In this case, the frequency inverter transforms an AC current
Get Price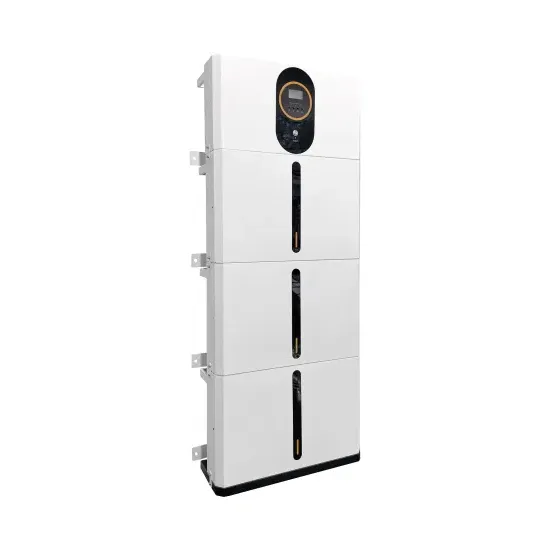
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get Price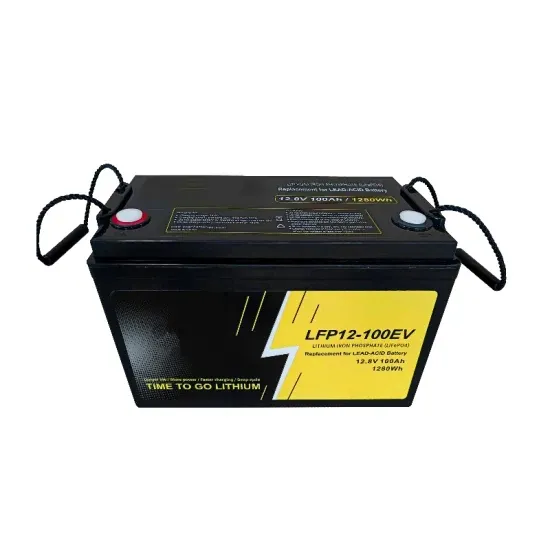
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
An inverter is a key component that converts DC power into AC power for household appliances and is commonly used in solar energy
Get Price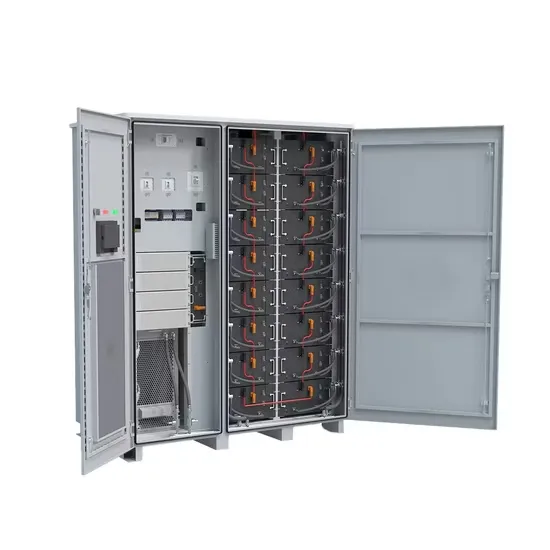
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
What is a High-Frequency Inverter? A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency, typically above
Get Price
What is a high frequency inverter and what should be paid
A high frequency inverter is a device that converts direct current to alternating current. High frequency inverters are inverters suitable for household DC and AC conversion.
Get Price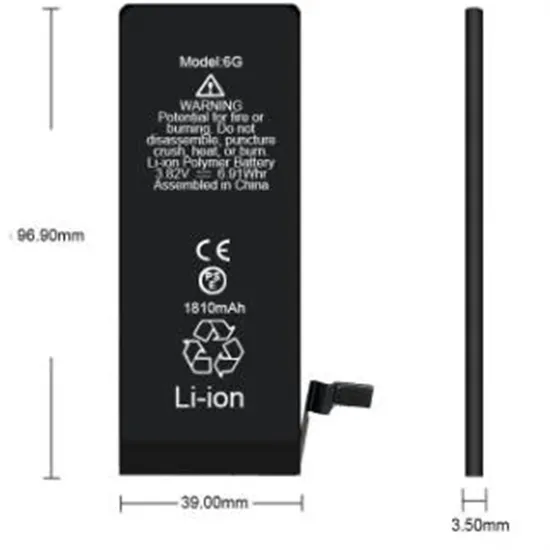
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few
Get Price
What is a High-Frequency Power Inverter?
This article provides an overview of high-frequency inverter topologies, design considerations, applications, and advantages versus traditional lower
Get Price
Harmonic Overload: Impacts Of High-Frequency Switching on
During the CIGRE Grid of the Future symposium and workshop, harmonics were recognized as a critical focus in modern electrical systems, where high-frequency switching technologies and
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High Frequency
What are high frequency inverters? An inverter that converts DC power to AC power at a high frequency, also known as a transformerless inverter, does not use a transformer. The
Get Price
What is a High-Frequency Power Inverter?
This article provides an overview of high-frequency inverter topologies, design considerations, applications, and advantages versus traditional lower frequency inverters.
Get Price
Frequency inverter basics
This allows for frequency inverter servicing while the motor is being run from the incoming line, and can also be used to run the motor at constant speed at a
Get Price
High Frequency Inverter Board Assembly | Best Technology
What is high frequency inverter board? This guide covers its basics, how it works, function and application and differences from low-frequency ones.
Get Price
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
Operating Frequency Low-Frequency Inverter: Operates at a lower frequency, typically around 50Hz or 60Hz. Because its frequency is close to that of utility power, it is
Get Price
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a
High-Frequency Inverter: Utilizes high-frequency switching technology and miniaturized transformers, resulting in more compact and lightweight designs. However, high
Get Price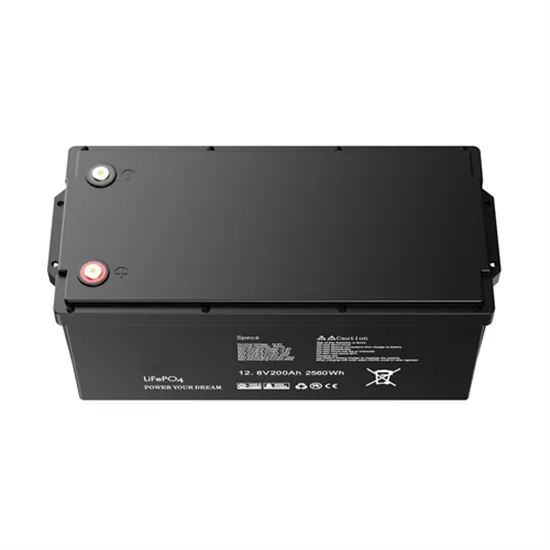
What is Frequency Converter? How it works?
The inverter uses three sets of high speed switching transistors to create DC "pulses" that emulate all three phases of the AC sine wave. These pulses not
Get Price
800VA Pure Sine Wave Inverter''s Reference Design
The pure Sine Wave inverter has various applications because of its key advantages such as operation with very low harmonic distortion and clean power like utility-supplied electricity,
Get Price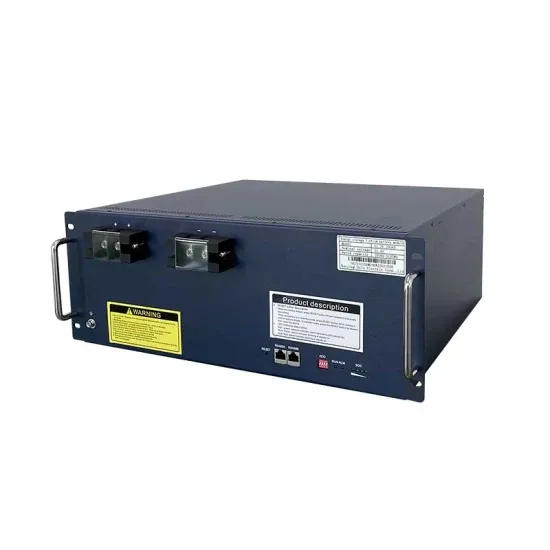
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for
Get Price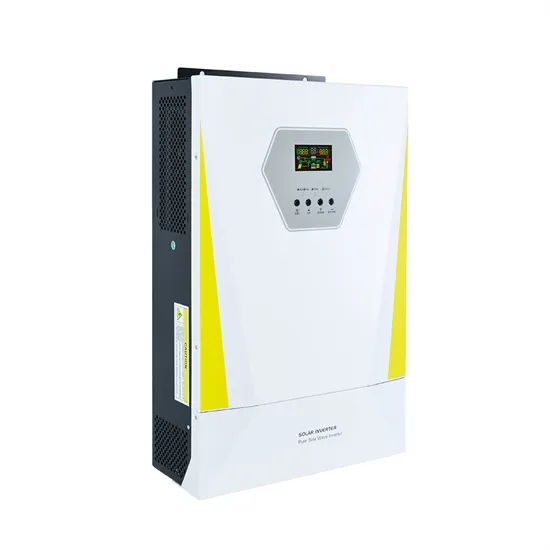
What is low frequency inverter? Why choose it?
There are two types of power inverters on the market: low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters. Whether the inverter is high
Get Price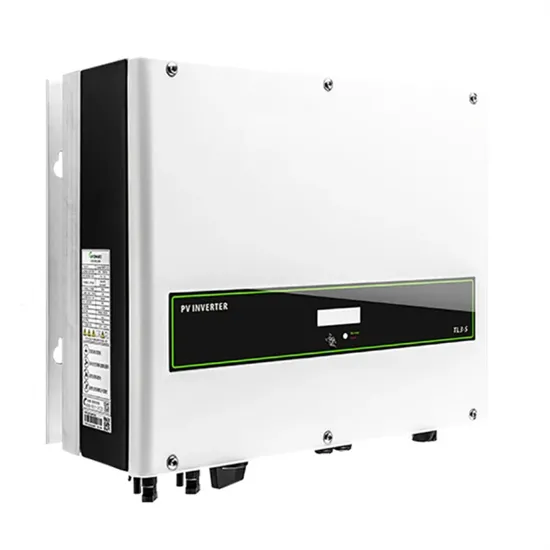
High Frequency Vs. Low Frequency Inverters Which is better?
High Frequency Vs. Low Frequency? Which Inverter is better?00:00 - intro00:43 - low frequency inverters02:15 - High Frequency Inverters03:17 - Comparison
Get Price
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in Modern Applications
High-frequency inverters are known for their high efficiency, which is one of their most significant advantages. By operating at higher frequencies, typically in the range of tens or hundreds of
Get Price
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency. They are typically less expensive, have smaller footprints, and have a lower tolerance for industrial loads.
Get Price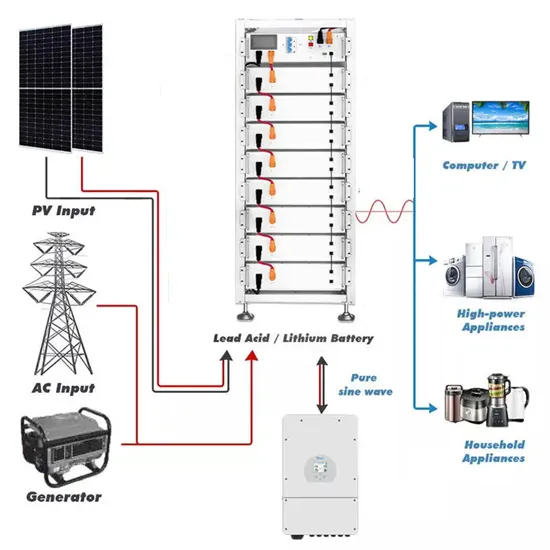
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency inverters - typically 20 kHz to 100 kHz. High-frequency inverters
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz.
Get Price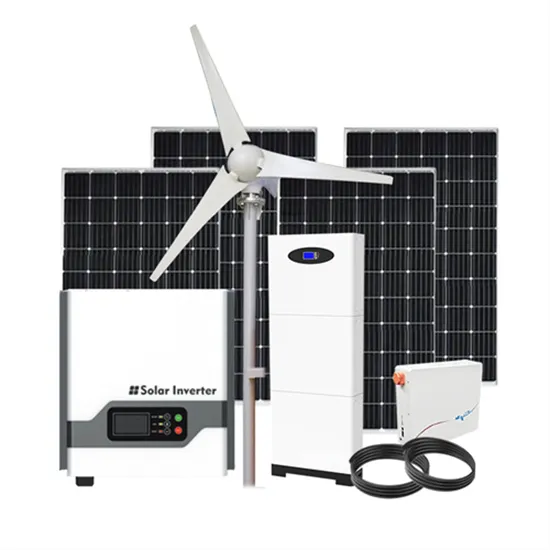
More related information
-
 What high-frequency inverter brand is good
What high-frequency inverter brand is good
-
 What is a high-frequency inverter
What is a high-frequency inverter
-
 What are the benefits of pure sine wave inverter
What are the benefits of pure sine wave inverter
-
 High-frequency inverter front-stage closed-loop control
High-frequency inverter front-stage closed-loop control
-
 What is a Greek PV inverter
What is a Greek PV inverter
-
 High-frequency 40W inverter production
High-frequency 40W inverter production
-
 How much is the price of high-frequency inverter in Bangladesh
How much is the price of high-frequency inverter in Bangladesh
-
 High-frequency smart inverter
High-frequency smart inverter
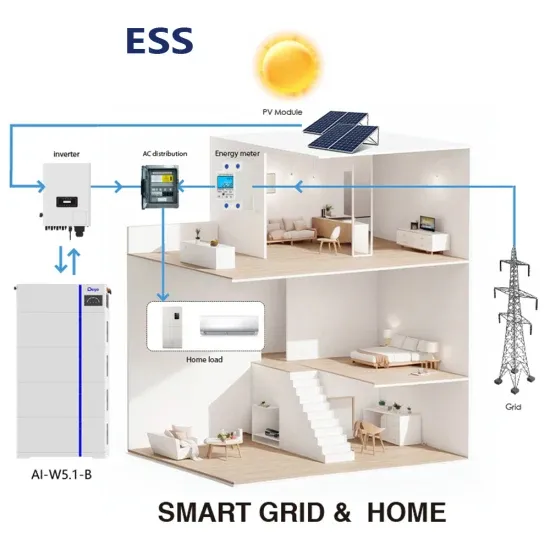
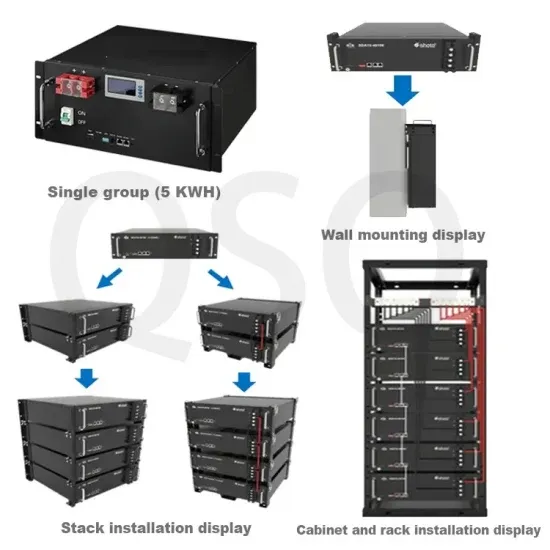
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


