A Review of Adaptive Control Methods for Grid-Connected PV Inverters
This research focuses on the discussion of PV grid-connected inverters under the complex distribution network environment, introduces in detail the domestic and international
Get Price
Industrial interconnection converters
ABB industrial frequency converters are commonly used to interconnect 50 Hz and 60 Hz systems. ABB manufactures a range of frequency converters with features to match the most
Get Price
(PDF) A Comprehensive Review on Grid Connected Photovoltaic Inverters
Different multi-level inverter topologies along with the modulation techniques are classified into many types and are elaborated in detail. Moreover, different control reference
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
High-frequency, high-power inverters are suitable for commercial and industrial use. The large capacity can power high-load electronic devices such as large air conditioners, industrial
Get Price
A Reliable Suppression Method of High Frequency Circulating
This paper introduces a method to reduce circulating current with high frequency in parallel inverters. The high frequency component of circulating current is generated by output voltage
Get Price
Introduction to Grid Forming Inverters
How much GFM do I need in the system? Each system is different and response to abnormal conditions vary, but it is good to have at least 25-30% grid forming resources in the system.
Get Price
(PDF) A Comprehensive Review on Grid Connected
Different multi-level inverter topologies along with the modulation techniques are classified into many types and are elaborated in detail.
Get Price
Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study
Unlike grid-following inverters, which rely on phase-locked loops (PLLs) for synchronization and require a stable grid connection, GFMIs
Get Price
What are the Types of Frequency Inverter? | inverter
These frequency converters are typically used in low-power applications and high-frequency applications. Frequency inverters are
Get Price
High-Frequency Soft-Switching Transformerless Grid
The two soft-switching structure of RDCLI and RPI can be used in the inverter link of the isolated (with high-frequency or low-frequency isolation transformers) grid-connected inverter system,
Get Price
A Comprehensive Review on Multilevel Inverters for Grid-Tied
Multi-level inverters (MLIs) have been widely used in recent years due to their various advantages in industrial and grid-connected applications. Traditional MLI topologies
Get Price
Inertia and the Power Grid: A Guide Without the Spin
Grid frequency, which is a measure of the balance of supply of electricity and demand, can drop if a large power plant or transmission fails. Inertia resists this drop in frequency, giving the grid
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
To conclude, power-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters each have pros and cons and are perfect fits for different application scenarios. When choosing an
Get Price
Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes, topologies and
Isolated inverters include a galvanic isolation, low-frequency on the grid side or high-frequency inside the topology, but losses of the transformer, especially in high power
Get Price
High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
The inverter steps up the voltage using lightweight transformers or inductors, followed by the conversion to AC. Low-Frequency Inverters: Low-frequency inverters use heavy, iron-core
Get Price
Grid-tie inverter
A grid-tie inverter converts direct current (DC) into an alternating current (AC) suitable for injecting into an electrical power grid, at the same voltage and frequency of that power grid.
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency Inverters and High
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power efficiency, space saving, or suitability
Get Price
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter:
Weight The same power inverter industrial frequency inverter is far heavier than the high-frequency inverter, high frequency inverter is small in size, light in
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
High-frequency, high-power inverters are suitable for commercial and industrial use. The large capacity can power high-load electronic devices such as large
Get Price
Transformerless Grid-Connected Inverters:
Abstract The rapid growth of renewable energy sources and the increasing demand for efficient power conversion have spurred significant advancements
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power
Get Price
Improving frequency stability in grid-forming inverters with
The increasing utilization of renewable energy sources in low-inertia power systems demands advanced control strategies for grid-forming inverters (GFMs).
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for
Get Price
On Grid Inverter, Grid Tie Inverter | inverter
Good price and high quality 600 watt grid tie inverter is a compact unit, which directly converts 12V/ 24V/ 48V DC into 120V/ 240V AC for 28V-40V solar panels appliances. Smart grid tie
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get Price
Grid Connected Inverter Reference Design (Rev. D)
Description This reference design implements single-phase inverter (DC/AC) control using a C2000TM microcontroller (MCU). The design supports two modes of operation for the inverter:
Get Price
Grid-tie inverter
OverviewPayment for injected powerOperationTypesDatasheetsExternal links
A grid-tie inverter converts direct current (DC) into an alternating current (AC) suitable for injecting into an electrical power grid, at the same voltage and frequency of that power grid. Grid-tie inverters are used between local electrical power generators: solar panel, wind turbine, hydro-electric, and the grid. To inject electrical power efficiently and safely into the grid, grid-tie inverters
Get Price
Why Frequency Inverters Are More Suitable for Off-Grid
Discover why frequency inverters are ideal for off-grid use with superior shock resistance, inductive load performance, and long lifespan. Make the best choice for reliable power.
Get Price
(PDF) Disturbance Decoupling in Grid-Forming
Insufficient damping and inertia are the one of the most tough challenges in the grid-connected power system with high penetration of
Get Price
Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study
Unlike grid-following inverters, which rely on phase-locked loops (PLLs) for synchronization and require a stable grid connection, GFMIs internally establish and regulate
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Is the grid-connected inverter industrial frequency or high frequency ]
What is a grid-tie inverter?
A grid-tie inverter converts direct current (DC) into an alternating current (AC) suitable for injecting into an electrical power grid, at the same voltage and frequency of that power grid. Grid-tie inverters are used between local electrical power generators: solar panel, wind turbine, hydro-electric, and the grid.
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
What is a grid-interactive inverter?
In the United States, grid-interactive power systems are specified in the National Electrical Code (NEC), which also mandates requirements for grid-interactive inverters. Grid-tie inverters convert DC electrical power into AC power suitable for injecting into the electric utility company grid.
How does a grid tie inverter work?
A high-quality modern grid-tie inverter has a fixed unity power factor, which means its output voltage and current are perfectly lined up, and its phase angle is within 1° of the AC power grid. The inverter has an internal computer that senses the current AC grid waveform, and outputs a voltage to correspond with the grid.
What is the difference between a low frequency and high frequency inverter?
Low-frequency inverter: heavy and capable of surge power, lower efficiency, more reliable, expensive. High-frequency inverter: lightweight, not capable of surges, more efficient, less reliable, cheaper. I’m an off-grid enthusiast.
What is a high switching frequency inverter (sci)?
High switching frequency devi ces are preferably harmonics . Moreover, SCI improves the grid po wer factor, suppresses t he current harmonics, and shows high robustness to the grid disturbances. Due to the development of sophisticated to LCI. The SCIs are further classified into current source inverter (CSI) and voltage source inverter (VSI).
More related information
-
 Inverter transformation from industrial frequency to high frequency
Inverter transformation from industrial frequency to high frequency
-
 High frequency replaces industrial frequency inverter
High frequency replaces industrial frequency inverter
-
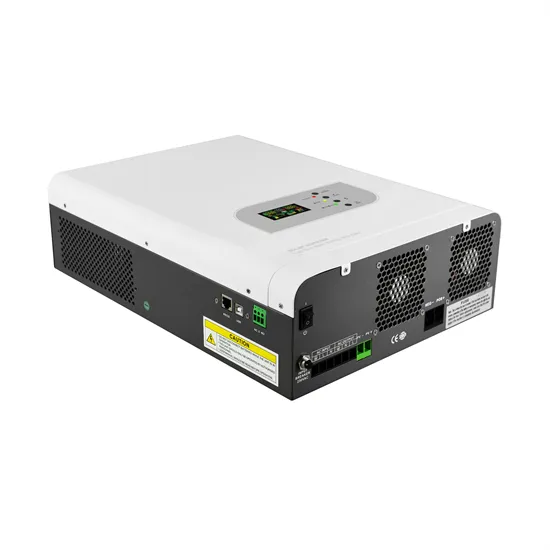 96v 20kw industrial frequency sine wave inverter
96v 20kw industrial frequency sine wave inverter
-
 The frequency on the high-voltage side of the inverter is too high
The frequency on the high-voltage side of the inverter is too high
-
 Austria high frequency power inverter
Austria high frequency power inverter
-
 Congo Brazzaville Industrial Frequency Off-Grid Inverter Company
Congo Brazzaville Industrial Frequency Off-Grid Inverter Company
-
 Home use industrial frequency sine wave inverter
Home use industrial frequency sine wave inverter
-
 Kiribati high frequency inverter
Kiribati high frequency inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

