Green and Sustainable Cellular Base Stations: An Overview and
Energy efficiency and renewable energy are the main pillars of sustainability and environmental compatibility. This study presents an overview of sustainable and green cellular
Get Price
Satellite Ground Station Basics
Explore the fundamentals of satellite ground stations, including their architecture, receiving and transmitting processes, and key specifications.
Get Price
Energy-efficiency schemes for base stations in 5G heterogeneous
In today''s 5G era, the energy efficiency (EE) of cellular base stations is crucial for sustainable communication. Recognizing this, Mobile Network Operators are actively prioritizing EE for
Get Price
What is a base station?
In telecommunications, a base station is a fixed transceiver that is the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile client devices.
Get Price
Glossary: Base station (in communications)
[A mobile phone base station is] a transmission and reception station in a fixed location, consisting of one or more receive/transmit antenna, microwave dish, and electronic circuitry,
Get Price
Basestation
A base station (BS) is defined as a fixed communication facility that manages radio resources for one or more base transceiver stations (BTSs), facilitating radio channel setup, frequency
Get Price
Energy‐Efficient Base Stations | part of Green Communications
This chapter aims a providing a survey on the Base Stations functions and architectures, their energy consumption at component level, their possible improvements and the major problems
Get Price
Fixed Station vs Base Station?
Handhelds are even defined by equipment, and per FCC as Steve also suggested, handheld is a sub-type of mobile where regulations don''t specify separate rules, Base stations
Get Price
(PDF) Energy Efficient Designs for Green Base Stations
The increasing demand for cellular communication services requires high number of cellular base stations distributed over land resulting in greater demands on energy usage, and high pollution
Get Price
Power Base Station
Base station power refers to the output power level of base stations, which is defined by specific maximum limits (24 dBm for Local Area base stations and 20 dBm for Home base stations)
Get Price
Base Station Switching Problem for Green Cellular Networks
One potential strategy is to switch off some of the under-utilized base stations during off-peak hours. In this paper, we propose a binary Social Spider Algorithm to give guidelines for
Get Price
Teltronic Introduces New Green Communications
Spain''s Teltronic has introduced its new GBS (Green Base Station) during the Critical Communications World event. This next-generation TETRA
Get Price
UHF Base Stations for Urban and Indoor Communication
What Is a UHF Base Station? A UHF base station is a fixed communication system operating within the 300 MHz to 3 GHz frequency range. Known for its ability to penetrate obstacles,
Get Price
Teltronic Introduces New Green Communications Base Station
Spain''s Teltronic has introduced its new GBS (Green Base Station) during the Critical Communications World event. This next-generation TETRA base station integrates
Get Price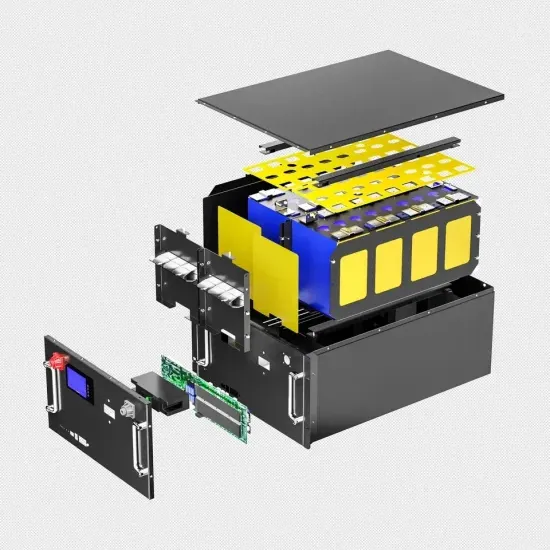
IREE Oriented Active RIS-Assisted Green communication
Fortunately, the channel between the base station and the RIS can be considered quasi-static, as the positions of both the RIS and the base station remain fixed.
Get Price
Communication Base Station Green Energy | HuiJue Group E-Site
First, green energy solutions face intermittency issues – solar panels can''t guarantee 24/7 uptime during monsoon seasons. Second, legacy infrastructure lacks smart energy routing capabilities.
Get Price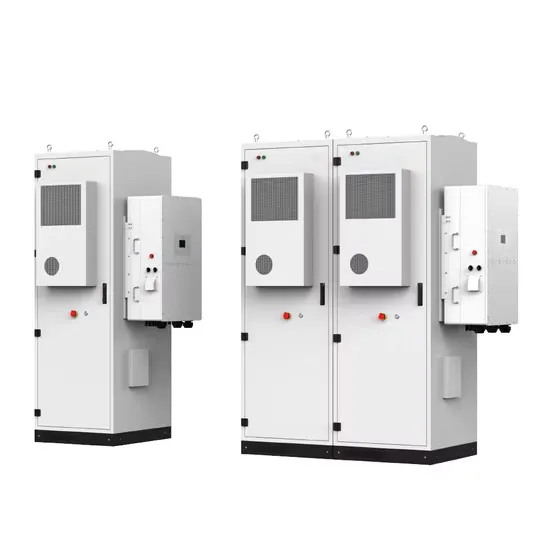
How to configure simpleRTK2B as static base station
Static base station configuration with u-blox ZED-F9P to use fixed coordinates instead of automatic Survey In.
Get Price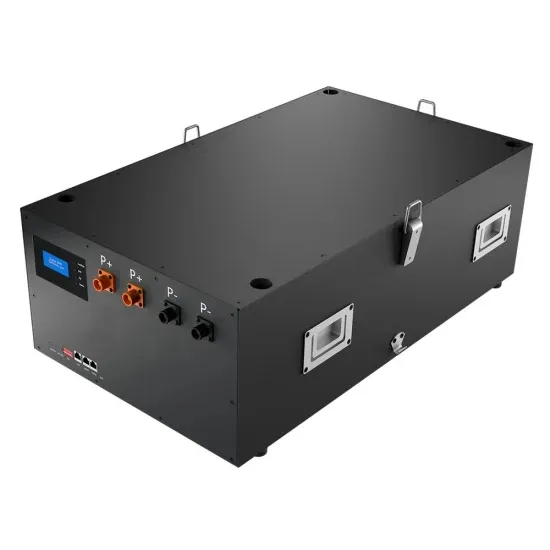
The Central Role of Base Stations in Two-Way Radio
What is a Base Station in Two-Way Radio Communication? A base station in the context of two-way radio communication refers to a fixed, central hub that
Get Price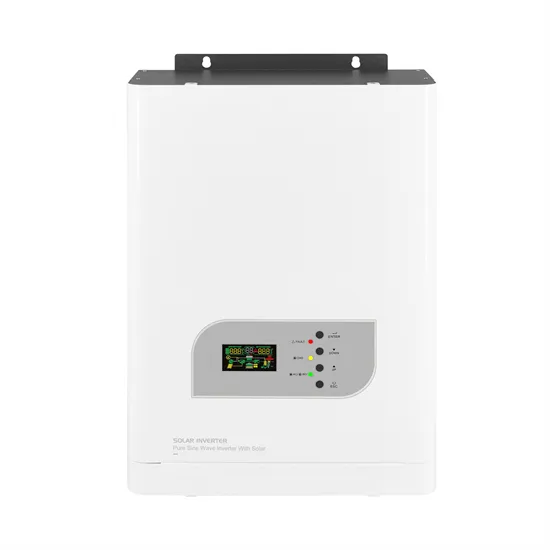
EMF
Some base stations have radio communications dishes (shaped like a drum) that connect the base station to the rest of the base station network. top What are 2G and 3G networks? 3G, or
Get Price
Energy-efficient 5G for a greener future
Compared to earlier generations of communication networks, the 5G network will require more antennas, much larger bandwidths and a higher density of base stations. As a
Get Price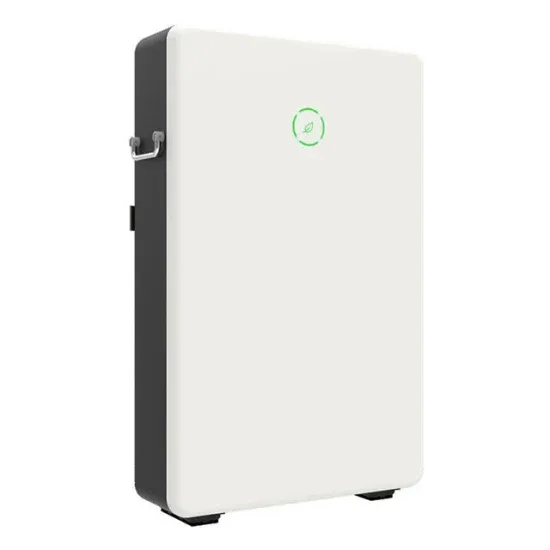
051207-F1610-FAP-25220-IJFET.docx
In order to improve the energy efficiency of the base station, energy is collected from renewable resources (wind and solar energy), and traditional energy consumption is reduced without
Get Price
What is a Base Station in Telecommunications?
What is a Base Station? A base station is a critical component in a telecommunications network. A fixed transceiver that acts as the central
Get Price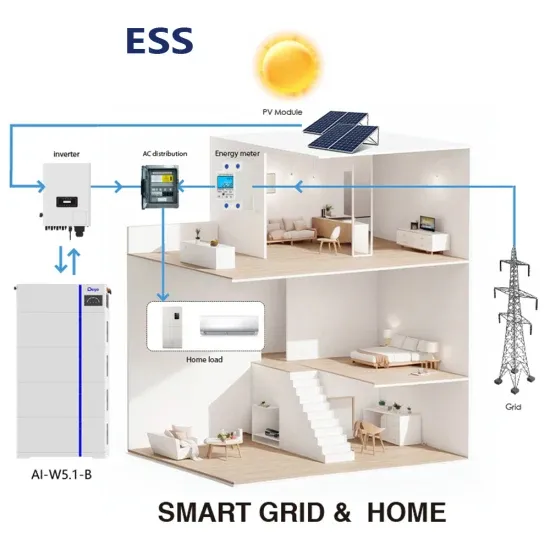
What is a Base Station?
A base station works as the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile devices. It is a fixed transceiver capable of sending and
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Communication green base station is fixed]
Are green cellular base stations sustainable?
This study presents an overview of sustainable and green cellular base stations (BSs), which account for most of the energy consumed in cellular networks. We review the architecture of the BS and the power consumption model, and then summarize the trends in green cellular network research over the past decade.
How does a green base station work?
The green base station uses solar panels to generate electricity and store it during daytime by charging high-capacity rechargeable lithium–ion batteries. The stored energy from rechargeable batteries will be used to power the base station during the weather-related disaster when electricity supply from the grid is disrupted.
What is a base station in telecommunications?
In telecommunications, a base station is a fixed transceiver that is the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile client devices. A base station serves as a central connection point for a wireless device to communicate.
Is NTT DoCoMo a green base station?
By Mar. 2015, NTT DOCOMO has successfully tested its green base station with dual source technology which is claimed to save 95% of solar and off-peak usage and provide reduced electricity consumption by more than 90%. In the United States, less than 1% of base stations are powered by renewable energy but that figure is slowly increasing.
How do cellular base stations work?
Most transceivers in the cellular base stations are run by 48 VDC to charge the batteries and power the communication equipment. The air conditioning of the base station runs at 220 VAC. These base stations can be powered by two types of diesel generators.
How does a base station communicate with a client device?
Generally, if client devices wanted to communicate to each other, they would communicate both directly with the base station and do so by routing all traffic through it for transmission to another device. Base stations in cellular telephone networks are more commonly referred to as cell towers.
More related information
-
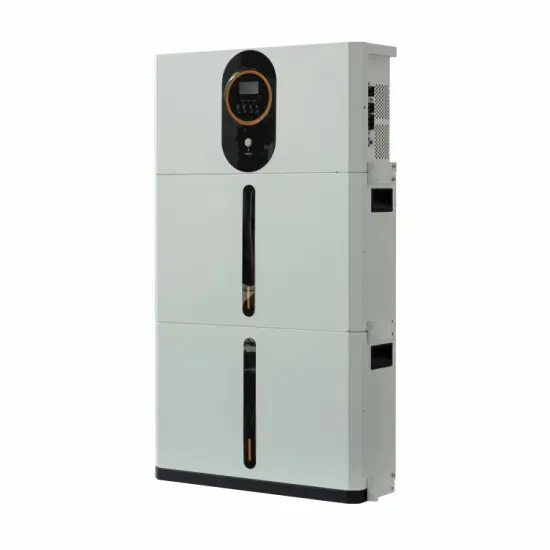 Bangladesh communication green base station photovoltaic power generation
Bangladesh communication green base station photovoltaic power generation
-
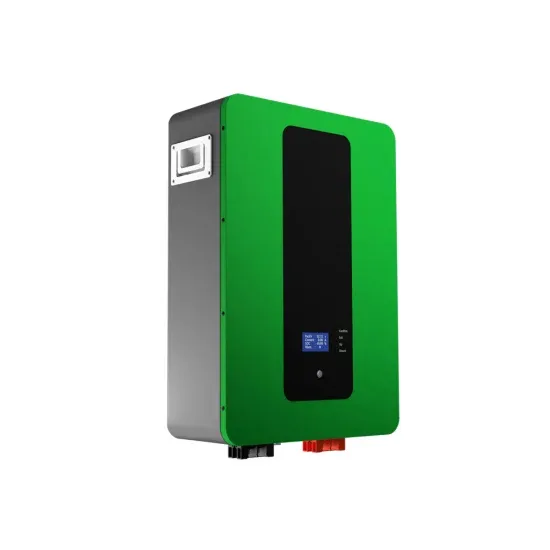 Tonga Mobile Communication Green Base Station Hybrid Power Supply
Tonga Mobile Communication Green Base Station Hybrid Power Supply
-
 Communication Green Base Station Photovoltaic Power Generation
Communication Green Base Station Photovoltaic Power Generation
-
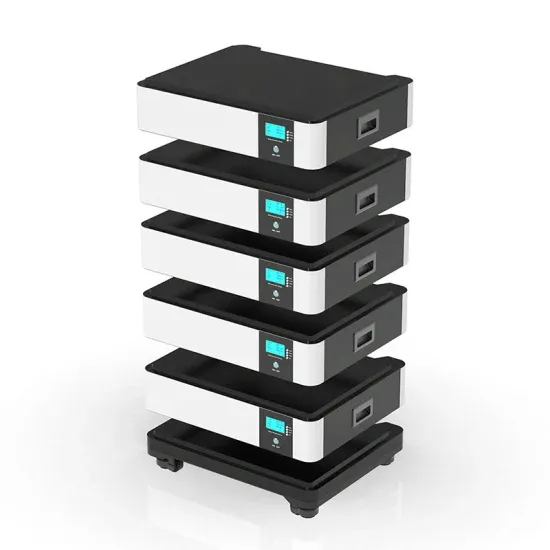 Install 5G communication green base station
Install 5G communication green base station
-
 Mobile communication green base station lightning protection price
Mobile communication green base station lightning protection price
-
 Mobile communication green base station is installed on the 5th floor
Mobile communication green base station is installed on the 5th floor
-
 The company s communication green base station
The company s communication green base station
-
 Network Green Base Station and Communication Green Base Station
Network Green Base Station and Communication Green Base Station
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


