How does a high
Now, the main difference between high - frequency and low - frequency inverters lies in how they handle the conversion process, and this difference has a bunch of implications
Get Price
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
In most regions, the standard inverter frequency for AC power systems is 50 or 60 Hz, representing the number of complete cycles per second. This inverter frequency is
Get Price
Which is Better Low Frequency or High-frequency
Introduction Inverters convert DC power into AC power to operate AC equipment and devices. They utilize power electronic switching at different frequencies to
Get Price
The Impact of an Overlaid Ripple Current on Battery
Fast-switching semiconductors induce ripple currents on the high-voltage DC bus in the electric vehicle (EV). This paper describes the methods used in the
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Power frequency inverters are typically heavier than high-frequency inverters because of their hue abuser and larger transformers. On the other hand, high-frequency
Get Price
(PDF) The Effect of High Switching Frequency on Inverter Against
The latest generation of Inverter using the high switching frequency to obtain the inverter with good efficiency, small in sizes and lightweight.
Get Price
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and
In most regions, the standard inverter frequency for AC power systems is 50 or 60 Hz, representing the number of complete cycles per
Get Price
Inverter PWM Control | SpringerLink
An usual way of regulating the voltage is via the PWM control, which outputs high-frequency switching signals to the inverter and generates the AC voltage waveform from the
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
These inverters are mostly found in applications with high volume or weight needs, such as aerospace, mobile power supplies, electric vehicles, or other fields. Power Frequency
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
The high frequency inverter can deliver the same power at higher frequency with a much smaller and lighter transformer, as a result, the HF inverter is often called transformer
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
The transformation of a high-frequency inverter steps up or down the voltage as needed, adjusting it to the desired level for the application. For
Get Price
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
Understand the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters with this quick article.
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
The high frequency inverter can deliver the same power at higher frequency with a much smaller and lighter transformer, as a result, the HF
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
The transformation of a high-frequency inverter steps up or down the voltage as needed, adjusting it to the desired level for the application. For example, 12V DC can be converted from a solar
Get Price
Inverters, Types and Voltages
However, not all inverters are created equal. This blog post explores the key differences between low voltage and high voltage inverters as well as low frequency and high
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
The choice between a low-frequency and high-frequency inverter will depend on your specific needs, such as the type of loads you expect to
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power
Get Price
Difference Between High and Low Frequency Inverter
Here we need to add a detail: high-frequency inverters are inverted under high voltage conditions, that is, they can use the high-voltage DC input from the solar panel to
Get Price
CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
An inverter uses this feature to freely control the speed and torque of a motor. This type of control, in which the frequency and voltage are freely set, is called pulse width modulation, or PWM.
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverters: From Photovoltaic, Wind, and
High-Frequency Inverters: From Photovoltaic, Wind, and Fuel-Cell-Based Renewable- and Alternative-Energy DER/DG Systems to Energy-Storage Applications S.K. Mazumder, Sr.
Get Price
How Does a Frequency Inverter Work?
Frequency Control: The frequency of the output AC voltage is determined by the switching frequency of the IGBTs in the inverter stage. For
Get Price
Step-wave Superposition Inverter|Home Energy Storage
A Staircase Waveform Inverter is a type of power electronic device that features a stepped waveform output and is widely used to convert direct current (DC) to high-quality alternating
Get Price
Harmonics and Harmonic Frequency in AC Circuits
Harmonics and harmonic distortion is the difference between the ideal sinusoidal waveform the supply voltage or the load current waveform should look like, and what it really is as a result of
Get Price
Difference Between High and Low Frequency Inverter
Why is the difference so big? Because it is determined by the orientation of their respective working principles: for high-frequency inverters, the inversion logic is inverted at
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get Price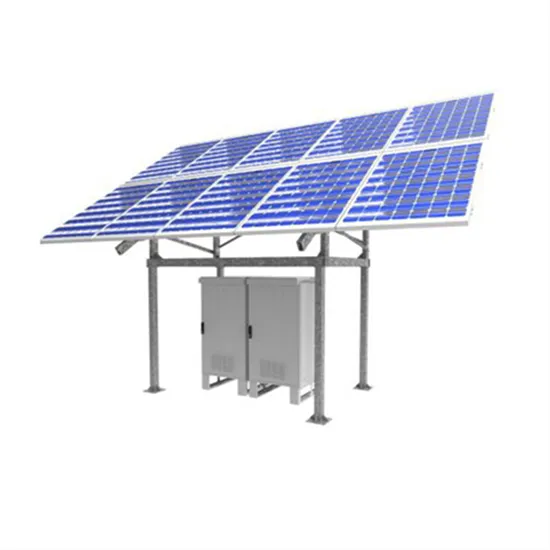
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
The choice between a low-frequency and high-frequency inverter will depend on your specific needs, such as the type of loads you expect to power and the conditions in which
Get Price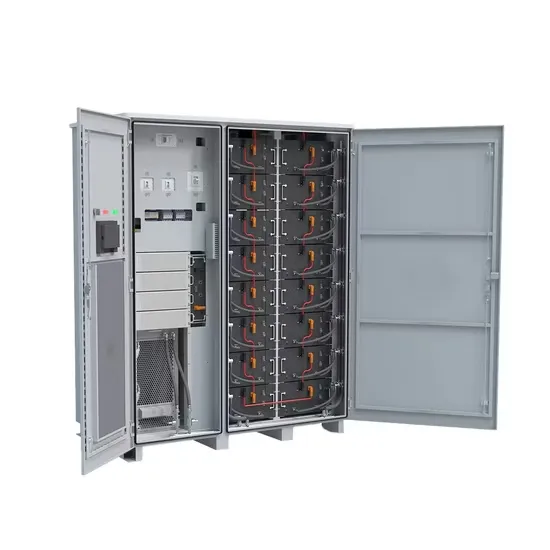
Reduction of Harmonics in Output Voltage of Inverter
The frequency of the reference signal,, determines the inverter output frequency,, and its peak amplitude, controls the modulation index and then in turn RMS output voltage.
Get Price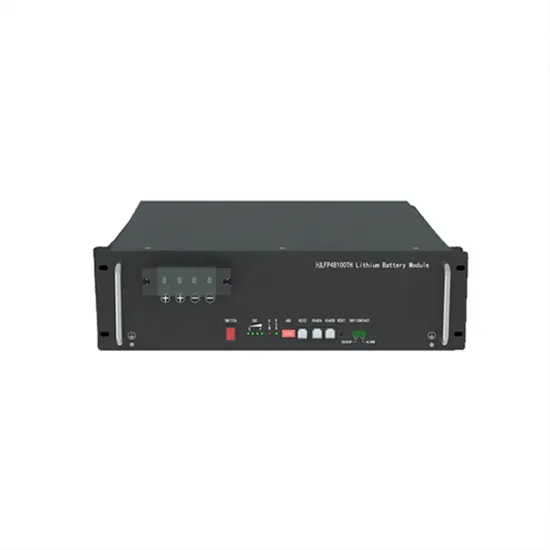
6 FAQs about [Does a high-frequency inverter have a superimposed voltage ]
What is a high frequency inverter?
The high frequency inverter can deliver the same power at higher frequency with a much smaller and lighter transformer, as a result, the HF inverter is often called transformer-less inverter, or TL inverter.
What determines a high or low frequency inverter?
Size and tolerances of the transistors used in the inversion process, and the speed at which they operate determines the classification of high or low frequency. The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency.
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
Here is the major difference of them: Thanks to the heavy-duty transformer, low frequency inverters have much higher peak power capacity and reliability. The transformer handles higher power spikes with longer duration than high-frequency inverters when it comes to driving inductive loads such as electric motor, pump, compressor, air conditioners.
Does victron use a high frequency inverter?
Victron combines both inverters, which they call Hybrid HF or Combined high frequency and line frequency technologies. What frequency inverter does growatt use? Growatt uses a high-frequency inverter. Which one is best? Low or high frequency? The best inverter is the low-frequency inverter.
How do high frequency power inverters convert DC to AC?
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz. Low frequency inverter circuit diagram
What is a standard inverter frequency?
In most regions, the standard inverter frequency for AC power systems is 50 or 60 Hz, representing the number of complete cycles per second. This inverter frequency is essential for the proper functioning of electrical devices and systems, as it dictates the speed at which motors rotate, lights flicker, and electronic components operate. 2.
More related information
-
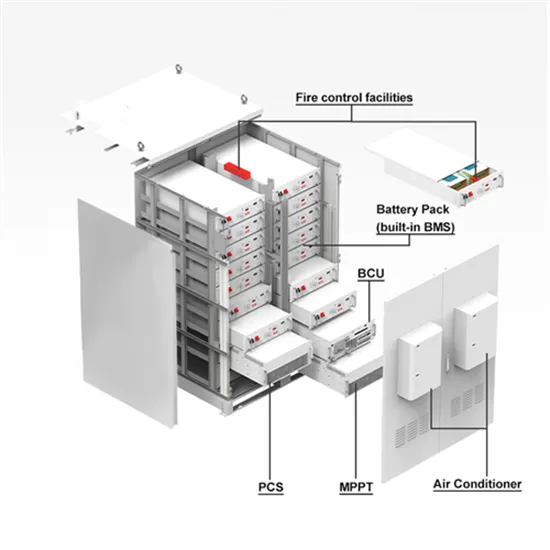 High-frequency inverter front-stage closed-loop control
High-frequency inverter front-stage closed-loop control
-
 Energy storage inverter rated voltage
Energy storage inverter rated voltage
-
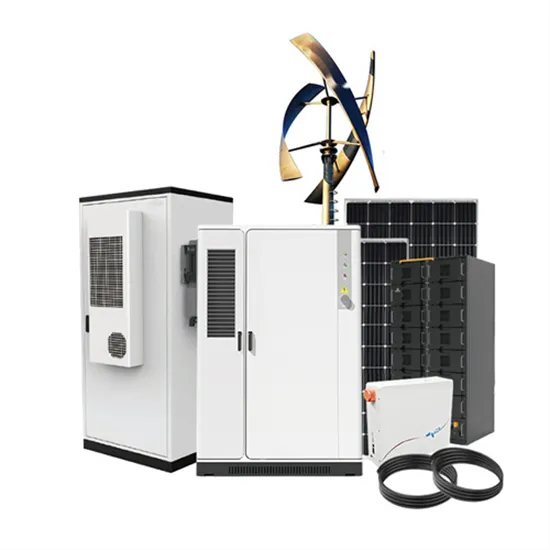 Wide voltage inverter power generation system
Wide voltage inverter power generation system
-
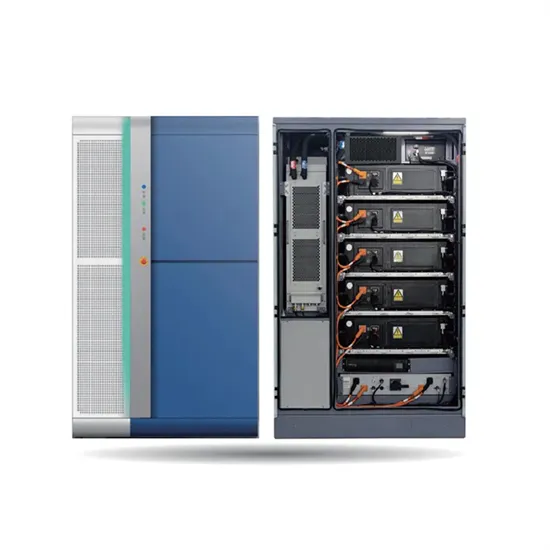 American standard inverter output voltage
American standard inverter output voltage
-
 72v inverter voltage protection
72v inverter voltage protection
-
 Can the inverter voltage be adjusted higher
Can the inverter voltage be adjusted higher
-
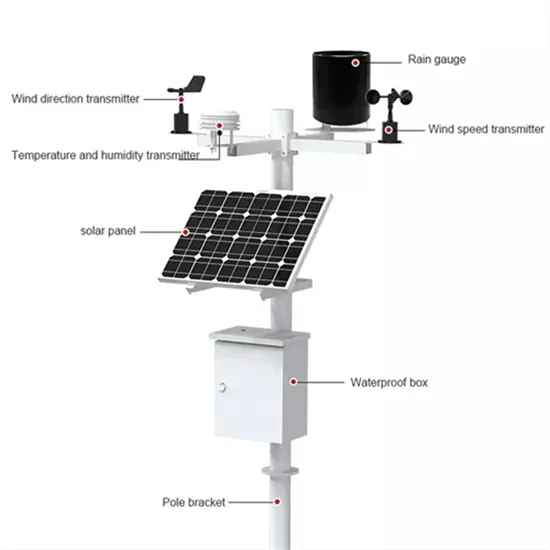 Voltage Source Inverter Products
Voltage Source Inverter Products
-
 Inverter input voltage DC12DC24
Inverter input voltage DC12DC24
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


