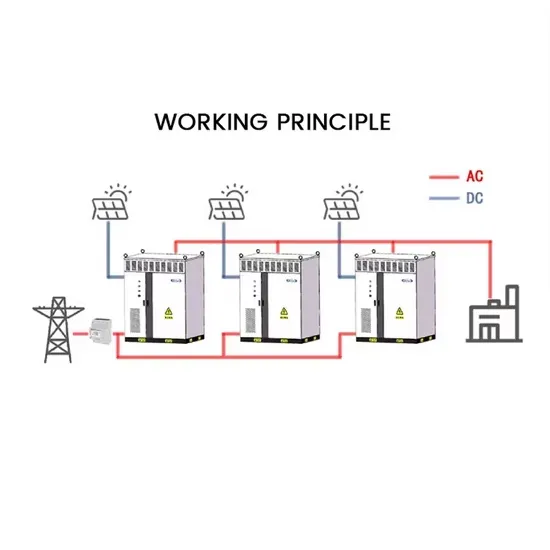
Inverter Amp Draw Calculator: Let''s Simplify It
Our inverter amp draw calculator will help you determine the amps being pulled from your inverter to avoid depletion.
Get Price
Inverter Current Calculator & Formula Online Calculator Ultra
Calculating the current draw of an inverter is essential in designing and troubleshooting electrical and electronic systems. This process ensures compatibility with
Get Price
How Many Amps Does an Inverter Draw?
Understanding the current draw of an inverter at different powers is an important part of designing and selecting a power system. This article provides current calculations for
Get Price
How to Calculate Currents for 3000W Inverter Operation?
How do you calculate the current draw from a 3000-watt inverter? To calculate the current draw from a 3000-watt inverter, follow these steps: Determine Voltage: Identify the
Get Price
How many amps does a 3000 watt inverter draw?
In general, a 3000 Watt inverter can draw as much as 350 Amps if it''s running on a 12V battery bank. If the 3000W inverter is running on a 24V battery bank, it can draw up to
Get Price
How Many Batteries for 5000 Watt Inverter?
Well, if you wondered how many amperes does a 5000 watt inverter draw? Then here is the answer: a 5000 watt inverter will draw 416.66
Get Price
Inverter Current Calculator
Click "Calculate" to find out the current the inverter will draw from the battery or DC power source. This calculated current is essential for battery selection, cable sizing, and protecting your
Get Price
Inverter Amp Draw Calculator
Inverters with a greater DC-to-AC conversion efficiency (90-95%) draw fewer amps, whereas inverters with a lower efficiency (70-80%) draw
Get Price
How Much Power an Inverter Draws with No Load
To find out how much power an inverter draws without any load, multiply the battery voltage by the inverter no load current draw. A 1000 watt 24V inverter with a 0.4 no load current has a
Get Price
CPAP 12volt battery supply when camping
A rough calculation when working out the power draw of an inverter is for every 100 watt at 240 volt, you can expect the inverter to draw about 10 amps from your 12 volt battery.
Get Price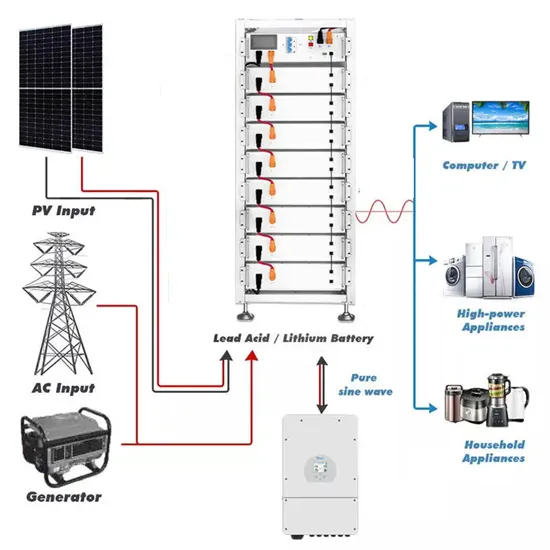
How Much Power an Inverter Draws with No Load
Understanding the current draw of an inverter at different powers is an important part of designing and selecting a power system. This article
Get Price
How much power does an inverter draw?
How much current is drawn from a 12V or 24V battery when running a battery inverter? Documented in this article are common questions relating to the inverter draw (inverter amp
Get Price
Inverter Amp Draw Calculator: Let''s Simplify It
Our inverter amp draw calculator will help you determine the amps being pulled from your inverter to avoid depletion.
Get Price
Aims Power 12v 3000 watt inverter/charger maximum
Before you get to the fuse, I would make sure the wiring can handle 3000 watts. I had a 12 volt inverter 200 watts I used 4/0 for, and I
Get Price
Inverter Power Draw: How Much Power Does An Inverter Use
What Factors Influence How Much Power Does an Inverter Draw from a Battery? Inverter power draw from a battery depends on several factors, including inverter efficiency,
Get Price
How Much Power Do My Caravan Appliances Draw?
Discover how much power your caravan appliances use with real-life examples, simple calculations, and expert tips. Learn how to plan your off-grid
Get Price
Inverter Amp Draw Calculator
Inverters with a greater DC-to-AC conversion efficiency (90-95%) draw fewer amps, whereas inverters with a lower efficiency (70-80%) draw more current. Note: The results
Get Price
How Many Amps Can a Cigarette Lighter Handle
However, the actual current capacity may vary depending on the vehicle''s electrical system and the quality of the socket itself. While a 12-volt
Get Price
How Many Amps Does a 2000 Watt Inverter Draw
The maximum amps (current) drawn by a 2000 watts inverter depends on its conversion efficiency and voltage rating of the battery bank. A
Get Price
How Many Amps Does a 100, 300, 500, 600, 750,
In the case of 4000 watts power of an inverter, if we take 12 volts as the voltage of the inverter, then the number of amps the inverter will draw
Get Price
Inverter Current Calculator, Formula, Inverter Calculation
Inverter current is the electric current drawn by an inverter to supply power to connected loads. The current depends on the power output required by the load, the input voltage to the
Get Price
How Many Amps Does A Mini Split Use? (2.3 To 27.3
In general, we can say that mini splits draw anywhere between 2.3 amps and 27.3 amps. This is the smallest 6,000 BTU vs the biggest 6-ton mini split. Here
Get Price
How many amps does a 2500 watt inverter use?
A 5000-watt inverter on a 24 volt system draws approximately 208 amps (5000 watts / 24 volts = 208.33 amps). This calculation assumes 100% efficiency, so actual power
Get Price
How much current does a 12V inverter draw?
How much current does a 12V inverter draw? Formula: 12 volt inverters require approximately one (1) amp of DC input for each 10 watts of AC output. What size wire do I
Get Price
How many amps does a 2500 watt inverter use?
How many amps does a 5000-watt inverter draw from a 24 volt system? A 5000-watt inverter on a 24 volt system draws approximately 208 amps (5000 watts / 24 volts =
Get Price
How many amps does a 3000 watt inverter draw?
In general, a 3000 Watt inverter can draw as much as 350 Amps if it''s running on a 12V battery bank. If the 3000W inverter is running on a 24V
Get Price
Inverter Current Draw Calculation
300 / 10 = 30A This appliance will draw 30A from your 12V batteries when running through an inverter. DETAIL: Watts are Watts and remain the same whether running from 240VAC or
Get Price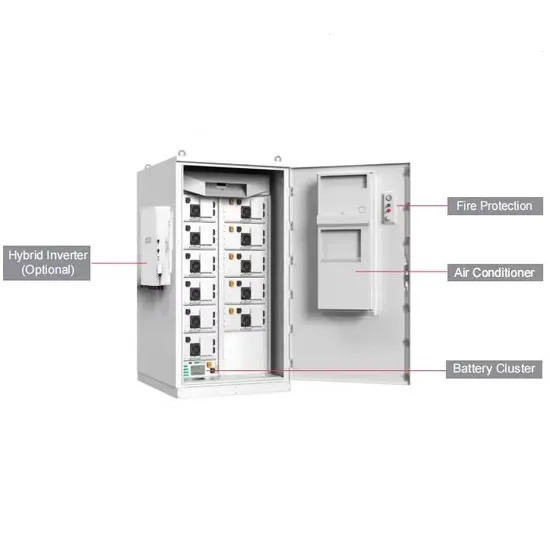
6 FAQs about [How much current does a 24 volt inverter draw ]
How much power does a 24V inverter draw?
To find out how much power an inverter draws without any load, multiply the battery voltage by the inverter no load current draw. A 1000 watt 24V inverter with a 0.4 no load current has a power consumption of 9.6 watts. 24V x 0.4 = 9.6 watts If you want to figure out the no load current in amps, divide the watts consumption by the battery voltage.
What is inverter current?
Inverter current is the electric current drawn by an inverter to supply power to connected loads. The current depends on the power output required by the load, the input voltage to the inverter, and the power factor of the load. The inverter draws current from a DC source to produce AC power.
How much current does a 3000 watt inverter draw?
If the 3000W inverter is running on a 24V battery bank, it can draw up to 175 Amps of current. If the battery bank is rated at 48V, the amp draw will not exceed 90 Amps. This is assuming the DC-to-AC conversion efficiency of the inverter (@ 3000 Watts) is around 85%.
How much current does an inverter draw?
The current drawn is approximately 104.17 amps. Understanding how much current your inverter draws is vital for several reasons: Battery Bank Sizing: Knowing the current helps determine how many batteries you need and how long they will last. Cable Sizing: Undersized cables can overheat or fail.
How do you calculate dc current from an inverter?
To calculate the DC current draw from an inverter, use the following formula: Inverter Current = Power ÷ Voltage Where: If you’re working with kilowatts (kW), convert it to watts before calculation: Inverter Current = 1000 ÷ 12 = 83.33 Amps So, the inverter draws 83.33 amps from a 12V battery. Inverter Current = 3000 ÷ 24 = 125 Amps
How many amps do inverters draw?
Inverters with a greater DC-to-AC conversion efficiency (90-95%) draw fewer amps, whereas inverters with a lower efficiency (70-80%) draw more current. Note: The results may vary due to various factors such as inverter models, efficiency, and power losses. Here is the table showing how many amps these inverters draw for 100% and 85 % efficiency.
More related information
-
 How many watts does a 24 volt 15a inverter generate
How many watts does a 24 volt 15a inverter generate
-
 How much current does a 60w inverter draw
How much current does a 60w inverter draw
-
 How much power does a 24 volt inverter have
How much power does a 24 volt inverter have
-
 How much current does a photovoltaic panel draw in a home
How much current does a photovoltaic panel draw in a home
-
 How much current 12v etc drives the inverter
How much current 12v etc drives the inverter
-
 How many watts does a 48 volt inverter carry
How many watts does a 48 volt inverter carry
-
 24 volt inverter primary
24 volt inverter primary
-
 12v 24 volt inverter
12v 24 volt inverter
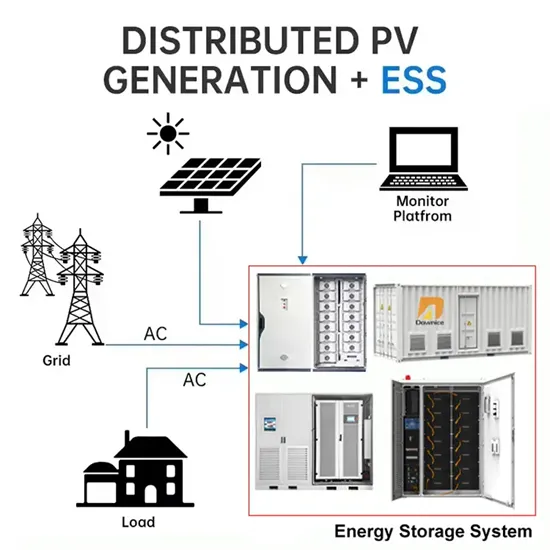
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.