
How does a Three Phase Inverter Work? | inverter
Three-phase inverters play a crucial role in converting direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) in various applications, from industrial machinery to renewable
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter 180 Degree Conduction Mode (Working
Three phase inverter 180 degree conduction mode is explained with the following points:1. Three phase inverter 180 degree conduction mode 2. Basics of Three
Get Price
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
What is the Purpose of an Inverter Drive? The purpose of an inverter drive is to convert AC mains (single-phase or three-phase) into a smoothed DC (direct current) supply to
Get Price
Three Phase VSI with 120° and 180° Conduction Mode
In this conduction mode of three phase inverter, each thyristor conducts for 180°. Thyristor pair in each arm i.e. (T1, T4), (T3, T6) and (T5, T2) are turned on with a time interval of 180°. It
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter 180 Degree Conduction Mode (Working
Three phase inverter 180 degree conduction mode is explained with the following points: 1. Three phase inverter 180 degree conduction modemore
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter | Introduction, Basic working, Circuit
Basic introduction to what you mean by 3 phase inverters. 2. Construction of the circuit diagram of three phase inverters. 3. Working principle of a three phase inverter.
Get Price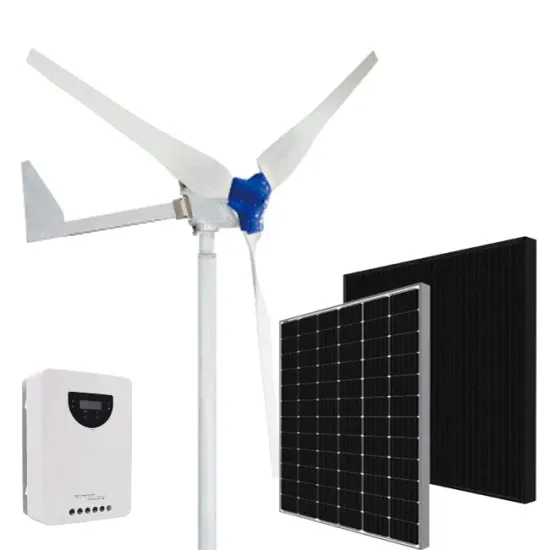
Three Phase VSI with 120° and 180° Conduction Mode
In this conduction mode of three phase inverter, each thyristor conducts for 180°. Thyristor pair in each arm i.e. (T1, T4), (T3, T6) and (T5, T2) are turned on
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter Circuit
So here we will discuss the working of an ideal three-phase converter circuit, neglecting all the issues related to a practical 3 phase inverter. A 3 phase inverter circuit
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter 180 Degree Conduction Mode
Three phase inverter 180 degree conduction mode is explained with the following points: 1. Three phase inverter 180 degree conduction mode
Get Price
Understanding Split Phase Inverters: A Complete Guide
Curious about what is a split phase inverter? They are very important to today''s power systems. They convert direct current into split-phase alternating current. They make our
Get Price
Power inverter
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). [1] The resulting AC
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter
This technical article illustrates the working of the three phase power electronics inverter in the 180 degree conduction mode. The operation
Get Price
Several working modes of energy storage inverter
Similar to the working logic of "self-use" mode, the biggest difference is that the inverter will enter Idle mode in self-use mode without PV energy & battery SOC=Min SOC, and
Get Price
3-Phase Inverter
To generate a balanced and synchronized ac output waveform, these switches are precisely controlled. Each switch operates at specific intervals, ensuring that only one
Get Price
How does a Three Phase Inverter Work? | inverter
Three-phase inverters play a crucial role in converting direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) in various applications, from
Get Price
Lecture 23: Three-Phase Inverters
One might think that to realize a balanced 3-phase inverter could require as many as twelve devices to synthesize the desired output patterns. However, most 3-phase loads are
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter : Circuit, Working, Types & Its
This Article Discusses an Overview of What is a Three Phase Inverter, Circuit, Working, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages & Its Applications.
Get Price
Three-Phase Inverters
The primary features and benefits of three-phase inverters over single-phase inverters are highlighted in this section. We will go through numerous three-phase inverter types, their
Get Price
The Principle Of Parallel Mode Working On Off Grid Inverter
The principle of Parallel mode working When parallel system works on same phase like 230V, you just need to connect Parallel cable and current sharing cable, then inverters will compete and
Get Price
How to Choose the Operating Mode of Solar Inverter?
So which working mode can maximize the use of photovoltaic energy and meet customer requirements as much as possible? What are the
Get Price
Three Phase Bridge Inverter Explained
This article outlines the definition and working principle of three phase bridge inverter. 180 degree conduction mode of operation, formula for phase & line voltages of three
Get Price
Design and Implementation of a Three-Phase Inverter Operated
Three phase inverters are widely used to control different industrial process. Power electronics based inverters are very popular for fast response and precise control. In this paper an IGBT
Get Price
Three Phase Bridge Inverter | Working Principle:
Three Phase Bridge Inverter | Working Principle: The basic three phase bridge inverter is a six-step inverter. A step is defined as a change in the firing sequence. A 3-phase thyristor bridge
Get Price
Different Types of Inverters and Their Applications
In case of industrial load, a three-phase AC supply is used, and for this, we have to use a three-phase inverter. In this type of inverter, six
Get Price
What is a Three-Phase Inverter? | inverter
Modular design is a key direction for future three-phase inverter design. By dividing inverters into multiple independent modular units, quick installation, maintenance, and
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter : Circuit, Working, Types & Its Uses
This Article Discusses an Overview of What is a Three Phase Inverter, Circuit, Working, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages & Its Applications.
Get Price
3-Phase Inverter
The document provides an overview of 3-phase inverters, detailing their types, working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter Circuit
So here we will discuss the working of an ideal three-phase converter circuit, neglecting all the issues related to a practical 3 phase
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter
This technical article illustrates the working of the three phase power electronics inverter in the 180 degree conduction mode. The operation of the six thyristors and the
Get Price
Power Electronics
The pole voltages in a three phase inverter are equal to the pole voltages in single phase half bridge inverter. The two types of inverters above have two
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Three-phase inverter working mode is best]
What is mode 3 in a 3 phase inverter?
Mode 3 operation of a three phase inverter in 180 degree conduction mode Image used courtesy of Rakesh Kumar, Ph.D. Mode 4 corresponds to a 180 to 240 degree period. During this period, the thyristors T2, T3, and T4 are turned on. This can be seen in Fig. 6. On the load side, the current enters phase b and leaves via phase a and phase c.
What is a single phase & 3-phase inverter?
The single phase & 3-phase inverters mainly include two conduction modes like 120-degree & 180-degree which are discussed below. In 180 degrees conduction mode, every device is carried at 180 degrees and they are triggered at 60 degrees intervals. The 3-phase balanced load figure is shown below.
How a 3 phase inverter circuit works?
So here we will discuss the working of an ideal three-phase converter circuit, neglecting all the issues related to a practical 3 phase inverter. A 3 phase inverter circuit diagram converts DC voltage into balanced three-phase AC supply using six switching devices. What is a Three Phase Inverter?
How many conduction modes are there in a 3 phase inverter?
However in three-phase inverters , this voltage is distributed across three phases to create a balanced three-phase AC output . There are two primary conduction modes in both single-phase and three-phase inverters i.e.. 120-degree conduction mode and the 180-degree conduction mode.
What are the advantages of a 3 phase inverter?
A three-phase inverter has three arms which are usually delayed with a 120° angle to produce a 3-phase AC supply by changing a DC supply. The advantages of three phase inverter include the following. A three-phase inverter transmits more power. It has high efficiency & stable voltage regulation.
What is a three phase bridge inverter?
A three phase bridge inverter is a device which converts DC power input into three phase AC output. Like single phase inverter, it draws DC supply from a battery or more commonly from a rectifier. A basic three phase inverter is a six step bridge inverter. It uses a minimum of 6 thyristors.
More related information
-
 Voltage-source inverter working mode
Voltage-source inverter working mode
-
 Which three-phase inverter is best in Fiji
Which three-phase inverter is best in Fiji
-
 Japanese industrial frequency three-phase inverter
Japanese industrial frequency three-phase inverter
-
 Three-phase inverter series output
Three-phase inverter series output
-
 Composition of three-phase inverter
Composition of three-phase inverter
-
 Three-phase three-level grid-connected inverter
Three-phase three-level grid-connected inverter
-
 Photovoltaic three-phase inverter 30kw
Photovoltaic three-phase inverter 30kw
-
 42kW three-phase inverter
42kW three-phase inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


