Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
An inverter (or power inverter) is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage. While DC power is common
Get Price
Inverter Voltage Calculator, Formula, Inverter Voltage Calculation
It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC). The output voltage of an inverter is
Get Price
Understanding inverter voltage
In the realm of power electronics, the inverter voltage is a critical parameter that dictates its performance, compatibility, and safety. Understanding the intricacies of inverter
Get Price
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
The nominal AC output power refers to the peak power the inverter can continuously supply to the main grid under normal conditions. It is almost similar to the rated
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
OverviewInput and outputBatteriesApplicationsCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
A typical power inverter device or circuit requires a stable DC power source capable of supplying enough current for the intended power demands of the system. The input voltage depends on the design and purpose of the inverter. Examples include: • 12 V DC, for smaller consumer and commercial inverters that typically run fro
Get Price
How does an inverter work?
The inverter device''s role is to control the voltage and frequency of the power supply and seamlessly change the rotation speed of motors used in home
Get Price
Inverter Output Voltage Calculation calculation for Electrical
Popularity: ⭐⭐⭐ Inverter Output Voltage Calculation This calculator provides the calculation of the output voltage of an inverter for electrical engineering applications.
Get Price
Voltage Source Inverter
Voltage Source Inverters abbreviated as VSI are the type of inverter circuits that converts a dc input voltage into its ac equivalent voltage at the output. It is
Get Price
Commonly Used Types of Modulation Schemes in Inverters
Key Takeaways Modulation involves adjusting the on and off duration of inverter switches under constant input DC voltage to achieve controlled inverter output voltage. The most popular
Get Price
What is the output voltage of the inverter? Learn some basics
When installing an inverter for the motor, it usually saves more than 10% of the power consumption. The output characteristic is not the usual sinusoidal AC voltage, so if you use
Get Price
CHAPTER 2
at desired output voltage and frequency. The dc power input to the inverter is obtained from an existing power supply network or from a rotating alternator through a rectifier or a battery, fuel
Get Price
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications: A Simple
How to read solar inverter specifications: A simple guide to understanding technical details like efficiency ratings, input/output specs,
Get Price
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
An inverter (or power inverter) is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage. While DC power is common in small gadgets, most
Get Price
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
Appliances that need DC but have to take power from AC outlets need an extra piece of equipment called a rectifier, typically built from electronic components called diodes,
Get Price
CHAPTER 2
inverter (VSI) is one in which the dc source has small or negligible impedance. The. voltage at the input terminals is constant. A current–source inverter (CSI) is fed with. source. controlled turn
Get Price
Power inverter
The AC output voltage of a power inverter is often regulated to be the same as the grid line voltage, typically 120 or 240 VAC at the distribution level, even when there are changes in the
Get Price
How to Calculate the Maximum Output Power of a Power Inverter
In this article, we go over how to calculate the maximum output power of a power inverter from the DC battery supplying it.
Get Price
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
Appliances that need DC but have to take power from AC outlets need an extra piece of equipment called a rectifier, typically built from
Get Price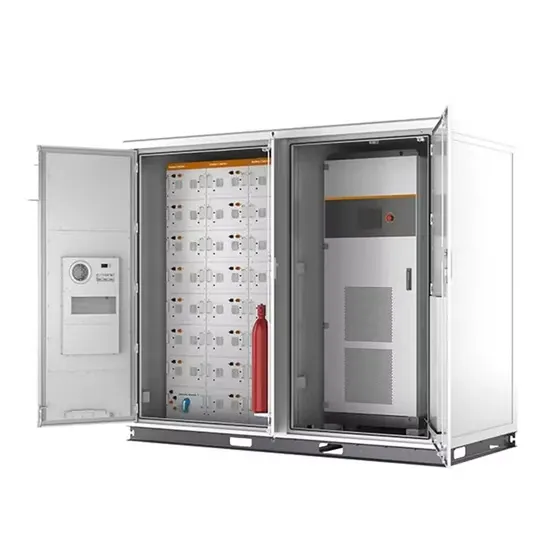
What is a Single Phase Output Inverter?
A single phase output inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power with a single
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power calculations and inverter
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Input and Output: What is the
Inverters are devices that play an important role in modern, green, and clean electrical systems. They work by converting the power obtained
Get Price
What does the inverter voltage specifications represent?
This is the inverter''s AC range (relating to its nominal output). Since grid voltage fluctuates constantly, the inverter has to adjust to that voltage within a given window. For instance, the
Get Price
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
This is a step-up transformer with more windings in the secondary (yellow zig-zag, right-hand side) than the primary, so it boosts a small AC
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Input and Output: What is the Relationship
Inverters are devices that play an important role in modern, green, and clean electrical systems. They work by converting the power obtained from the DC source, which is the input source of
Get Price
Everything You Need to Know About the Split Phase Inverter
Output Voltage and Frequency: Match the inverter''s output voltage to the rated voltage of your electrical devices (typically 110V or 220V) and the output frequency to the
Get Price
What is the output voltage of the inverter? Learn some
When installing an inverter for the motor, it usually saves more than 10% of the power consumption. The output characteristic is not the usual sinusoidal AC
Get Price
How To Read And Interpret An Inverter Specification
Output Voltage Output Voltage states the AC voltage produced by the inverter, usually 120V or 230V, depending on the applicable regional standards. It is important to match it with the
Get Price
Nominal and maximum power of an inverter: Are they
Hence, when purchasing a DC/AC inverter, you should refer to the nominal power. In other words, if your installer tells you that you need a 1000
Get Price
6 FAQs about [What is the inverter output voltage ]
What is the AC output voltage of a power inverter?
The AC output voltage of a power inverter is often regulated to be the same as the grid line voltage, typically 120 or 240 VAC at the distribution level, even when there are changes in the load that the inverter is driving. This allows the inverter to power numerous devices designed for standard line power.
What is inverter output?
The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input source into alternating current (AC).
How does a power inverter work?
The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry. The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source.
What do you need to know about input power inverters?
Here are some important specifications that you need to know about input power inverters. Input Voltage: The input voltage supplied from the DC source to the inverter follows the inverter voltage specifications, which start from 12V, 24V, or 48V.
What is inverter voltage?
Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC).
What determines the output voltage of an inverter?
The output voltage of an inverter is determined by the DC input voltage and the modulation index. The modulation index represents the ratio of the inverter’s AC output voltage to its maximum possible AC output voltage.
More related information
-
 What is the maximum output voltage of the inverter
What is the maximum output voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the inverter output voltage
What is the inverter output voltage
-
 Medium frequency inverter output voltage
Medium frequency inverter output voltage
-
 Inverter output voltage through
Inverter output voltage through
-
 What is the output voltage of a 550 photovoltaic panel
What is the output voltage of a 550 photovoltaic panel
-
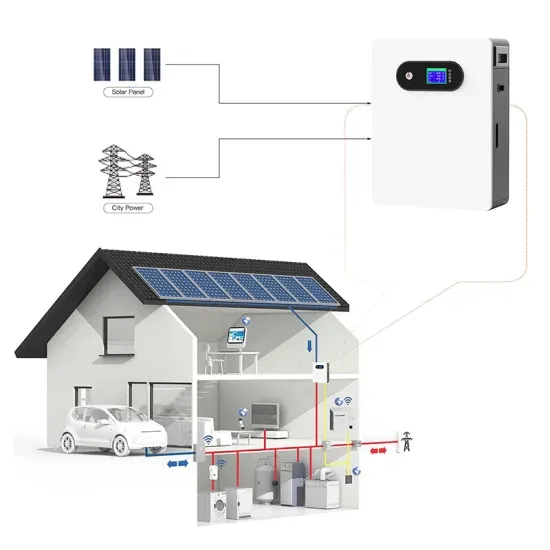 Inverter output voltage is over 1 000 volts
Inverter output voltage is over 1 000 volts
-
 The inverter output voltage is low after rectification
The inverter output voltage is low after rectification
-
 High voltage inverter maximum output current
High voltage inverter maximum output current
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


