How to Build a Boost Converter Circuit: Explained with
I have explained comprehensively how to build a boost converter circuit for converting a low level DC voltage inputs to a higher level DC voltage
Get Price
Maximum Constant Boost Control of the Z-Source Inverter
This paper proposes two maximum constant boost control methods for the Z-source inverter, which can obtain maximum voltage gain at any given modulation index without producing any
Get Price
Power Topology Considerations for Solar String Inverters
This application note outlines the most relevant power topology considerations for designing power stages commonly used in Solar Inverters and Energy Storage Systems (ESS).
Get Price
High performance of three-level T-type grid-connected
A three-phase three-level transformerless T-type grid-connected inverter system with three-level boost maximum power point tracking converter is introduced in this article for
Get Price
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings
When selecting an inverter, understanding voltage ratings ensures proper system compatibility, efficiency, and longevity. Key ratings to focus on include rated
Get Price
Maximum power extraction and DC-Bus voltage
The DC-Bus voltage will reduce the substantially if the output power is raised in steps, for example, since the energy stored in the capacitor is inadequate to
Get Price
Designing a Boost Inverter to Interface between Photovoltaic
Thus if an output voltage higher than the input one is needed, a boost dc-dc converter must be used between the dc source and inverters. Depending on power and voltage level involved,
Get Price
(PDF) Comparison between different PWM control
In this paper, four PWM control methods: simple boost, maximum boost, maximum constant boost, and modified space vector PWM control are
Get Price
Boost Efficiency and Save on BoS with Fixed String Voltage
Two modules are connected in series to each H1500 Power Optimizer, and the optimizers regulate string voltage. You no longer need to size strings based on open-circuit
Get Price
Three-level boost inverter with capacitor voltage self
In this paper, a novel boost network composed of two power switches, two capacitors, and two diodes is proposed to overcome these shortcomings. Meanwhile, a corresponding modulation
Get Price
A Single-Input Multi-Output Inverter with Voltage
Multi-load wireless power transfer systems generally require the configuration of multiple transmitting coils. Using traditional single-output
Get Price
Constant Boost Control of the Z-Source Inverter to Minimize
Pulsewidth-modulation (PWM) control for the Z-source inverter has to be modified to utilize the shoot-through states for voltage boost. Fig. 2 shows the traditional carrier-based PWM
Get Price
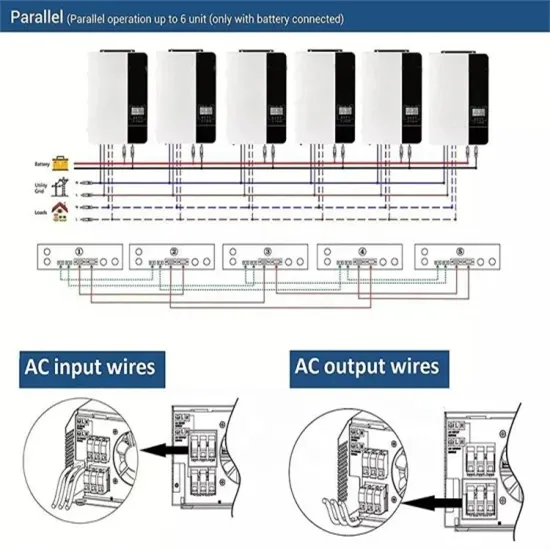
SolaX X1 BOOST G4 | Single Phase Solar String Inverter
The X1-BOOST G4 offers flexible adaptability with support for parallel operation of up to 5 inverters. Its smart load management ensures seamless integration
Get Price
Maximum Constant Boost Control of the Z-Source Inverter
Abstract: This paper proposes two maximum constant boost control methods for the Z-source inverter, which can obtain maximum voltage gain at any given modulation index without
Get Price
Photovoltaic inverter boost circuit
Consequently,inverters need to have the ability to boost the output voltage of PV in order to maintain a stable AC voltage for the load. The traditional voltage source inverter is a step
Get Price
Basics of Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Solar Charge
What is MPPT? MPPT or Maximum Power Point Tracking is algorithm that included in charge controllers used for extracting maximum available power from PV module under certain
Get Price
boost
In this circuit diagram by EEVBlog, the MPPT is designed as a boost converter. In my view, this has a drawback: it only works if the PV array output voltage is lower than the
Get Price
A review on single-phase boost inverter technology for low power
This article comprehensively covers four critical components of the system, namely boosting topologies, voltage and current control methods, Maximum Power Point Tracking
Get Price
Basic Calculation of a Boost Converter''s Power Stage
Basic Configuration of a Boost Converter Figure 1-1 shows the basic configuration of a boost converter where the switch is integrated in the used IC. Often lower power converters have the
Get Price
Common ground type five level inverter with voltage boosting for
The integrated boost inverter is operated so that it suppresses the SC charging current and boosts the input voltage. The extended structure of the proposed topology was also discussed.
Get Price
A Single-Stage Grid-Connected High Gain Buck–Boost Inverter
This GCSS transfers power from PV to grid while tracking maximum power point (MPP) continuously. The proposed system has several desirable features such as low
Get Price
Maximum boost control of the Z-source inverter
This paper explores control methods for the Z-source inverter and their relationships of voltage boost versus modulation index. A maximum boost control is presented to produce the
Get Price
About Schneider Inverter and Boost
The inverter supports a broad range of solar array sizes and comes with integrated MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) optimizers, ensuring maximum power output. It can be
Get Price
SolaX X1 BOOST G4 | Single Phase Solar String Inverter
The X1-BOOST G4 offers flexible adaptability with support for parallel operation of up to 5 inverters. Its smart load management ensures seamless integration with heat pumps, smart
Get Price
New boost type single phase inverters for photovoltaic
In recent years, single-stage boost inverters with common ground have shaped the inverter markets due to the many benefits associated with
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Inverter boost maximum voltage]
How does a maximum boost control work in a Z-source inverter?
Abstract: This paper explores control methods for the Z-source inverter and their relationships of voltage boost versus modulation index. A maximum boost control is presented to produce the maximum voltage boost (or voltage gain) under a given modulation index.
Can bridgetopology be used as a boost inverter?
The full bridgetopology can however be used as a boost inverter that can greater an output ac voltage higher than the input dc voltage. A traditional design methodology is the use of buck inverter. One of the characteristics of the most classical inverter is that it produces an AC output instantaneous voltage always lower than the dc input voltage.
What is a maximum boost control?
A maximum boost control is presented to produce the maximum voltage boost (or voltage gain) under a given modulation index. The control method, relationships of voltage gain versus modulation index, and voltage stress versus voltage gain are analyzed in detail and verified by simulation and experiment. References is not available for this document.
Can a Schneider boost inverter be upgraded?
It can be upgraded with Schneider Boost batteries to maximize self consumption Integrated MPPT optimizers for maximum power output. Supports wider MPPT voltage range. Low conversion losses due to DC coupling. Scalable in system capacity by connecting multiple battery modules per inverter.
How does a boost inverter work?
The boost inverter consists of two boost converters as shown in Fig 3(b). The output of the inverter can be controlled by one of the two methods: (1) Use a duty cycle D for converter A and a duty cycle of (1- D) for converter B. (2) Use a differential duty cycle for each converter such that each converter produces a dc-biased sine wave output.
What is a Schneider boost solar inverter?
The inverter supports a broad range of solar array sizes and comes with integrated MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) optimizers, ensuring maximum power output. It can be upgraded with Schneider Boost batteries to maximize self consumption Integrated MPPT optimizers for maximum power output.
More related information
-
 High voltage inverter maximum output current
High voltage inverter maximum output current
-
 50kw inverter maximum AC voltage
50kw inverter maximum AC voltage
-
 Single-phase inverter maximum voltage
Single-phase inverter maximum voltage
-
 What is the maximum output voltage of the inverter
What is the maximum output voltage of the inverter
-
 New Zealand High Voltage Grid-connected Photovoltaic Inverter Communication
New Zealand High Voltage Grid-connected Photovoltaic Inverter Communication
-
 Does the inverter have dual voltage
Does the inverter have dual voltage
-
 60kw output voltage 800v inverter
60kw output voltage 800v inverter
-
 Inverter wide voltage regulation
Inverter wide voltage regulation
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.