What does a substation do?
Between OPPD''s generating stations and your home is a big, gray, industrial-looking facility with many vital jobs. Substations help ensure the safe, efficient
Get Price
How many volts is the energy storage power supply? | NenPower
The voltage of energy storage power supplies can vary widely based on the technology used and the specifications of individual systems, but commonly ranges between
Get Price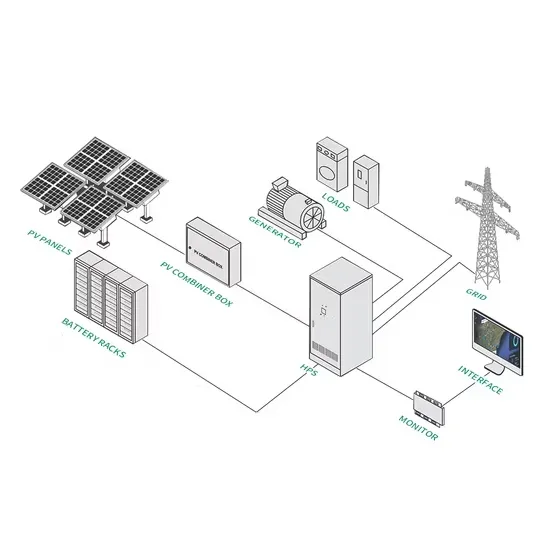
The Role of Substations in the Electrical Grid
Understanding Power Substations Power substations are essential components within an electrical system, acting as control points where electricity is converted, regulated, and
Get Price
Designing Electrical Substations for a Modernized
These substations convert or "step up" the voltage of electricity for efficient long-distance transmission. Transmission substations are where
Get Price
The basic things about substations you MUST know in the middle
Though much has been made of new battery storage technologies, which allow energy to be stored during periods of low-demand
Get Price
The basic things about substations you MUST know in the middle
Distribution substations typically operate at 11KV/0.4KV voltage levels and deliver electric energy directly to industrial and residential consumers. Note that distribution voltage
Get Price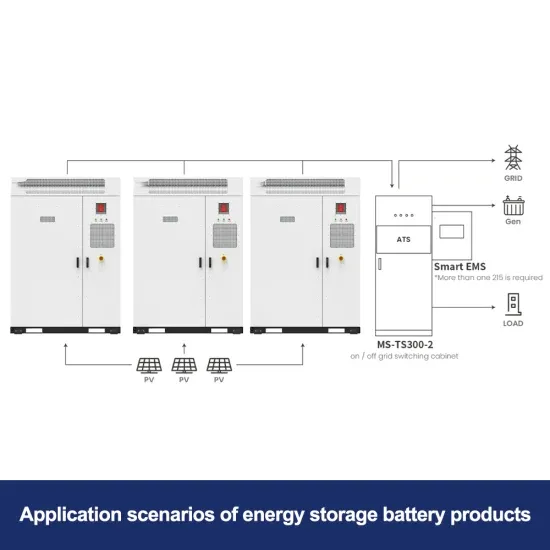
Complete Guide to Electrical Substations
There are three primary types of electrical substations as described below - Step-up substations: These substations increase the voltage for long-distance transmission. Step
Get Price
The Different Types of Substations and Their Functions
Distribution substations transform the high voltage from transmission levels to lower voltages (between 2,400 and 33,000 volts) that
Get Price
What is a substation? Behind the technology driving transmission
Though much has been made of new battery storage technologies, which allow energy to be stored during periods of low-demand to be used in those of high-demand, legacy
Get Price
HV, MV, and LV Substations: Differences and Applications
Voltage Range: Typically between 3.3 kV and 33 kV. Purpose: MV substations step down HV transmission voltages to levels suitable for distribution to industrial and
Get Price
How Does the U.S. Power Grid Work?
Once flowing energy arrives at substations along transmission lines, the voltage decreases, allowing lines to further distribute that energy. But you might wonder how this
Get Price
Complete Guide to Electrical Substations
There are three primary types of electrical substations as described below - Step-up substations: These substations increase the
Get Price
Electrical Substations Explained: Key Functions and
One of the most critical functions of a substation is voltage transformation. Electrical power is generated at relatively low voltages
Get Price
How many volts does the energy storage power supply use for
The energy storage power supply typically utilizes a nominal voltage of 48 volts, which is optimal for efficient energy conversion and storage. However, voltages can vary
Get Price
1926.966
The employer shall provide guards around all live parts operating at more than 150 volts to ground without an insulating covering unless the location of the live parts gives sufficient clearance
Get Price
Fundamentals of Modern Electrical Substations
As we can see, there is a reverse proportion between power losses and voltage level in the 2nd degree. For example, if we increase voltage 10 times, power losses will be 100 times smaller.
Get Price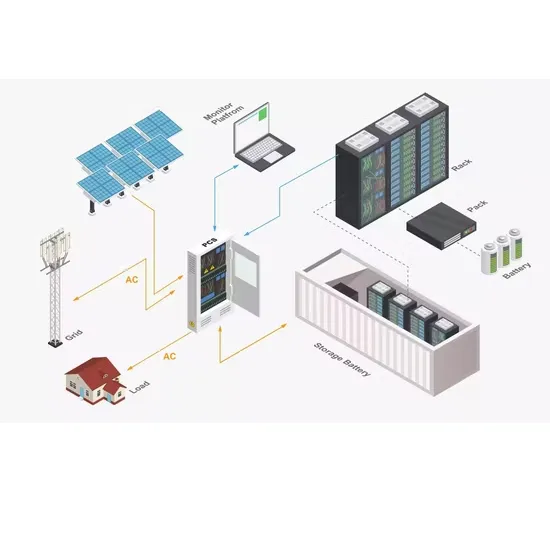
Transmission Lines and Substation Types
The article provides an overview of transmission lines—overhead, underground, and subtransmission—and explains how they are used to transport electrical
Get Price
Grid-Scale Battery Storage: Frequently Asked Questions
What is grid-scale battery storage? Battery storage is a technology that enables power system operators and utilities to store energy for later use. A battery energy storage system (BESS) is
Get Price
The Different Types of Substations and Their Functions
Distribution substations transform the high voltage from transmission levels to lower voltages (between 2,400 and 33,000 volts) that can be safely distributed to homes,
Get Price
Battery Energy Storage Systems Report
This information was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the U.S. Government. Neither the U.S. Government nor any agency thereof, nor any of their
Get Price
How many volts is the energy storage power supply?
How many volts is the energy storage power supply? The voltage of energy storage power supplies can vary widely based on the technology used
Get Price
Electrical Substations Explained: Key Functions and Importance
One of the most critical functions of a substation is voltage transformation. Electrical power is generated at relatively low voltages (typically around 11-33 kV), which must be
Get Price
Electrical substation
[6] Distribution substation - These substations further lower the subtransmission voltage to one that can be used to supply most industrial, commercial, and
Get Price
HV, MV, and LV Substations: Differences and
Voltage Range: Typically between 3.3 kV and 33 kV. Purpose: MV substations step down HV transmission voltages to levels suitable for
Get Price
Substation configuration and build types | National Grid
A double busbar substation typically provides an SQSS compliant connection, as it has a supply of reserve power in case of fault. Mesh corner substations /
Get Price
What is Substation and How Do They Work?
Q2. How do substations differ from transformer stations? Transformer stations manage high/medium-voltage systems, while substations cater to broader
Get Price
Types of Substations and Functions
As the demand for electrical power continues to grow, it can be met through power generation substations. There are different types of power generation substations, including thermal,
Get Price
How It Works: Electric Transmission
Typical transmission voltages include 115 kV, 138 kV, 230 kV, 345 kV, 500 kV, and 765 kV. Sub-transmission networks, used to transmit power over shorter distances, use 34 kV, 46 kV, or 69
Get Price
How many volts is the energy storage power supply?
The voltage of energy storage power supplies can vary widely based on the technology used and the specifications of individual systems, but
Get Price
6 FAQs about [How Many Volts of Energy Storage Power Supply Are Used in Substations]
What voltage does a distribution substation operate at?
Go back to contents ↑ Distribution substations typically operate at 11KV/0.4KV voltage levels and deliver electric energy directly to industrial and residential consumers. Note that distribution voltage level may vary in countries worldwide. Distribution feeders transport power from the distribution substations to the end consumers’ premises.
What is the voltage range of a LV substation?
Voltage Range: Typically below 1 kV (e.g., 415V, 230V). Purpose: LV substations further step down MV voltages to supply end consumers, including residential, commercial, and small-scale industrial users. Key Components: Distribution Transformers: Step down MV to LV (e.g., 11 kV to 415V).
What are the functions of a substation?
One of the most critical functions of a substation is voltage transformation. Electrical power is generated at relatively low voltages (typically around 11-33 kV), which must be stepped up to much higher levels (up to 765 kV or higher) for long-distance transmission.
What is a high voltage substation?
When electricity reaches local distribution networks, substations step down the voltage to levels appropriate for industrial or residential use (typically between 400V and 11kV). High-voltage electricity is more efficient for transmission, but it can be dangerous if directly supplied to end users.
What are the components of a substation?
The primary components of a substation include: Transformers: These devices change the voltage levels of electricity to make it suitable for either long-distance transmission (high voltage) or local distribution (low voltage). They consist of a core and windings that convert electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
What is a low voltage substation?
Low Voltage (LV) Substations Voltage Range: Typically below 1 kV (e.g., 415V, 230V). Purpose: LV substations further step down MV voltages to supply end consumers, including residential, commercial, and small-scale industrial users. Key Components:
More related information
-
 How many volts does photovoltaic energy storage power supply use
How many volts does photovoltaic energy storage power supply use
-
 How much energy storage power supply is there
How much energy storage power supply is there
-
 How is Cape Verde s ESS energy storage power supply
How is Cape Verde s ESS energy storage power supply
-
 How to connect the power supply of the new energy storage communication base station
How to connect the power supply of the new energy storage communication base station
-
 How much does Latvia Huijue energy storage power supply cost
How much does Latvia Huijue energy storage power supply cost
-
 How much does Nauru Huijue energy storage power supply cost
How much does Nauru Huijue energy storage power supply cost
-
 How much does Moldova s lithium energy storage power supply cost
How much does Moldova s lithium energy storage power supply cost
-
 How much does Tanzanian energy storage power supply cost
How much does Tanzanian energy storage power supply cost
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


