The Effects Of Temperature On Solar Panel Power Production
Unfortunately, it''s a different story with temperature. As the temperatures of the solar cells rise above 25 degrees Celsius, the current rises very slightly, but the voltage
Get Price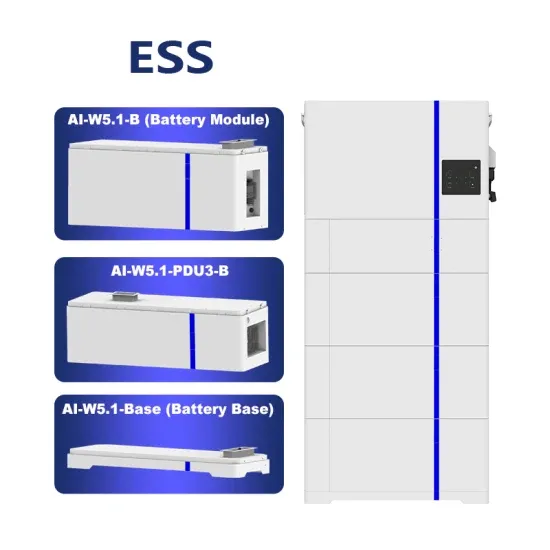
The output current of the solar panel decreases
Photovoltaic modules are tested at a temperature of 25° C - about 77° F, and depending on their installed location, heat can reduce output efficiency by 10-25%. As the
Get Price
Temperature and Solar Radiation Effects on
As a result, a decrease in solar radiation level reduces the panel power. On the other hand, there is an inverse proportion between temperature
Get Price
Solar Performance and Efficiency
The conversion efficiency of a photovoltaic (PV) cell, or solar cell, is the percentage of the solar energy shining on a PV device that is converted into
Get Price
Light Intensity & Solar PV Module Performance
Current from a solar panel decreases linearly with decreasing irradiance, while the voltage drops logarithmically. However, there is significant variation among solar panels with
Get Price
current
I am confused on how voltage and current work in a solar cell. I know that current is affected by the amount of sunlight the cell receives from the sun, and the
Get Price
Why Does Solar Cell Efficiency Decreases With
The I-V curve, or current-voltage curve, illustrates how the current output of a solar cell varies with the applied voltage. As temperature rises, the
Get Price
Why does the current of solar panels decrease? | NenPower
The current produced by solar panels can decrease due to several factors: 1. Temperature increase, 2. Shading on the panels, 3. Dirt or debris accumulation, 4. Electrical
Get Price
The Impact of Temperature on Solar Panel
In this article, we delve deeper into the effects of temperature on solar panel efficiency and explore how temperature fluctuations can affect their
Get Price
PV Panel output voltage
Solar panels, unless heavily shaded have a remarkably high and consistent voltage output even as the intensity of the sun changes. It is predominantly the current output
Get Price
What is the short circuit current of solar panels? | NenPower
The short circuit current of solar panels refers to the maximum current a solar cell can produce under short-circuit conditions, typically denoted as Isc. 1. The short circuit current
Get Price
Residential Solar Panels Efficiency | Understanding Photovoltaic
Solar energy has become an increasingly popular renewable energy source in recent years. As the world moves towards more sustainable and environmentally-friendly power sources, solar
Get Price
The Role of Temperature in Solar PV Performance
Generally, as the temperature increases, the efficiency of solar panels decreases. This happens because, while higher temperatures can
Get Price
Why Does Solar Cell Efficiency Decreases With Temperature?
The I-V curve, or current-voltage curve, illustrates how the current output of a solar cell varies with the applied voltage. As temperature rises, the curve shifts, indicating a
Get Price
, Temperature effects on the I-V curve of a PV cell.
The efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) panels decreases as the panels'' temperature increases.... | Cooling, Photovoltaics and Solar Cells | ResearchGate, the
Get Price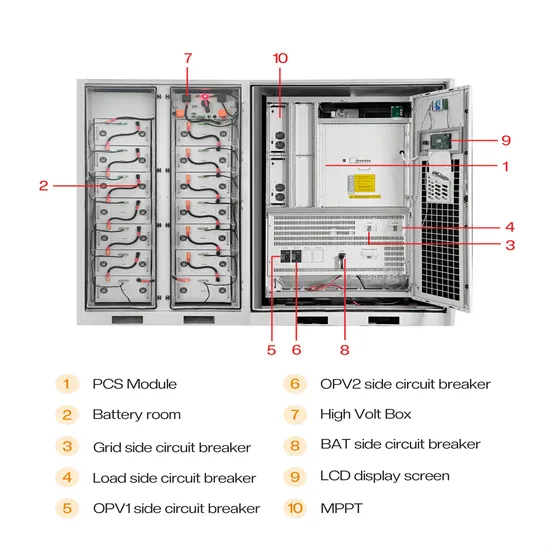
From efficiency to eternity: A holistic review of photovoltaic panel
The most dependable part of photovoltaic (PV) power systems are PV modules. Under normal operating conditions, the PV module will continue to function properly for 25
Get Price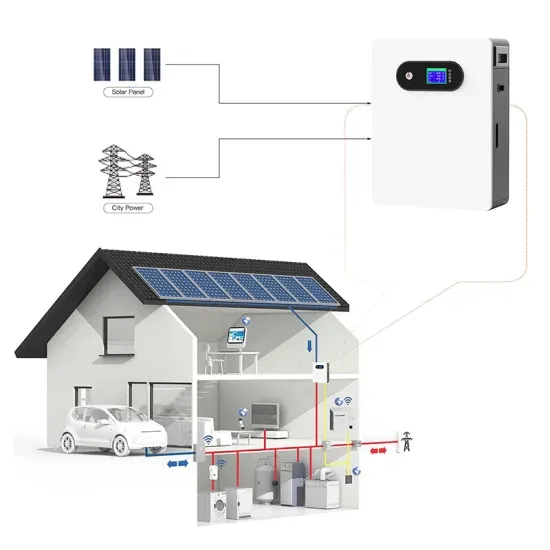
How Long Do Solar Panels Last? – Forbes Home
Want to get solar panels but not sure how long they last? This guide will teach you everything you need to know about lifespan and what
Get Price
Why do solar panels generate a high voltage but a low current
Current decreases when voltage increases in solar cells due to the way photovoltaic materials respond to light and generate electricity. Solar cells have a
Get Price
Effect of high temperature on the voltage or current of
As the temperature of the solar panel increases, its output current increases exponentially, while the voltage output is reduced linearly.
Get Price
Name _______________________ Class
This article examines how the efficiency of a solar photovoltaic (PV) panel is affected by the ambient temperature. You''ll learn how to predict the power output of a PV panel at different
Get Price
Why does the current of solar panels decrease?
The current produced by solar panels can decrease due to several factors: 1. Temperature increase, 2. Shading on the panels, 3. Dirt or debris
Get Price
Does Temperature Affect Solar Panels? Unveiling the Facts and
The essence of the effect of temperature on solar panel efficiency lies in how output voltage, not current, changes with temperature. When the temperature rises, the output
Get Price
Temperature and Solar Radiation Effects on Photovoltaic Panel
As a result, a decrease in solar radiation level reduces the panel power. On the other hand, there is an inverse proportion between temperature and panel power. In other
Get Price
What Are the Effects of Temperature on Solar Panel Efficiency?
Counterintuitively, if the panels become too hot, they will actually produce less electricity. Overheating reduces solar panel efficiency, impacting the percentage of sunlight the panel can
Get Price
Photovoltaic (PV) Cell: Characteristics and Parameters
The article provides an overview of photovoltaic (PV) cell characteristics and key performance parameters, focusing on current-voltage
Get Price
The Role of Temperature in Solar PV Performance
Generally, as the temperature increases, the efficiency of solar panels decreases. This happens because, while higher temperatures can increase the current slightly, they cause
Get Price
Why Does Power Output Lower When Solar Panel Temperature
As the temperature rises, the output voltage of a solar panel decreases, leading to reduced power generation. For every degree Celsius above, the solar panel''s output current
Get Price
Light Intensity & Solar PV Module Performance
Current from a solar panel decreases linearly with decreasing irradiance, while the voltage drops logarithmically. However, there is
Get Price
Effects Of Shade On Solar Panels
Effect Of Shading On Series And Parallel Connected Solar PV Modules? Effect Of Shading In Series Connections If you desire to plot shades on your panels, there are better
Get Price
6 FAQs about [The current of photovoltaic panels decreases]
Does solar panel voltage increase or decrease?
radiation level, there is a little increase in panel voltage. Similarly, panel power increases in proportion to solar radiation level. On the other hand, panel temperature leads to a little increase in panel current while it decreases the panel voltage proportionally. Panel power
How does temperature affect the voltage output of a PV panel?
The voltage output is greater at the colder temperature. The effect of temperature can be clearly displayed by a PV panel I-V (current vs. voltage) curve. I-V curves show the different combinations of voltage and current that can be produced by a given PV panel under the existing conditions.
Does ambient temperature affect PV panel power?
In other words, panel power decreases as the ambient temperature increases. In this study, the equivalent circuit of the panel is simulated at PSIM and MATLAB using the catalogue data of the PV panel and the temperature and the solar radiation effects on the PV panel power are examined.
Do solar cells change the power output of a solar panel?
Solar cells are a technology that can convert solar energy into electrical energy. The power output of a solar panel is proportional to the amount of solar radiation it receives. The purpose of this research is to investigate the changes in the power output of a solar panel with varying levels of solar radiation and temperature.
How does solar radiation affect panel power?
Therefore, solar radiation level has a direct effect on the panel power. As a result, a decrease in solar radiation level reduces the panel power. On the other hand, there is an inverse proportion between temperature and panel power. In other words, panel power decreases as the ambient temperature increases.
Does panel voltage increase or decrease?
increase in panel current while it decreases the panel voltage proportionally. Panel power decreases since the voltage decrease rate is more than the increase in current rate. The appropriate for the obtained power values. This research was supported by TUBITAK Research Fund (No: 115E104). The authors would like to thank for support.
More related information
-
 How many watts of current are there in 90 photovoltaic panels
How many watts of current are there in 90 photovoltaic panels
-
 Negative current appears in photovoltaic panels
Negative current appears in photovoltaic panels
-
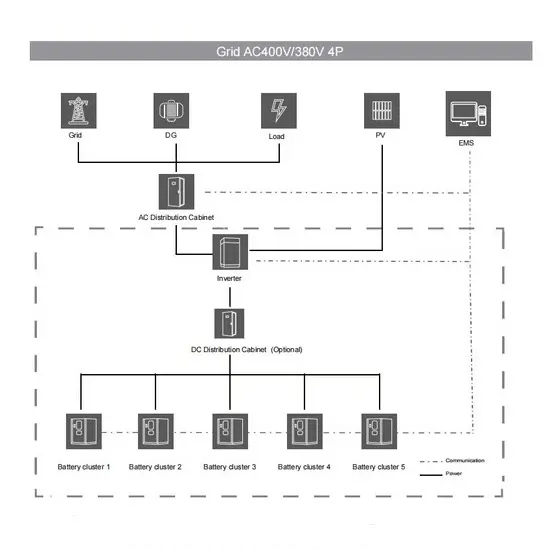 Current and power of photovoltaic panels
Current and power of photovoltaic panels
-
 How much current can 18 photovoltaic panels generate
How much current can 18 photovoltaic panels generate
-
 What is the approximate current of photovoltaic panels
What is the approximate current of photovoltaic panels
-
 Small equipped with solar photovoltaic panels
Small equipped with solar photovoltaic panels
-
 Bicrystalline and monocrystalline photovoltaic panels
Bicrystalline and monocrystalline photovoltaic panels
-
 Huawei Israel solar photovoltaic panels
Huawei Israel solar photovoltaic panels
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


