Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes, topologies and
The latest and most innovative inverter topologies that help to enhance power quality are compared. Modern control approaches are evaluated in terms of robustness,
Get Price
A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
In this review, the global status of the PV market, classification of the PV system, configurations of the grid-connected PV inverter, classification of various inverter types, and
Get Price
How to Decide on the Right Inverter for Your Grid-Tied System
Choosing the right inverter for your grid-tied system requires careful consideration of various factors, including the size of your solar array, the level of shading, and your budget constraints.
Get Price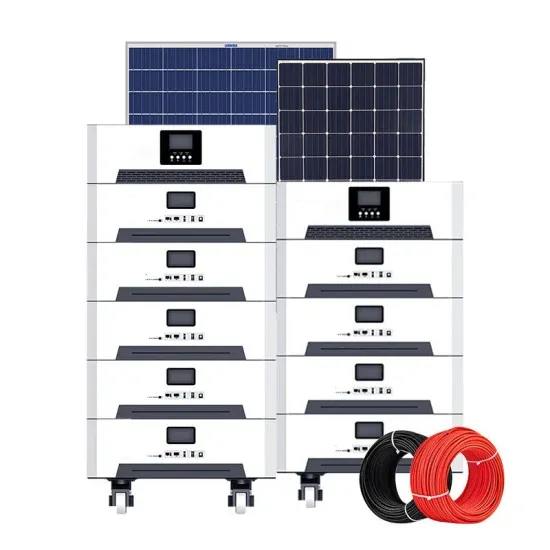
output
But with advancement of technology and decrease in price for PV modules, in past few decades, PV inverters connected to the grid have advanced significantly and have turned out to be a
Get Price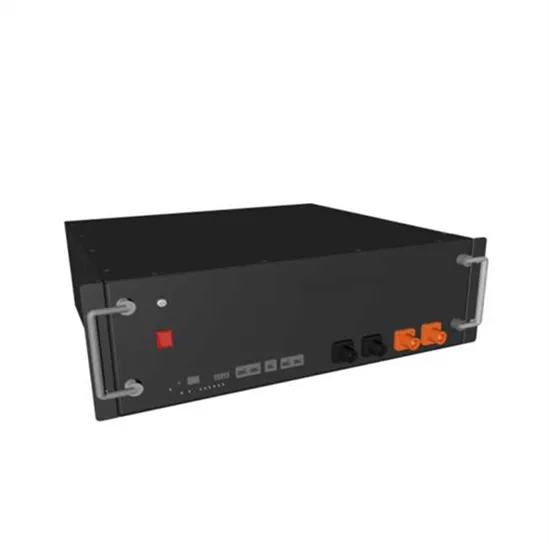
(PDF) A Comprehensive Review on Grid Connected Photovoltaic Inverters
This review article presents a comprehensive review on the grid-connected PV systems. A wide spectrum of different classifications and configurations of grid-connected
Get Price
(PDF) A Comprehensive Review on Grid Connected
This review article presents a comprehensive review on the grid-connected PV systems. A wide spectrum of different classifications and
Get Price
Inverter types and classification | AE 868: Commercial Solar
Before these strings are connected to the utility grid, a power conditioning unit is required as an interface between the array and the grid. Designers can use one central inverter as illustrated
Get Price
Control of Grid-Connected Inverter | SpringerLink
For ensuring an efficient operation of the grid-connected system, with PV or wind generators, it is essential for inverters to have an optimum operation. An effective inverter
Get Price
A Comprehensive Review on Grid Connected Photovoltaic
Different multi-level inverter topologies along with the modulation techniques are classified into many types and are elaborated in detail. Moreover, different control reference
Get Price
Improved vector selection model predictive control strategy
Abstract Conventional inverter control methods reduce the grid inertia and are susceptible to parameter variations, resulting in a gradual weakening of grid stability. To
Get Price
A Review of Grid-Connected Inverters and Control Methods
Various control strategies, including voltage and current control methods, are examined in detail, highlighting their strengths and limitations in mitigating the effects of grid imbalance.
Get Price
Control Design of Grid‐Connected Three‐Phase Inverters
Abstract This chapter discusses the most fundamental control functions of a three-phase grid-connected inverter are included in the dynamic model such as the AC current
Get Price
Three vector modulation model predictive control of grid-connected inverter
The grid-connected inverter is the essential equipment for power conversion, and its performance directly affects the output power quality of the power generation system [1], [2],
Get Price
A Review of Current Control Schemes in Grid Connected Inverters
Grid connected inverters (GCI)s are attracting the attention of the researchers and industrialists due to the advantages it offers to the grid, such as providing backup, stability, support, inertia,
Get Price
Optimized Power Management of Grid-Connected
Integrating renewable energy into grids is challenging, especially with weak infrastructure. Grid-tied inverters (GTIs) convert DC power from
Get Price
Design Power Control Strategies of Grid-Forming Inverters
Strategy II has good tracking performance for both active and reactive power with an acceptable settling time. The low PCC voltage has a larger impact for Strategy I because its power control
Get Price
Research on Solar PV Grid-connected Inverter Selection
When selecting a PV inverter, it should first consider that it has sufficient rated power to meet the requirements of the equipment for electric power under the maximum load, as well as the
Get Price
GRID-CONNECTED SOLAR PV SYSTEMS Design
cluding quantity, make and model number of the solar modules and inverter. Provide a site specific full system design including all shading issues, orientation and tilt, along with the
Get Price
Grid Connected Inverter Reference Design (Rev. D)
The high efficiency, low THD, and intuitive software of this reference design make it fast and easy to get started with the grid connected inverter design. To regulate the output current, for
Get Price
A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control
In this review, the global status of the PV market, classification of the PV system, configurations of the grid-connected PV inverter, classification of various inverter types, and
Get Price
LCL Filter Design and Performance Analysis for Grid
So LCL filter has come into wide use in the inverter. What is the most difficult is that how to select the parameter and control resonance. In this paper, with the three-phase PV grid-connected
Get Price
How to Decide on the Right Inverter for Your Grid-Tied
Choosing the right inverter for your grid-tied system requires careful consideration of various factors, including the size of your solar array, the level of shading,
Get Price
Solar Integration: Inverters and Grid Services Basics
If you have a household solar system, your inverter probably performs several functions. In addition to converting your solar energy into AC power, it can
Get Price
Inverter Transformers for Photovoltaic (PV) power plants:
In this paper, the author describes the key parameters to be considered for the selection of inverter transformers, along with various recommendations based on lessons learnt. This
Get Price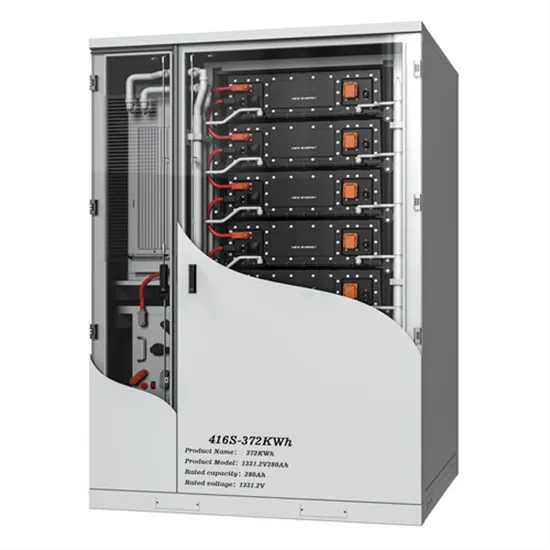
GRID-CONNECTED SOLAR PV SYSTEMS Design
9 INVERTER SELECTION 13 Multiple inverters 13 Inverter sizing 13 Array peak power 13 Array peak power – inverter sizing 13 Array de-rating formula 14 Matching inverter/array voltage 15
Get Price
A Comprehensive Review on Grid Connected Photovoltaic Inverters
Different multi-level inverter topologies along with the modulation techniques are classified into many types and are elaborated in detail. Moreover, different control reference
Get Price
Solar Transformers: Sizing, Inverters, and E-Shields
Learn all about transformer sizing and design requirements for solar applications—inverters, harmonics, DC bias, overload, bi-directionality, and more.
Get Price
Part 3: How to Design Grid-Connected Solar PV Inverters, Strings
This is a the third installment in a three-part series on residential solar PV design. The goal is to provide a solid foundation for new system designers and installers. This section
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Grid-connected inverter power selection]
What is the control design of a grid connected inverter?
The control design of this type of inverter may be challenging as several algorithms are required to run the inverter. This reference design uses the C2000 microcontroller (MCU) family of devices to implement control of a grid connected inverter with output current control.
What are the requirements for grid-connected inverters?
The requirements for the grid-connected inverter include; low total harmonic distortion of the currents injected into the grid, maximum power point tracking, high efficiency, and controlled power injected into the grid. The performance of the inverters connected to the grid depends mainly on the control scheme applied.
Can grid-connected PV inverters improve utility grid stability?
Grid-connected PV inverters have traditionally been thought as active power sources with an emphasis on maximizing power extraction from the PV modules. While maximizing power transfer remains a top priority, utility grid stability is now widely acknowledged to benefit from several auxiliary services that grid-connected PV inverters may offer.
What is a grid-connected inverter?
In the grid-connected inverter, the associated well-known variations can be classified in the unknown changing loads, distribution network uncertainties, and variations on the demanded reactive and active powers of the connected grid.
What control strategy is used for a grid-tied inverter?
The control strategy used for the grid-tied inverter is classified into a single loop, double loop, and triple loop systems. A single loop control system is applied when only one variable (current or voltage) is required to be regulated and measured.
What is the role of inverter in grid-tied PV systems?
Controllers Reference Frames In grid-tied PV systems, inverter plays a prominent role in energy harvesting and integration of grid-friendly power systems. The reliability, performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of inverters are of main concern in the system design and mainly depend on the applied control strategy.
More related information
-
 Guinea-Bissau communication base station inverter grid-connected backup power supply
Guinea-Bissau communication base station inverter grid-connected backup power supply
-
 Professional communication base station inverter grid-connected module power supply
Professional communication base station inverter grid-connected module power supply
-
 Communication base station inverter grid-connected installation power supply
Communication base station inverter grid-connected installation power supply
-
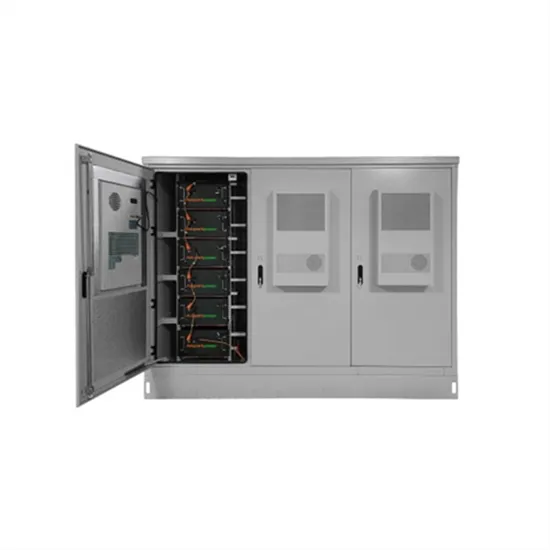 Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter power conversion
Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter power conversion
-
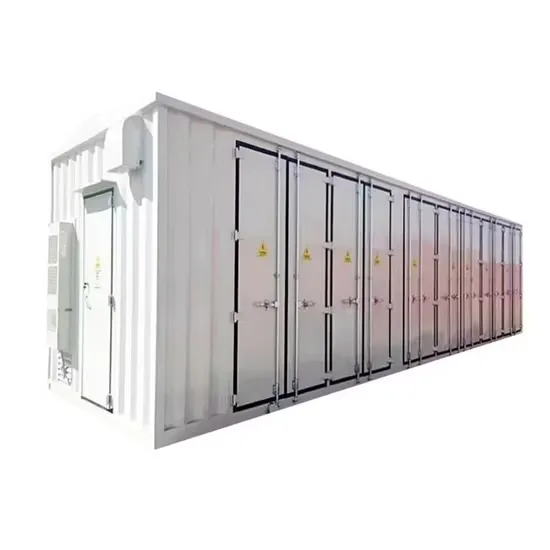 Samoa Photovoltaic Power Generation Grid-Connected Inverter
Samoa Photovoltaic Power Generation Grid-Connected Inverter
-
 Grid-connected inverter constant power grid connection
Grid-connected inverter constant power grid connection
-
 Wind power grid-connected inverter
Wind power grid-connected inverter
-
 Guatemala communication base station inverter grid-connected power generation
Guatemala communication base station inverter grid-connected power generation
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


