A study on the energy storage scenarios design and the business
From the standpoint of load-storage collaboration of the source grid, this paper aims at zero carbon green energy transformation of big data industrial parks and proposes three
Get Price
Planning and Dispatching of Distributed Energy Storage Systems
Firstly, we propose a framework of energy storage systems on the urban distribution network side taking the coordinated operation of generation, grid, and load into
Get Price
Grid-Scale Battery Storage: Frequently Asked Questions
Is grid-scale battery storage needed for renewable energy integration? Battery storage is one of several technology options that can enhance power system flexibility and enable high levels of
Get Price
Grid-Side Converter
A grid side converter is defined as a component of the doubly-fed induction generator that connects to the grid through a reactance and transformer, facilitating the output of current on
Get Price
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
ESSs use more electricity for charging than they can provide when discharging and supplying electricity. Because of this difference, EIA publishes data on both gross generation and net
Get Price
SOURCE-SIDE ENERGY STORAGE AND GRID-SIDE
In this paper, a two-stage energy storage allocation optimization model for planning and operation is constructed, in which the planning-side energy storage capacity allocation strategy and the
Get Price
Coordinated optimization of source‐grid‐load‐storage for wind
Build a coordinated operation model of source‐grid, load, and storage that takes into account the mobile energy storage characteristics of electric vehicles (EVs), to improve the
Get Price
Research on interval optimization of power system considering
Considering the low utilization rate of energy storage system under uncertainty of source-load and the coarse demand response mechanism, an interval optimization model of
Get Price
Coordinated Scheduling Strategy for
Developing a novel source-grid-load-storage integrated system in urban industrial zones abundant in new energy is a crucial approach for
Get Price
fenrg-2022-1023474 1..11
According to the comparison, although energy storage integration can improve the voltage quality of the distribution network, it will result in the harmonic content increasing with the source-grid
Get Price
The difference between power supply side, grid-side and user-side
Energy storage is mainly divided into three camps: power supply side, grid side and user side, each of which has unique functions and characteristics.
Get Price
Integration and control of grid‐scale battery energy storage
Beyond the traditional applications of battery energy storage systems (BESSs), they have also emerged as a promising solution for some major operational and planning
Get Price
Differentiation between grid-side energy storage and power
This study proposes a hybrid energy storage system (HESS) based on superconducting magnetic energy storage (SMES) and battery because of their complementary characteristics for the grid
Get Price
Research and Application of "Source-Network-Load-Storage"
With the rapid development of new energy and DC, new technologies such as energy storage are emerging, and the characteristics of power grids are becoming more and more complex. The
Get Price
Research status and development trend of generation-grid-load-storage
<p indent="0mm">The development of a "generation-grid-load-storage" type integrated system with heterogeneous energy flows is necessary to construct a high-quality energy industry and
Get Price
Research on Capacity Allocation of Grid Side Energy Storage
Power system with high penetration of renewable energy resources like wind and photovoltaic units are confronted with difficulties of stable power supply and peak regulation ability. Grid
Get Price
What energy storage is used for source, grid, load and storage?
During peak usage times, energy storage systems can discharge stored energy to alleviate grid strain, while during off-peak hours, they can capture excess energy and store it
Get Price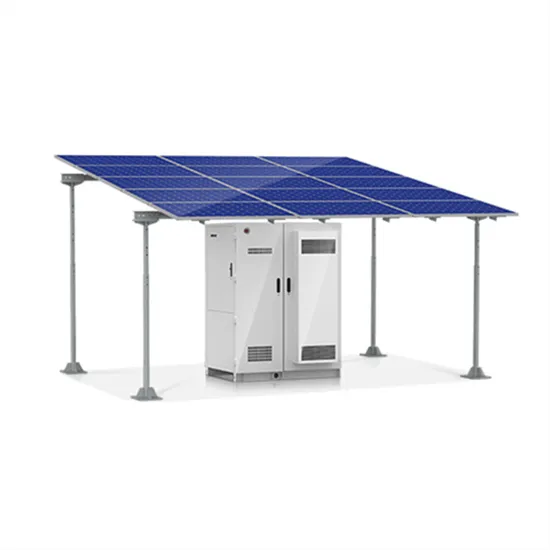
Optimized scheduling study of user side energy storage in cloud energy
Operation mode The main sources of customers for the cloud energy storage operators are energy storage users who expect to benefit from the peak-to-valley load
Get Price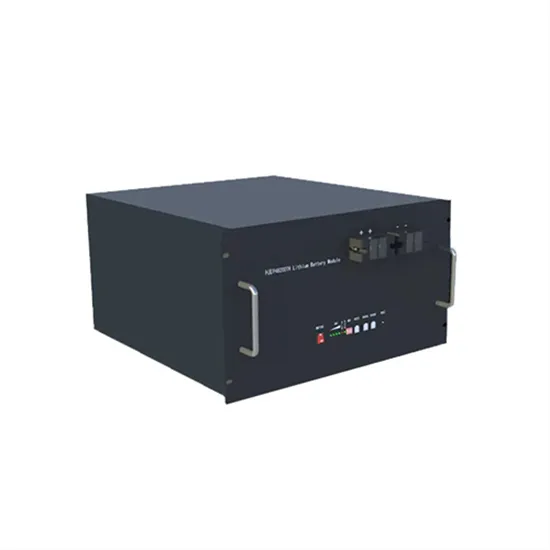
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
ESSs use more electricity for charging than they can provide when discharging and supplying electricity. Because of this difference, EIA publishes data on both gross
Get Price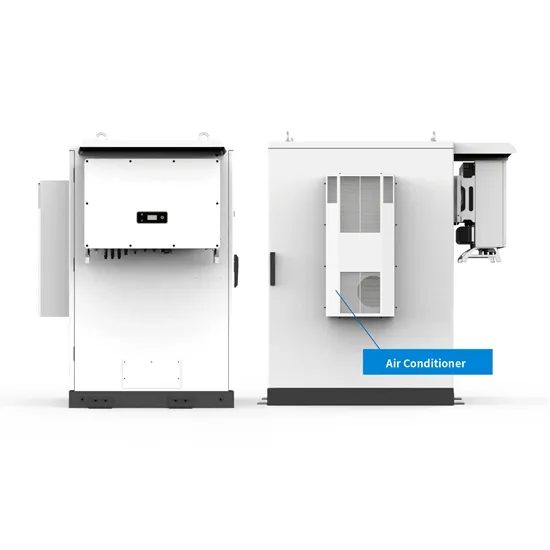
Energy storage on the load side of the power grid
The power grid side connects the source and load ends to play the role of power transmission and distribution; The energy storage side obtains benefits by providing services such as peak
Get Price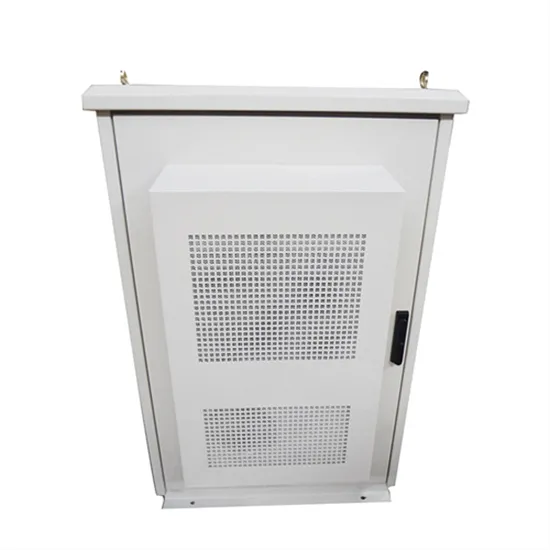
Differences between source-grid-load-storage microgrid
Abstract: Aiming at the problem of optimal resource allocation between microgrids with different source load characteristics, a source grid load and energy storage management method
Get Price
Source-load coordinated dispatching model taking into account
The source-load coordinated dispatching can effectively improve the flexibility and reliability of the power system by coordinating the dispatchable resources of the generation
Get Price
What energy storage is used for source, grid, load and
During peak usage times, energy storage systems can discharge stored energy to alleviate grid strain, while during off-peak hours, they can
Get Price
The difference between power supply side, grid-side and user
Energy storage is mainly divided into three camps: power supply side, grid side and user side, each of which has unique functions and characteristics.
Get Price
Grid Scale Energy Storage: An In-Depth Look
Grid-scale is different in terms of battery size and use cases than residential scale or commercial and industrial sale. Here is a breakdown of the
Get Price
Load Shifting: What Is It and How Does It Work?
Load shifting is an electricity management technique that shifts load demand from peak hours to off-peak hours of the day. In this article, we explore what is load
Get Price
Grid Scale Energy Storage: An In-Depth Look
Grid-scale is different in terms of battery size and use cases than residential scale or commercial and industrial sale. Here is a breakdown of the differences between the three
Get Price
6 FAQs about [The difference between grid-side energy storage and source-grid-load storage]
What is the difference between power grid and energy storage?
The power grid side connects the source and load ends to play the role of power transmission and distribution; The energy storage side obtains benefits by providing services such as peak cutting and valley filling, frequency, and amplitude modulation, etc.
How do grid-scale energy storage systems work?
To overcome this challenge, grid-scale energy storage systems are being connected to the power grid to store excess electricity at times when it’s plentiful and then release it when the grid is under periods of especially high demand.
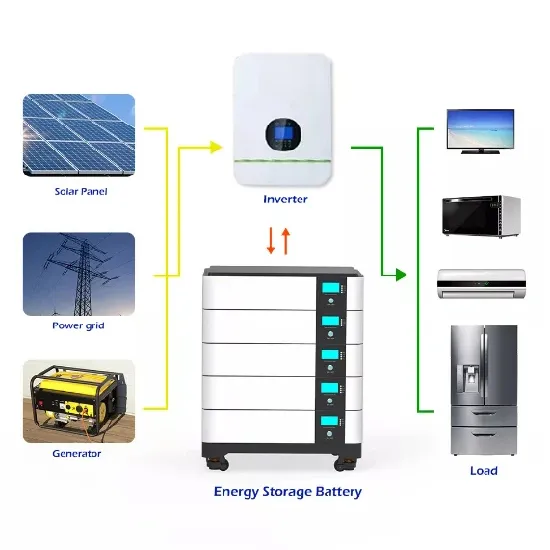
What is an energy storage system?
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or device, which is discharged to supply (generate) electricity when needed at desired levels and quality. ESSs provide a variety of services to support electric power grids.
How does energy storage work?
In this case, the energy storage side connects the source and load ends, which needs to fully meet the demand for output storage on the power side and provide enough electricity to the load side, so a large enough energy storage capacity configuration is a must.
What is a battery energy storage system?
A battery energy storage system (BESS) is an electrochemical device that charges (or collects energy) from the grid or a power plant and then discharges that energy at a later time to provide electricity or other grid services when needed.
What are the benefits of grid-scale battery storage?
Another factor is where the batteries are stored, as batteries kept in higher or very low temperatures can experience a shorter lifespan. Energy systems that use grid-scale battery storage are more reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly. A top benefit is the ability to stabilize the grid during fluctuations from renewable sources.
More related information
-
 Thailand grid-side energy storage power station
Thailand grid-side energy storage power station
-
 Cape Verde accelerates grid-side energy storage
Cape Verde accelerates grid-side energy storage
-
 Israel grid-side energy storage government subsidies
Israel grid-side energy storage government subsidies
-
 Price query of French grid-side energy storage cabinet factory
Price query of French grid-side energy storage cabinet factory
-
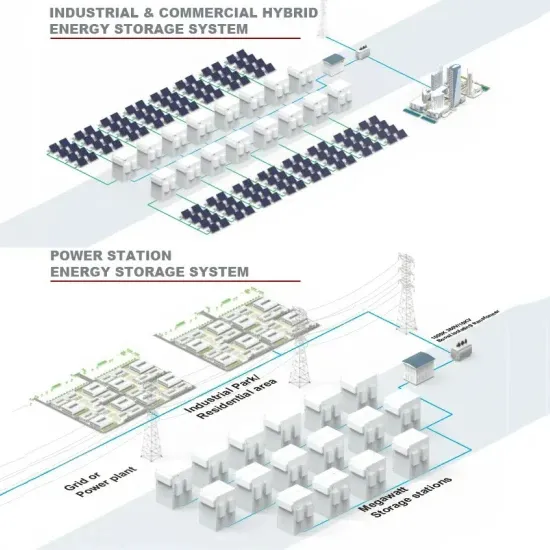 Grid-side energy storage power system
Grid-side energy storage power system
-
 South African grid-side energy storage cabinet brand
South African grid-side energy storage cabinet brand
-
 Egypt grid-side energy storage cabinet supplier
Egypt grid-side energy storage cabinet supplier
-
 Grid-side large-scale energy storage applications
Grid-side large-scale energy storage applications
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


