Inverter Efficiency: Understanding How Much Power You''re
Most modern inverters have efficiency ratings between 90% and 98%. Let''s break it down: If you feed 1000 watts of DC power into your inverter and it outputs 950 watts of AC
Get Price
How does the power factor tool work
How is the resulting power factor at the inverter''s output calculated? To have a better understanding of this matter, we first need to set all the parameters that RatedPower
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Power Ratings: kW vs kVA Explained
kW refers to the real or usable power output of an inverter. kVA represents the total power capacity it can carry, including power lost in phase difference (reactive power). For example,
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power calculations and inverter
Get Price
What is the Inverter kVA Rating, and the Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid
It indicates the total capacity of electrical power that can be delivered by the inverter, including the power used effectively (apparent power or kW) and the power lost or not used directly
Get Price
Microwave oven power
Our Panasonic microwave oven seemed to be down on power so I measured it by heating a litre of water and measuring before/after temps etc. Its a 1100W inverter oven. I
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power
Get Price
Inverter Peak Power vs Rated Power: What it is and
Understand the key differences between inverter peak power and rated power. Discover the importance of both, how they affect your appliances.
Get Price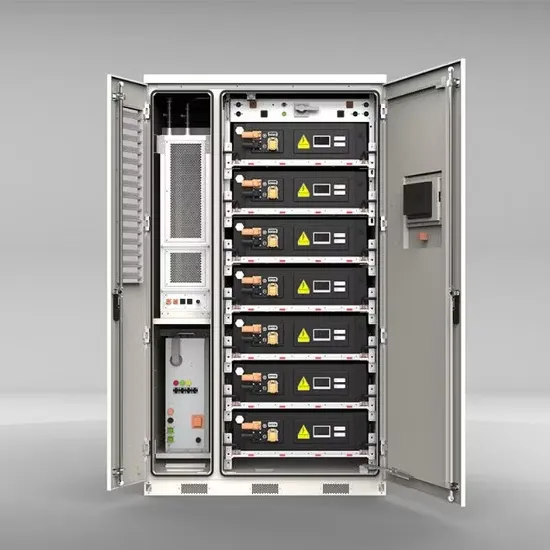
Solar Panel Performance
Hey all. I have a question about an "underperforming" 220W portable panel (Renogy 220 E Flex). I completed a Voc (24.9V) and Isc (8a) test so getting 200W with a
Get Price
Nominal and maximum power of an inverter: Are they
But what is the nominal power of the DC/AC inverter? This is the first value that an inverter displays; for example, an indicative form could
Get Price
Why Does Power Inverter Output Power Not Reach Rated Power
Wondering why your inverter isn''t delivering full power? Learn the top reasons why power inverters fall short of rated output and how to fix them. Expert tips included!
Get Price
Required vs Installed AC and DC power
Finding AC Power Installed The installed AC power (P a c i n s t a l l e d) is the sum of all Central Inverters'' power. The number of inverters needed (N i n v r e q) depends on the nominal power
Get Price
What''s the difference between rated power and peak power of
Rated power refers to the actual power or the continuous output power. For example, a 3000W inverter generator has 2800W rated power (most of them are rated at
Get Price
What do the Watts on an Inverter Mean?
Watts is the unit used to measure the output power of an inverter. Watt (W) is the power unit in the International System of Units, representing the amount of energy converted
Get Price
What is the Inverter kVA Rating, and the Top 5
It indicates the total capacity of electrical power that can be delivered by the inverter, including the power used effectively (apparent power or kW) and the
Get Price
Inverter Efficiency: Complete Guide and Calculator
Inverter efficiency can be a real head-scratcher You think you think you''ve finally worked out the best size inverter to run your appliances and then
Get Price
Inverter Peak Power vs Rated Power: What it is and Why It Matters
Understand the key differences between inverter peak power and rated power. Discover the importance of both, how they affect your appliances.
Get Price
Solar Panel Ratings Explained – Wattage, Current,
Solar panel ratings explained: Solar panel Wattage Rating: The Wattage rating of a solar panel is the most fundamental rating, representing
Get Price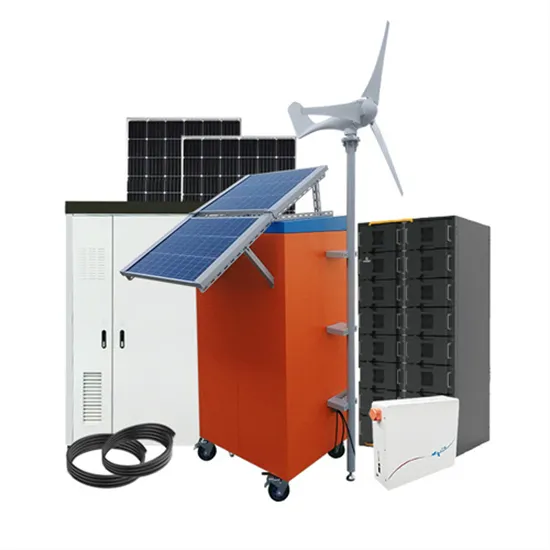
Decoding Inverter Parameters (Part I)
Therefore, when designing the power station, PV modules should be configured to operate at the rated input voltage while considering actual
Get Price
Understanding Rated Power vs Peak Power: What It
When choosing an inverter for your camping, caravanning, or 4WDing adventures, understanding the difference between rated power and peak
Get Price
Useful guide to inverter peak power and how to
Power inverters come in many specifications, which usually include rated power and inverter peak power. Rated power is continuous
Get Price
What''s the difference between rated power and peak power of
Rated power and peak power are different due to their meaning. The rated power determines the load capacity, and the peak power
Get Price
What is the difference between rated power and peak power of inverter?
Rated power and peak power are different due to their meaning. The rated power determines the load capacity, and the peak power determines whether the appliance can be
Get Price
A Guide to Solar Inverters: How They Work & How to Choose Them
What is a solar power inverter? How does it work? A solar inverter is really a converter, though the rules of physics say otherwise. A solar power inverter converts or inverts the direct current
Get Price
Nominal and maximum power of an inverter: Are they the same?
But what is the nominal power of the DC/AC inverter? This is the first value that an inverter displays; for example, an indicative form could be 500 W / 1000 W maximum. In
Get Price
What do the Watts on an Inverter Mean?
Watts is the unit used to measure the output power of an inverter. Watt (W) is the power unit in the International System of Units, representing
Get Price
Solar System Rated kW or kVA Difference between
When it comes to solar power systems, we are used same term kW or kVA for solar system but both are different. When a solar power system
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Inverter rated power actual power]
What is inverter kVA rating?
Inverter kVA rating measures the apparent power that an inverter can handle, expressed in kilovolt-amperes (kVA). It indicates the total capacity of electrical power that can be delivered by the inverter, including the power used effectively (apparent power or kW) and the power lost or not used directly (reactive power).
How to choose a power inverter?
But if the electrical motor with the inductive load, choose the capacity of the inverter, it must consider the starting power of the electrical appliances. Rated power and peak power are different due to their meaning. The rated power determines the load capacity, and the peak power determines whether the appliance can be started.
What is rated output power of inverter?
The rated output power of inverter is the continuous output power, which refers to the output power of the inverter under the rated voltage current. It is the power that can be continuously and stably output for a long time.
How much power does an inverter need?
It’s important to note what this means: In order for an inverter to put out the rated amount of power, it will need to have a power input that exceeds the output. For example, an inverter with a rated output power of 5,000 W and a peak efficiency of 95% requires an input power of 5,263 W to operate at full power.
What are inverter specifications?
Specifications provide the values of operating parameters for a given inverter. Common specifications are discussed below. Some or all of the specifications usually appear on the inverter data sheet. Maximum AC output power This is the maximum power the inverter can supply to a load on a steady basis at a specified output voltage.
Is a 10 kVA inverter enough?
For example, an inverter rated at 10 kVA with a power factor of 0.8 can only deliver 8 kW of real power. That means if your total appliance load is 10 kW, this inverter will not be enough.
More related information
-
 The real-time power of the inverter is greater than the rated power
The real-time power of the inverter is greater than the rated power
-
 The actual power used by the inverter is 1 2 times
The actual power used by the inverter is 1 2 times
-
 3kw inverter actual power
3kw inverter actual power
-
 Maldives Small Power Inverter Company
Maldives Small Power Inverter Company
-
 Serbia Photovoltaic Power Plant Inverter
Serbia Photovoltaic Power Plant Inverter
-
 Zambia supplies 12KW three-phase power inverter
Zambia supplies 12KW three-phase power inverter
-
 How much power does the inverter have
How much power does the inverter have
-
 Photovoltaic power inverter to combiner box
Photovoltaic power inverter to combiner box
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


