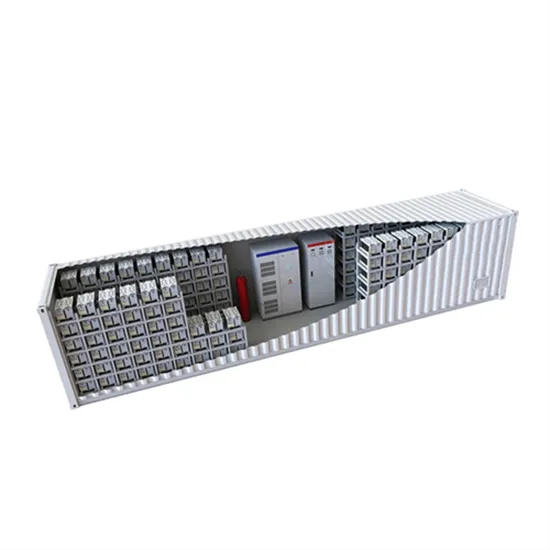

Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency. They are typically less expensive, have smaller footprints, and have a lower tolerance for industrial loads.
Get Price
What is a high frequency inverter and what should be paid
A high frequency inverter is a device that converts direct current to alternating current. High frequency inverters are inverters suitable for household DC and AC conversion.
Get Price
High frequency verses low frequency inverters
What is the difference between high, or low frequency inverters the pros and cons? I have seen a few posts someone said low was better for high surge load like AC units,
Get Price
What is a High-Frequency Power Inverter?
High-frequency inverters are used where small size, light weight and precision control are needed – motor drives, UPS, avionics, renewable energy, medical
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz.
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency Inverter: Which is
High frequency inverter: High frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology to chop DC power at high frequency through high-frequency switching tubes (such
Get Price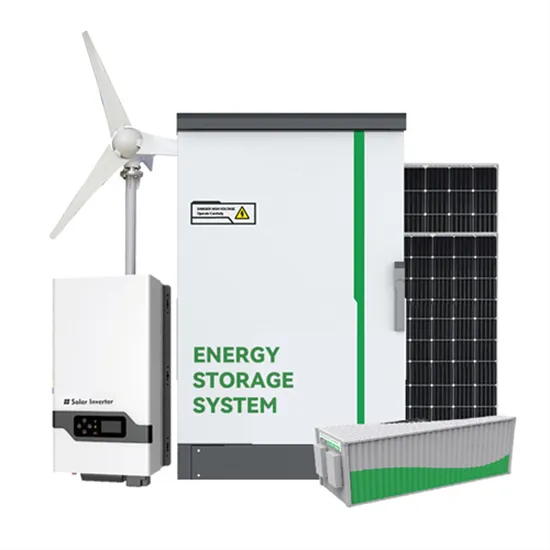
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
High-frequency inverters are known for their advanced technology and efficiency. But what is a high-frequency inverter? At its core, a high-frequency inverter converts DC to AC using
Get Price
The highest frequency and basic frequency of the
The highest frequency and basic frequency of the inverterThere are two definitions of fundamental frequency: a. The frequency corresponding
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High
The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency. They are typically less expensive, have smaller footprints, and have a lower tolerance for industrial loads.
Get Price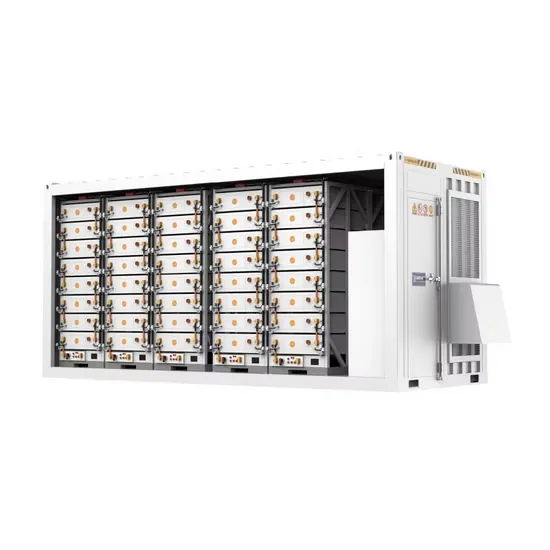
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High Frequency
What are high frequency inverters? An inverter that converts DC power to AC power at a high frequency, also known as a transformerless inverter, does not use a transformer. The
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get Price
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Which One Is Best?
A high-frequency inverter is a type of power inverter that uses advanced electronic switching technology to convert DC into AC. Instead of heavy transformers, these inverters use smaller,
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency inverters - typically 20 kHz to 100 kHz. High-frequency inverters
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
High frequency inverter: High frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology to chop DC power at high frequency through
Get Price
What are Low Frequency Toroidal Inverters?
So here I heard some inverters that are "low frequency toroidal inverters". 1. What are they? Example? 2. What is their advantage vs regular high frequency inverters? 3. Can
Get Price
Understanding Low Frequency Power Inverters
Applications and Benefits: Why Use Low Frequency Power Inverters? Low frequency power inverters offer several benefits over their high frequency counterparts, including: – Higher
Get Price
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in Modern Applications
High-frequency inverters are designed to be compatible with a wide input voltage range, allowing them to operate efficiently under varying input conditions. This flexibility makes them suitable
Get Price
Power inverter
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). [1] The resulting AC
Get Price
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in Modern
High-frequency inverters are designed to be compatible with a wide input voltage range, allowing them to operate efficiently under varying input conditions. This
Get Price
Frequency inverter
A frequency inverter enables the conversion of the electrical variable ''current''. The text contains information about setup and different types of inverters.
Get Price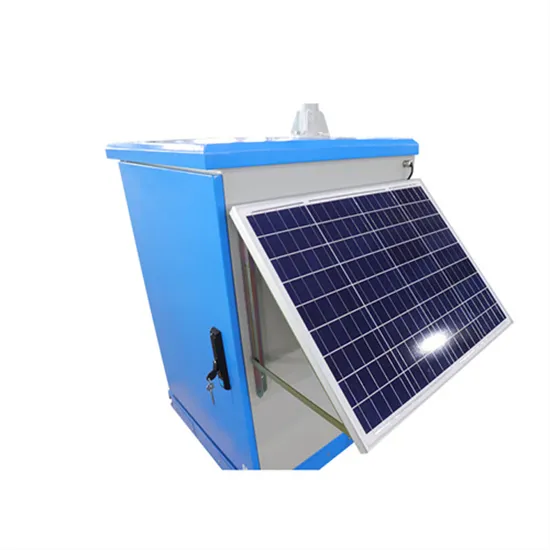
What is a High-Frequency Power Inverter?
High-frequency inverters are used where small size, light weight and precision control are needed – motor drives, UPS, avionics, renewable energy, medical equipment, etc.
Get Price
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in Modern
High-frequency inverters are known for their high efficiency, which is one of their most significant advantages. By operating at higher frequencies, typically in
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency,
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few
Get Price
What is high frequency solar power inverter
The inverter converts the direct current converted by the solar panel and stored in the battery into alternating current, which can be used to run household goods and electrical
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency inverters - typically 20 kHz to 100
Get Price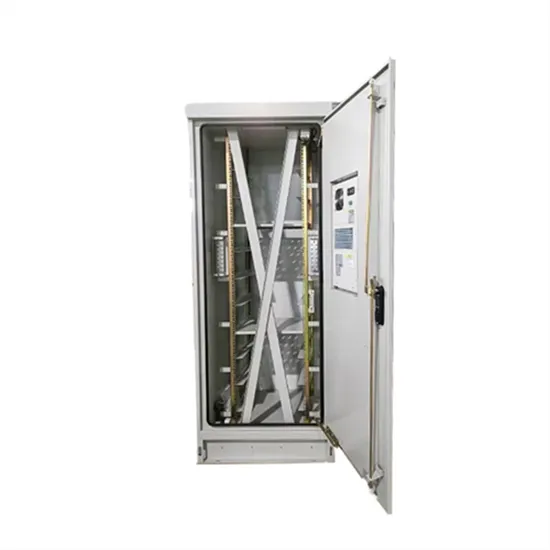
Inverters High or Low Frequency ? | DIY Solar Power Forum
Low-frequency inverters use high-speed switches to invert (or change) the DC to AC, but drive these switches at the same frequency as the AC sine wave which is 60 Hz (60
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
An inverter is a key component that converts DC power into AC power for household appliances and is commonly used in solar energy
Get Price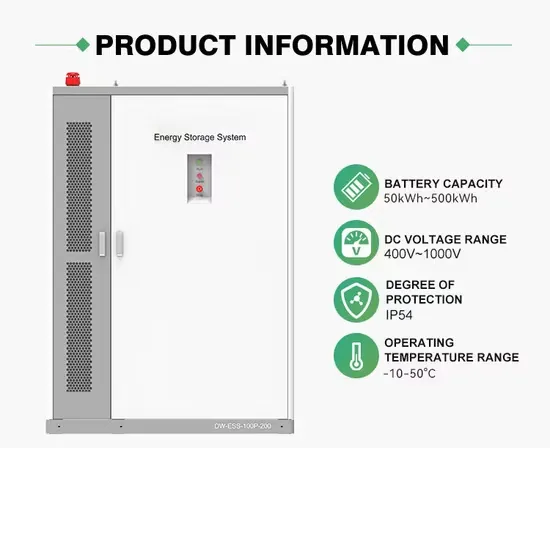
6 FAQs about [What is the use of high frequency inverter]
What is a high frequency inverter?
The high frequency inverter converts DC power into AC power using electronic components, such as capacitors and inductors. The high frequency output of a high frequency inverter is ideal for powering electronic devices, such as computers and televisions. High frequency inverters typically have an output of 20kHz or higher.
What are the advantages of high frequency inverters?
Volume and weight: Since high frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology and compact circuit design, their size and weight are usually much smaller than power frequency inverters. This gives high frequency inverters significant advantages in mobile power supplies, aerospace, electric vehicles, and other fields.
Are high-frequency inverters a good choice?
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high efficiency, but they also have the problem of relatively poor output waveform quality.
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
Here is the major difference of them: Thanks to the heavy-duty transformer, low frequency inverters have much higher peak power capacity and reliability. The transformer handles higher power spikes with longer duration than high-frequency inverters when it comes to driving inductive loads such as electric motor, pump, compressor, air conditioners.
Are power frequency inverters good?
In contrast, power frequency inverters can maintain high efficiency and stability under heavy load or overload. Output waveform quality: The output waveform quality of power frequency inverters is usually better than that of high frequency inverters.
How do high frequency power inverters convert DC to AC?
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz. Low frequency inverter circuit diagram
More related information
-
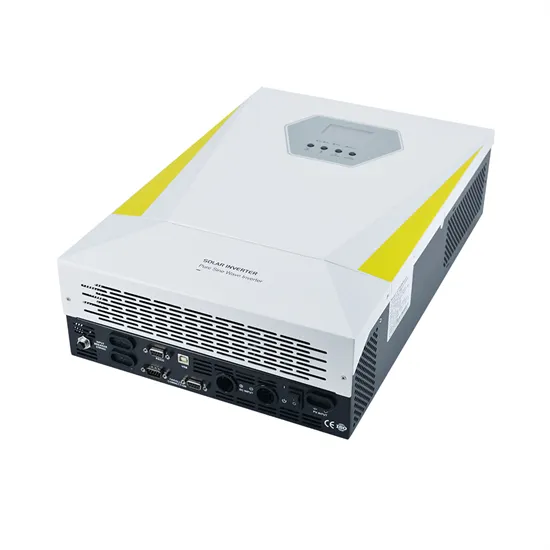 What is the price of high frequency inverter
What is the price of high frequency inverter
-
 Does the inverter use public frequency or high frequency
Does the inverter use public frequency or high frequency
-
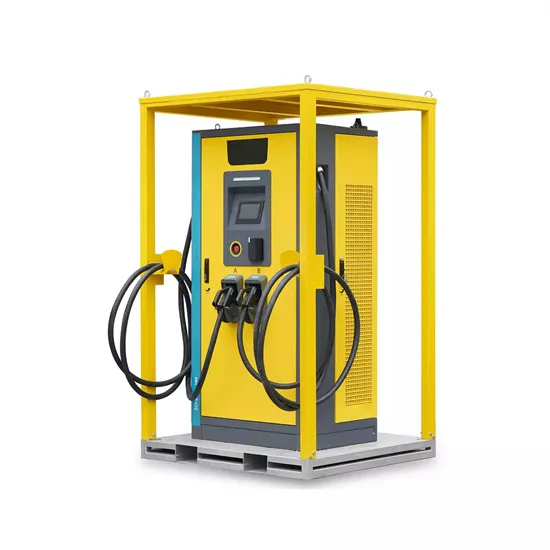 Indonesia high frequency inverter manufacturer
Indonesia high frequency inverter manufacturer
-
 Kiribati high frequency inverter
Kiribati high frequency inverter
-
 High frequency inverter to low frequency output
High frequency inverter to low frequency output
-
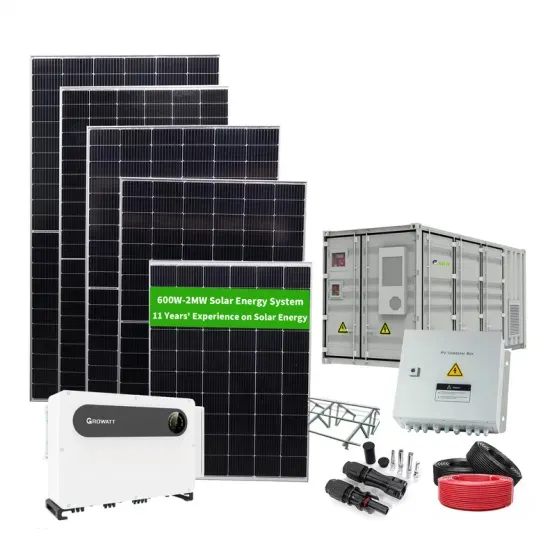 12v household high frequency sine wave inverter
12v household high frequency sine wave inverter
-
 High frequency inverter crystal
High frequency inverter crystal
-
 What size inverter should I use for a 120ah battery
What size inverter should I use for a 120ah battery
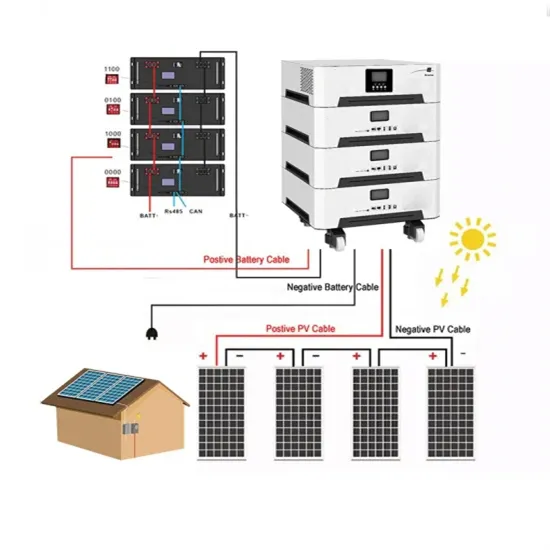
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


