Unraveling the Backbone of Electricity: A Deep Dive
Solar and wind, coupled with battery energy storage, can play a role in the baseload generation mix if the cost curve of storage continues to
Get Price
Grid-Scale Battery Storage: Frequently Asked Questions
What is grid-scale battery storage? Battery storage is a technology that enables power system operators and utilities to store energy for later use. A battery energy storage system (BESS) is
Get Price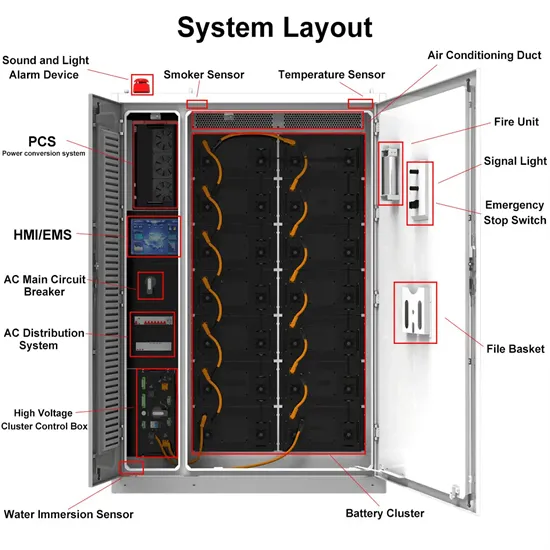
What is wind and solar energy storage power supply?
Wind and solar energy storage power supply refers to systems designed to capture and store energy generated from wind turbines and solar panels, allowing for
Get Price
What are wind and solar energy storage | NenPower
Various storage technologies are available to harness energy produced by wind and solar power. Electrochemical batteries, mechanical energy solutions like pumped hydro
Get Price
The Impact of Wind and Solar on the Value of Energy Storage
The purpose of this analysis is to examine how the value proposition for energy storage changes as a function of wind and solar power penetration. It uses a grid modeling
Get Price
What are the mechanical loading tests for solar panels?
Right) A simplified force diagram that simulates the effects of strong wind. One area constantly overlooked by the traditional solar markets like Europe, is the effects of strong wind
Get Price
THE ROLE OF STORAGE AND DEMAND RESPONSE
Demand response and energy storage are sources of power system flexibility that increase the alignment between renewable energy generation and demand. For example, demand
Get Price
Co-location: what is the impact on future battery
Co-location of batteries with solar or wind can reduce construction and maintenance costs, compared to a standalone battery. Constraints to the grid
Get Price
To Understand Energy Storage, You Must Understand
As is the case for renewables like wind and solar, the ELCC of energy storage declines the more you add to the grid. A great illustration of
Get Price
What Does ESS Mean? | Energy Storage Systems
What Does "ESS" Mean in Energy Storage? If you''ve researched solar panels, wind farms, or home batteries, you''ve likely seen the term "ESS." Let''s
Get Price
Diversion Dump Loads
Diversion Dump Loads What is a divert/dump load? When your batteries are full, you need to divert the excess power being generated to a separate load so your wind turbines
Get Price
What is wind and solar energy storage power supply?
Wind and solar energy storage power supply refers to systems designed to capture and store energy generated from wind turbines and solar
Get Price
Effective Load Carrying Capacity and Qualifying Capacity
As previously mentioned, effective load carrying capability (ELCC) is an output of probabilistic modeling, which assesses likely system needs and the potential for wind and solar resources
Get Price
Why Battery Storage is Becoming Essential for Solar
As the energy landscape evolves, hybrid solar and wind projects with integrated battery storage are becoming the new standard rather than the
Get Price
WIND AND SOLAR ON THE POWER GRID: MYTHS AND
This means that in a reliable electric power system (one that already meets its planning and operating reserve requirements) the addition of wind or solar requires no additional generation
Get Price
WIND AND SOLAR INTEGRATION ISSUES
WIND AND SOLAR INTEGRATION ISSUES Wind and solar power plants, like all new generation facilities, will need to be integrated into the electrical power system. This fact sheet addresses
Get Price
Why Battery Storage is Becoming Essential for Solar and Wind
As the energy landscape evolves, hybrid solar and wind projects with integrated battery storage are becoming the new standard rather than the exception. Industry analysts
Get Price
Co-location of battery energy storage: AC/DC coupling
Co-location of storage does not have a one-size-fits-all solution. Many technical solutions exist, all of which change the operational constraints and commercial
Get Price
STORAGE FOR POWER SYSTEMS
Storage can be located at a power plant, as a stand-alone resource on the transmission system, on the distribution system and at a customer''s premise behind the meter. Do wind and solar
Get Price
Wind and solar need storage diversity, not just capacity
In many renewable energy projects, storage is often treated as an auxiliary add-on rather than being systematically planned, relying on overall grid load patterns, dispatch
Get Price
Energy Storage Systems (ESS): The Future of Energy
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) are crucial in today''s energy landscape, playing a pivotal role in balancing energy supply and demand,
Get Price
Cost of electricity by source
Levelized cost: With increasingly widespread implementation of renewable energy sources, costs have declined, most notably for energy generated by solar
Get Price
Explainer: what does it actually mean to ''firm''
Storage is the best known way to firm renewables. As floods of cheap power come in, you can store it for later use. Storage can be performed
Get Price
To Understand Energy Storage, You Must Understand ELCC
As is the case for renewables like wind and solar, the ELCC of energy storage declines the more you add to the grid. A great illustration of this phenomenon, shown below,
Get Price
Wind, solar power aren''t worthless if there''s no wind or sun
2 days ago· Wind energy infrastructure doesn''t produce power if the air isn''t moving, and solar doesn''t generate power if the sun''s not out. But that doesn''t mean that either source of energy
Get Price
2024 ELCC Wind Solar and ESR Study Report
For example, the wind ELCC Study base case included load, conventional resources, all solar resources, and all other resources except for wind. The base case and subsequent change
Get Price
Explainer: what does it actually mean to ''firm'' renewables?
Storage is the best known way to firm renewables. As floods of cheap power come in, you can store it for later use. Storage can be performed by grid-scale batteries, where the
Get Price
Solar-Plus-Storage 101
This blog post will explain the terminology around solar-plus-storage, how many solar-plus-storage systems are in the country, and what they cost.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [What does wind solar and load storage mean ]
Why is energy storage important?
That storage will soak up excess renewable energy when the sun is shining and the wind is blowing. Then the storage will discharge that energy during periods with low renewable energy production, which is when the grid will need that energy most. By storing energy for later use, energy storage helps keep the grid reliable.
Does solar penetration affect energy storage?
In one study, the folks at NREL charted the relationship between solar penetration in California and the amount of 4-hour energy storage that would have an ELCC of 100% (see below). This example is fascinating because, up until ~11% solar penetration, solar actually reduces the grid reliability value of energy storage.
Can energy storage discharge electricity to the grid at any time?
That means that energy storage can discharge electricity to the grid at any time (as long as it’s charged). In general, this makes the ELCC of energy storage much higher than that of renewables since you can choose to dispatch energy storage during the times when the grid is most likely to experience electricity shortfalls.
Will energy storage clean up the electric grid?
It’s going to take a massive amount of energy storage to clean up the electric grid. That storage will soak up excess renewable energy when the sun is shining and the wind is blowing. Then the storage will discharge that energy during periods with low renewable energy production, which is when the grid will need that energy most.
How can renewable power be stored?
Storage is the best known way to firm renewables. As floods of cheap power come in, you can store it for later use. Storage can be performed by grid-scale batteries, where the power is stored directly.
Does energy storage ensure grid reliability?
By storing energy for later use, energy storage helps keep the grid reliable. But as we transition to a grid that runs primarily on clean energy and energy storage, grid operators must determine the extent to which energy storage ensures grid reliability.
More related information
-
 What does wind solar and electricity storage mean
What does wind solar and electricity storage mean
-
 What does wind power and solar energy storage mean
What does wind power and solar energy storage mean
-
 What are the wind solar and energy storage power stations in Zimbabwe
What are the wind solar and energy storage power stations in Zimbabwe
-
 What does the term wind and solar storage mainly refer to
What does the term wind and solar storage mainly refer to
-
 What are the wind and solar energy storage power stations in Malaysia
What are the wind and solar energy storage power stations in Malaysia
-
 What is wind solar and thermal storage
What is wind solar and thermal storage
-
 The prospects of wind solar load and storage
The prospects of wind solar load and storage
-
 What are the equipments of wind solar and energy storage power stations
What are the equipments of wind solar and energy storage power stations
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


