Cost of Electricity Generation by Source
Not all energy has been created equal – and that also applies to the cost of electricity generation. This also largely has to do with how much funding has gone into the
Get Price
Power stations KS3 | Y8 Science Lesson Resources
Common misconception Power stations generate most of the electricity that we use in the UK. Highlight how over half of UK electricity is now generated using
Get Price
How do power plants generate electricity?
What other power plants use renewable energy? In addition to the power plants mentioned above and generally referred to as "traditional," many
Get Price
Cost of Electricity Generation by Source
Not all energy has been created equal – and that also applies to the cost of electricity generation. This also largely has to do with how much
Get Price
The cost of electricity — open-electricity-economics 0.1
Electricity generation technologies vary dramatically in their cost structure. Some plants, such as nuclear, wind and solar power, have virtually zero variable costs. This is in stark contrast to
Get Price
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How much does it cost to generate electricity with different types of power plants? The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) has historical data on the average annual operation,
Get Price
Understand the electricity supply system | Homes and housing
Electricity is generated at power stations across Queensland. These power stations are fuelled by coal, gas, oil, biomass, water, wind, heat from the earth (geothermal) and sun. Queensland''s
Get Price
FactCheck: does coal-fired power cost $79/kWh and
AAP Image/Lukas Coch 80% of Australian energy comes from coal, coal-fired power, and it''s about $79 a kilowatt hour. Wind power is about
Get Price
Electricity statistics
Electricity generation from the combustion of coal, oil, and gas provides baseload, backup and peaker electricity supply. Generation from these fuels is around a quarter of New
Get Price
Open Electricity Economics: 3. The cost of electricity
Electricity generation technologies vary dramatically in their cost structure. Some plants, such as nuclear, wind and solar power, have virtually zero variable
Get Price
Economics of Power Generation: Know Modes of Operation, Cost
Economics of Power Generation refers to the analysis and management of various financial aspects involved in generating electrical power. It includes the study of costs, revenues,
Get Price
Economics of Power Generation
What is the Economics of the Power System? The economics of power generation is the process of calculating the cost of producing electrical energy per unit (i.e. KWH).
Get Price
Economics of Power Generation: Know Modes of
Economics of Power Generation refers to the analysis and management of various financial aspects involved in generating electrical power. It includes
Get Price
What is a thermal power plant? Steam power plant
Reheat also increases the power output of the cycle without increasing the steam consumption. Steam power plants running on solar
Get Price
Cost of electricity by source
Short-term fluctuations in fuel prices can have significant effects on the cost of energy generation in natural gas and oil fired power plants and to a lesser extent for coal fired power plants.
Get Price
Live UK Electricity Generation, Carbon Intensity & Demand – Energy
Real-time half-hourly data on UK electricity generation, renewable vs fossil fuel mix, power flow visualisation and carbon intensity from National Grid.
Get Price
Gas-fired power plant
Gas-fired power plant A cogeneration plant in Berlin Gas generates over 20% of world electricity Share of electricity production from gas A gas-fired power
Get Price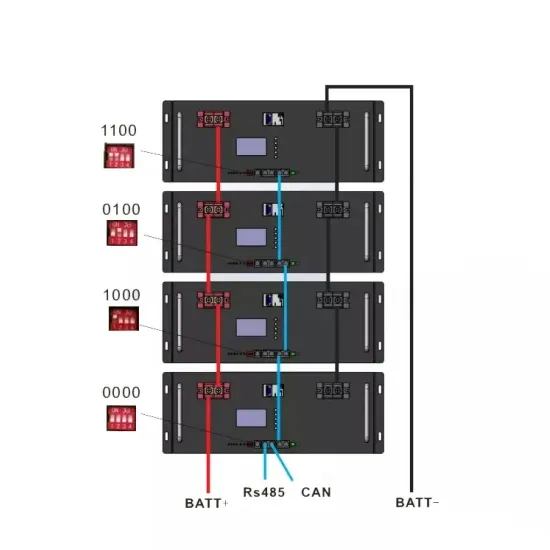
What is the electricity price of energy storage power station?
In summary, a synthesis of these factors establishes the framework for understanding how electricity prices at energy storage stations are calculated, revealing the
Get Price
Generating electricity
The electricity we use every day is the flow of negatively-charged particles called electrons. Electricity is generated by converting a different form of energy into
Get Price
Open Electricity Economics: 3. The cost of electricity
Electricity generation technologies vary dramatically in their cost structure. Some plants, such as nuclear, wind and solar power, have virtually zero variable costs: once they are built, they
Get Price
The cost of electricity — open-electricity-economics
Electricity generation technologies vary dramatically in their cost structure. Some plants, such as nuclear, wind and solar power, have virtually zero variable
Get Price
What Will It Cost To Generate Electricity?
A quick visual snapshot of how prices for different generating resources is expected to change in the coming decades.
Get Price
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In summary, a synthesis of these factors establishes the framework for understanding how electricity prices at energy storage stations are calculated, revealing the
Get Price
20.1 Electricity generation | Energy and the national
Electricity is generated in a power station. In previous grades, we have looked at how electricity is generated within coal-powered power stations and distributed to the country in the national
Get Price
Economics of the Power Industry
Natural Gas Combustion Turbine Generator (CTG) plants have the lowest capital cost at around $974 per Kilowatt, followed by Coal-Fired, Biomass, and Photovoltaic Solar. The most
Get Price
Costs of gas-fired power generation?
Gas-fired power generation explained 23% of global electricity generation in 2023, second only to coal at 35% of global electricity generation. Simply switching coal-fired power to gas-fired
Get Price
How to calculate the cost of generating electricity
How to calculate the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) In simple terms, the LCOE consists of calculating the total average cost of building and
Get Price
Electricity Generation
Plant set-up: Rankine Cycle Station Heat Rate: 2500 kcal/kwh Coal: Indonesian Coal with a gross calorific value of 4500 kcal/kg. Usable of this is about 4150 kcal/kg (Net CV) Power generation:
Get Price
Electricity in Great Britain
In 2008 nuclear electricity production was 53.2 TW·h, equivalent to 860 kWh per person. In 2014, 28.1 TW·h of energy was generated by wind power, which contributed 9.3% of the UK''s
Get Price
6 FAQs about [What is the price of electricity generated by the power station ]
How much does a power plant cost?
The Capital Costs vary among the power resources. Natural Gas Combustion Turbine Generator (CTG) plants have the lowest capital cost at around $974 per Kilowatt, followed by Coal-Fired, Biomass, and Photovoltaic Solar. The most expensive Capital Cost for a power plant is Offshore Wind. (5) Variable costs are the costs of day-to-day operations.
Why is cost important in power stations?
In any power station, the cost plays an important role. In some cases, the cost decides whether a certain station will be carried out or not. Moreover, the cost per unit generated would be the lowest possible. Economic problems will occur during the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electrical energy.
How do you calculate the total cost of a power station?
Fixed cost, which is independent of the energy generated and is fixed. Hence, the total cost of the power station can be expressed as (A + (B. kW) + (C. kWh)) (A + (B k W) + (C k W h)) Where,
What is the cost of generating electrical energy?
In general, the cost of generating electrical energy can be divided into as follows: It is independent of energy output. These costs vary approximately in direct proportion to the installed capacity of the plant, but it does not depend upon whether the plant supplied any energy or not. The fixed capital may be grouped under the following heads.
What is the cost structure of electricity generation technologies?
Cost structure of generation technologies. Electricity generation technologies vary dramatically in their cost structure. Some plants, such as nuclear, wind and solar power, have virtually zero variable costs: once they are built, they produce electricity virtually for free. This is in stark contrast to fossil fuel-based power plants.
How do fuel prices affect energy generation?
Short-term fluctuations in fuel prices can have significant effects on the cost of energy generation in natural gas and oil fired power plants and to a lesser extent for coal fired power plants. As renewable energies need no fuel, their costs are independent of world markets for fuels once built.
More related information
-
 Energy Storage Power Station Project Electricity Price
Energy Storage Power Station Project Electricity Price
-
 The price of electricity generated in photovoltaic power plants
The price of electricity generated in photovoltaic power plants
-
 Armenia mobile power station electricity price
Armenia mobile power station electricity price
-
 Zambia mobile power station electricity price
Zambia mobile power station electricity price
-
 What is the best way to generate electricity for Tajikistan s power station
What is the best way to generate electricity for Tajikistan s power station
-
 What is the total investment in the Liberian energy storage power station
What is the total investment in the Liberian energy storage power station
-
 What is the base station outdoor power supply module
What is the base station outdoor power supply module
-
 Botswana EPS Communication BESS Power Station Price
Botswana EPS Communication BESS Power Station Price
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


