Power Inverter Buying Guide | Eaton
A power inverter is a device that converts low-voltage DC (direct current) power from a battery to standard household AC (alternating current) power. An
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between 12V, 24V and
Not necessarily – it depends on your setup. 24V is more efficient for high-power systems and long cable runs, but 12V is simpler and more
Get Price
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Low-voltage inverters work with DC voltages ranging from 12V to 48V. These are often found in small systems like RVs, boats, cabins, and backup power for small homes. They
Get Price
What Appliances can run on a Power Inverter?
A power inverter is a device that takes in direct current (DC) and converts this into alternating current (AC) so it can power AC appliances. Firstly there are two
Get Price
What is the advantage of a 24v system over a 12v
Today, most systems are 24V or 48V and include a 230V AC inverter. This means the wiring of the house does not have to be different from
Get Price
Frequently Asked Questions About Power Inverters | DonRowe
Frequently Asked Questions about Power Inverters. Get answers to all of you power inverter questions including what a power inverter is and what it can be used for, how to size and
Get Price
Tips to Choose the Right Inverter for Homes: 12V or 24V
The voltage rating (12V inverter vs 24V inverter) indicates the DC input voltage that the inverter can handle. While both types serve the same
Get Price
12V vs 24V Inverter: What''s the difference between 12 and 24 Volt
Knowing the voltage of your inverter critical in order for everything to run correctly. Using the wrong voltage inverter can even lead to irreparable damage to your equipment. That''s why
Get Price
12V Inverter vs 24V Inverter — What Is The Difference & Which
This article will explore the differences between 12v inverter vs 24v inverter, considering factors such as energy loss, battery requirements, and suitability for different
Get Price
The Only Inverter Size Chart You''ll Ever Need
We have created a comprehensive inverter size chart to help you select the correct inverter to power your appliances.
Get Price
Inverter AC to DC Amperage Conversion Calculator
AC to DC Conversion Calculator The first step to sizing a battery pack when using a DC to AC power inverter is to know your DC amp rating.
Get Price
All About 24V Power Supplies You Need to Know
Discover the essentials of 24V power supplies, including types, features, applications, and troubleshooting tips, to power your devices safely and efficiently.
Get Price
Pure Sine Wave Inverter Selection: Reliable Power
A pure sine wave inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) electricity from batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that
Get Price
12V VS 24V Inverter: What are the Differences and
In this article, we''ll explore the key differences between 12V and 24V inverters, helping you make an informed decision for your specific application.
Get Price
Power Converters Explained: How to Change DC
Because batteries output DC power, you''ll need a DC to AC inverter in order to power most household devices (unless it''s a 12V
Get Price
12V vs 24V Inverters Key Differences and Which One is Right for
Voltage affects the overall performance of the inverter system. A 12V inverter is designed to handle lower power output and is typically suited for smaller applications, while a
Get Price
What Does an Inverter Do, and How Does It Work
An inverter converts DC power from batteries or solar panels into AC power for household appliances. It''s essential for off-grid systems, RVs, and backup
Get Price
How to Calculate How Long an Inverter Will Last
An inverter draws its power from the battery so the battery capacity and power load determines how long the inverter will last. Regardless of the size, the calculation steps are always the same.
Get Price
12V Vs. 24V Solar Panel (The Difference)
Why Some Solar Panels are 12V and 24V The voltage of a solar panel determines how much power it produces and is usually located on the
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between 12V, 24V and 240V Power
Not necessarily – it depends on your setup. 24V is more efficient for high-power systems and long cable runs, but 12V is simpler and more compatible with most camping and
Get Price
What is the advantage of a 24v system over a 12v system?
Today, most systems are 24V or 48V and include a 230V AC inverter. This means the wiring of the house does not have to be different from any other grid-connected household
Get Price
12V vs 24V Inverter: What''s the difference between 12
Knowing the voltage of your inverter critical in order for everything to run correctly. Using the wrong voltage inverter can even lead to irreparable damage to your
Get Price
Tips to Choose the Right Inverter for Homes: 12V or 24V
The voltage rating (12V inverter vs 24V inverter) indicates the DC input voltage that the inverter can handle. While both types serve the same purpose, they have distinct
Get Price
12V Inverter vs 24V Inverter — What Is The
This article will explore the differences between 12v inverter vs 24v inverter, considering factors such as energy loss, battery requirements, and
Get Price
12V vs 24V inverter
This article introduces how inverter works and compares 12V vs 24V inverter, including the applications, costs, and other differences, also provides a guide on choosing the
Get Price
How to Safely Connect Your Inverter to Electricity: A Complete
Learn how to safely connect your inverter to electricity with this step-by-step guide. Ensure efficient power backup with proper installation, essential tools, safety precautions, and expert tips.
Get Price
Watts, Volts, Amps Calculator – self2solar
Introduction Volts, amps and watts are electricity measurements. Volts measure the electrical potential, or the "push," that moves electrons through a circuit. In simpler terms,
Get Price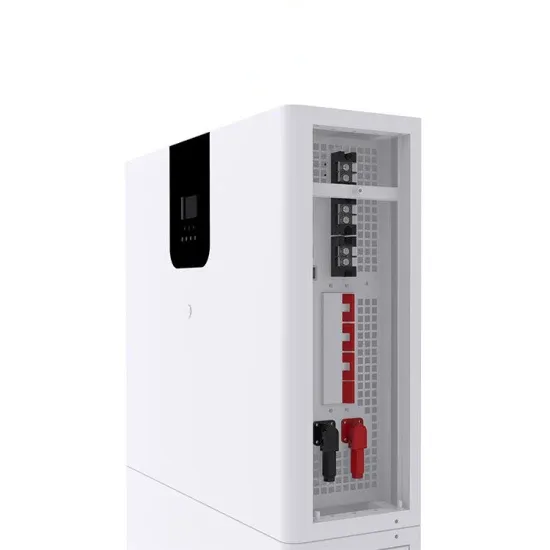
12V vs 24V Inverter: What''s The Difference & Which is Better
Torn between 12V and 24V inverters? Discover the key differences in efficiency, cost, and power capacity to determine which is better for your energy needs.
Get Price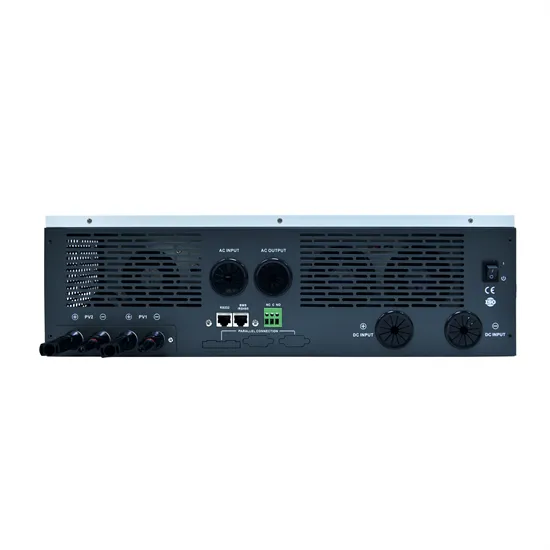
12V VS 24V Inverter: What are the Differences and How to Choose
In this article, we''ll explore the key differences between 12V and 24V inverters, helping you make an informed decision for your specific application.
Get Price
12V vs 24V inverter
This article introduces how inverter works and compares 12V vs 24V inverter, including the applications, costs, and other differences, also
Get Price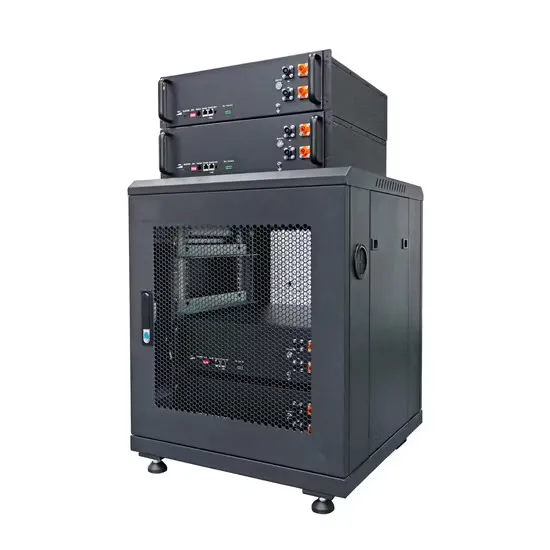
Advice on selecting an inverter – Sinetech
When the inverter operates appliances with high continuous load ratings for extended periods, it is not advisable to power the inverter with the same battery used to power your car or truck.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Is the voltage of a 24v inverter the same as household electricity ]
What is the difference between 12V vs 24V inverters?
Efficiency is an important factor when choosing between 12V vs 24V inverters. In general, 24V inverters are more efficient than their 12V counterparts, especially for larger systems. The efficiency difference becomes more noticeable as you increase the power demand of the system.
What is the difference between 12V and 24v battery systems?
It depends on your system’s size, the quality of the inverter, and your power needs. In general, 24V inverters are better for larger systems, while 12V inverters work well for smaller setups. When choosing between 12V and 24V battery systems, it’s important to understand their differences. Let’s take a look the table below:
Can a 12V inverter run on a 24v battery?
If you try to use a 12V inverter on a 24V battery it will be overloaded. Contrastingly, using a 24V inverter with a 12V battery will lead to a lack of electrical force. Knowing your inverter's voltage and what that means is critical in order for everything to run correctly.
Should I buy a 24V inverter?
24V Inverters: More efficient in larger systems since they require lower current, reducing energy loss and wire size. This can save energy, extend battery life, and use smaller components. However, the choice isn’t always simple. It depends on your system’s size, the quality of the inverter, and your power needs.
What is a 24V inverter?
24V Inverters: These systems generally offer higher efficiency, particularly in larger installations, thanks to lower current demands and reduced wire losses. This improved efficiency translates into energy savings, longer battery life, and potentially smaller system components.
How do I choose a 12 volt or 24 volt inverter?
Inverter size is another key consideration when choosing between a 12 volt and a 24 volt inverter. The size of the inverter determines its capacity to handle power loads. 12V Inverter Size: 12V inverters are typically available in smaller sizes and may have limitations in terms of the maximum power they can supply.
More related information
-
 Photovoltaic inverter connected to household electricity
Photovoltaic inverter connected to household electricity
-
 Can a 12v inverter power household electricity
Can a 12v inverter power household electricity
-
 Does a 24V inverter produce more electricity than a 12V inverter
Does a 24V inverter produce more electricity than a 12V inverter
-
 24V inverter low voltage protection
24V inverter low voltage protection
-
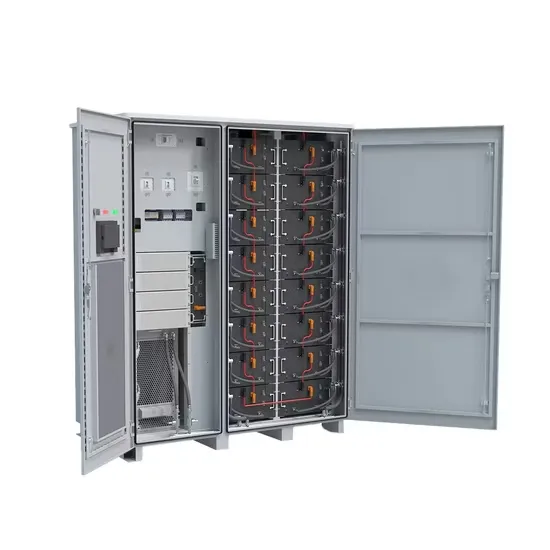 Can a 24v inverter be used with a 12v voltage
Can a 24v inverter be used with a 12v voltage
-
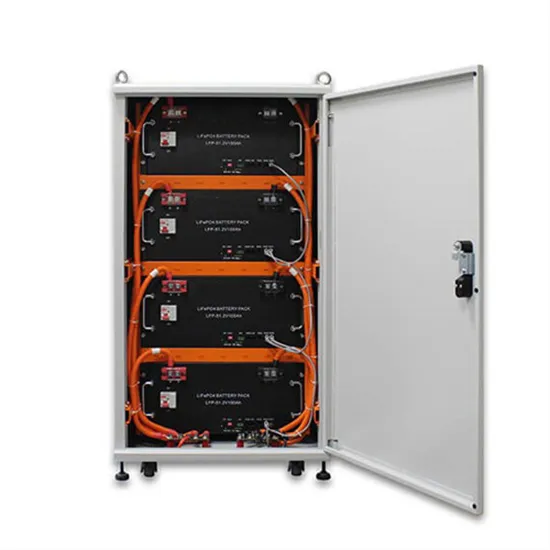 Connecting household electricity to 220v inverter
Connecting household electricity to 220v inverter
-
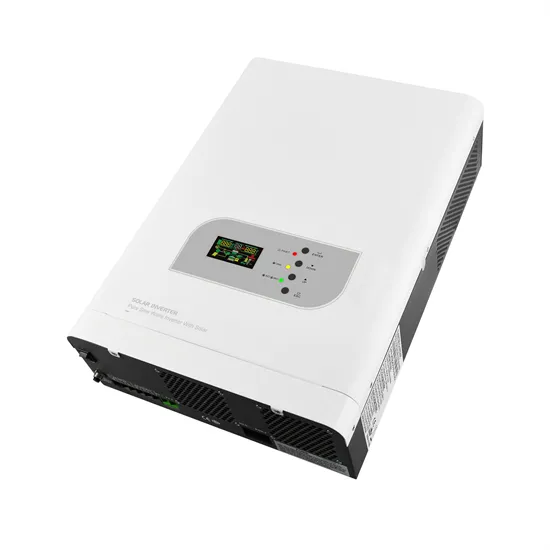 Battery with inverter minimum voltage
Battery with inverter minimum voltage
-
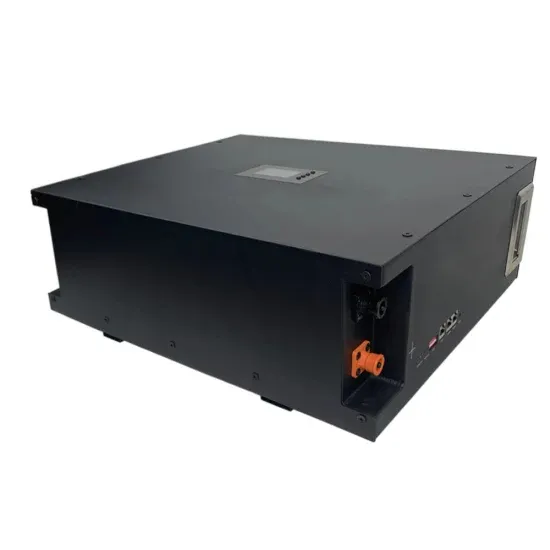 Solar panel voltage regulator and inverter
Solar panel voltage regulator and inverter
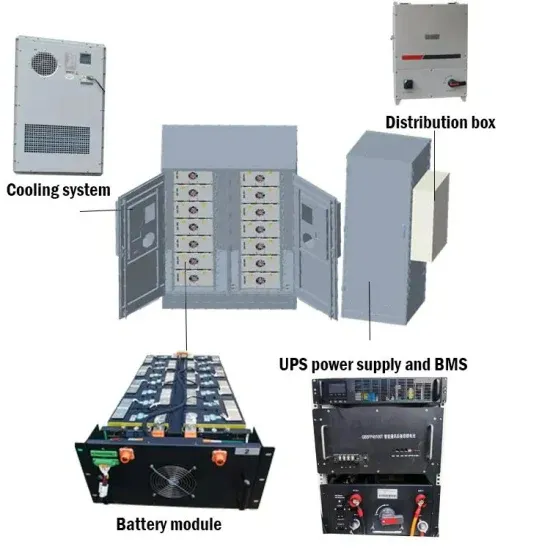
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


