Differences and similarities between low-voltage inverters and high
Low-Voltage: Generally less expensive due to lower safety requirements and less complex installation. High-Voltage: More expensive upfront due to the higher costs of components
Get Price
High Voltage or Low Voltage Batteries?
Each inverter comes with a Battery voltage range [V], this voltage indicates whether an inverter can manage a high or low voltage battery. Typical battery inverters that are rated at
Get Price
Whats is a High Voltage Hybrid inverter? What are Key
Explore the pivotal differences between high and low voltage hybrid inverters and how these variations can influence your choice in sustainable energy solutions.
Get Price
Low-voltage vs high-voltage power backup systems
However, as a general rule of thumb, high-voltage residential backup inverters and batteries tend to be more expensive than low-voltage inverters and batteries. To give you an idea of the cost
Get Price
Inverter vs Transformer Welders: Differences Explained
This simple technology takes a high-voltage, low-amperage current and reverses it into a low-voltage, high-amperage current. So, an AC high voltage input (110V, 220V, 380V,
Get Price
Low-voltage VS High-voltage Inverters: What''s the Difference
Inverter technology serves as the backbone of modern power conversion systems, facilitating the seamless transformation of DC to AC electricity. The distinction between low-voltage (LV) and
Get Price
High Voltage vs. Low Voltage Solar Panels: What You
The terms "high voltage" and "low voltage" can be a bit confusingespecially when you start to read different specs on manufacturer''s websites. Some
Get Price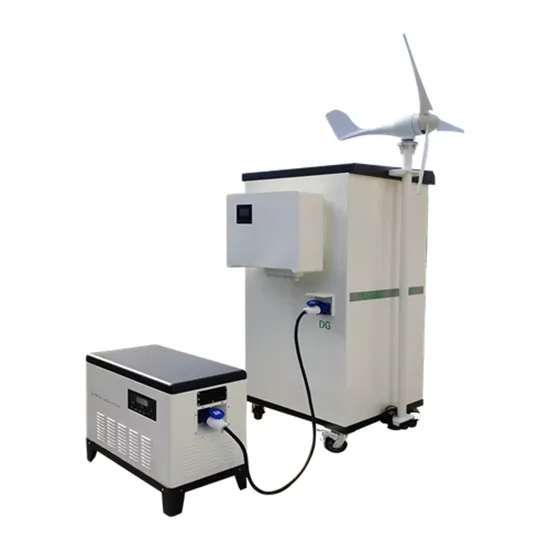
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar
Get Price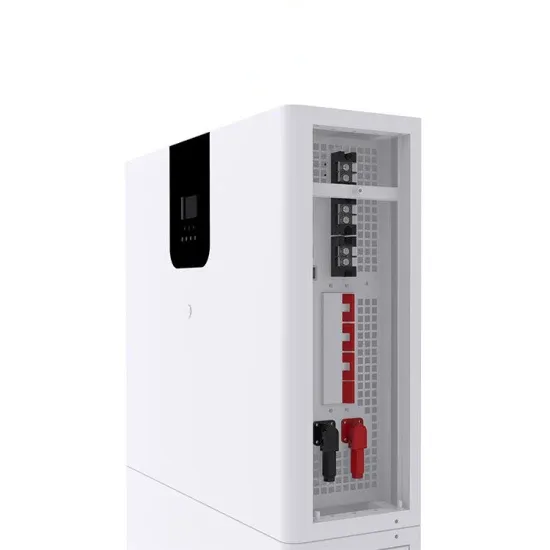
What does low voltage but high current mean?
String with lower voltage will always show higher current with lower voltage while the higher voltage string always shows higher/normal voltage and lower current. But if i restart
Get Price
The role and difference between high voltage inverter
To summarize, high-voltage inverters are mainly used for high-power applications in industry, while low-voltage inverters are suitable for low
Get Price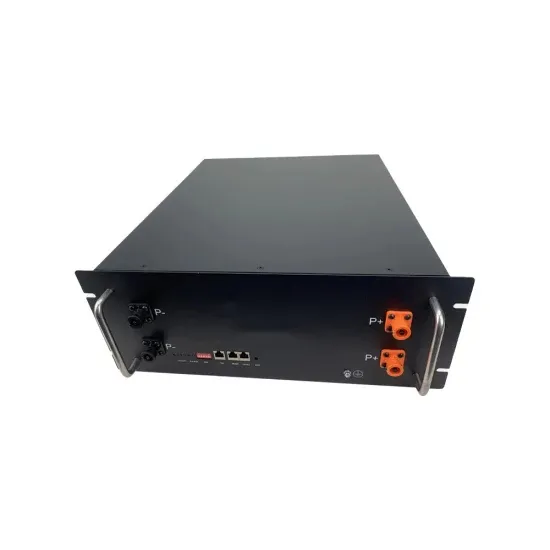
Inverters, Types and Voltages
However, not all inverters are created equal. This blog post explores the key differences between low voltage and high voltage inverters as well as low frequency and high
Get Price
Differences and similarities between low-voltage inverters and
Low-Voltage: Generally less expensive due to lower safety requirements and less complex installation. High-Voltage: More expensive upfront due to the higher costs of components
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
In the field of power electronics and energy conversion, inverters, as key equipment for power conversion, play a vital role. Inverters are capable
Get Price
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
When you hear the terms high-voltage and low-voltage inverters, you might wonder: does it really matter which one you choose? If you''re setting up a solar power system, buying a battery
Get Price
Low-voltage VS High-voltage Inverters: What''s the Difference
The distinction between low-voltage (LV) and high-voltage (HV) inverters extends beyond nominal voltage thresholds, encompassing design architectures, efficiency trade-offs, and application
Get Price
Is there a difference between a high voltage inverter and a low voltage
The choice between low-voltage and high-voltage hybrid inverters depends on system size, power requirements, and availability and investment opportunities. Low voltage is
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get Price
Is there a difference between a high voltage inverter and a low
The choice between low-voltage and high-voltage hybrid inverters depends on system size, power requirements, and availability and investment opportunities. Low voltage is
Get Price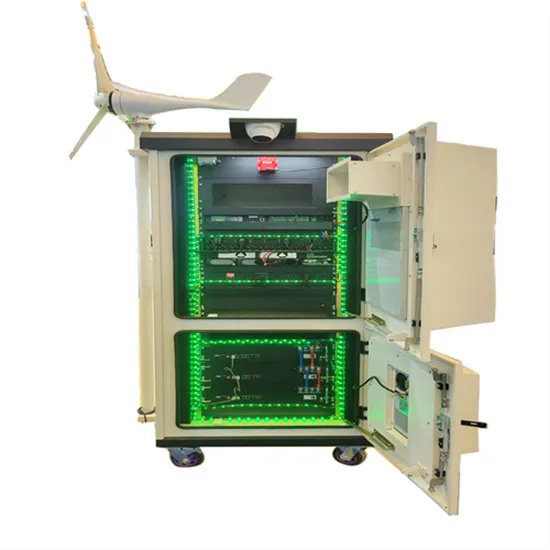
The role and difference between high voltage inverter and low voltage
To summarize, high-voltage inverters are mainly used for high-power applications in industry, while low-voltage inverters are suitable for low-power applications in homes and
Get Price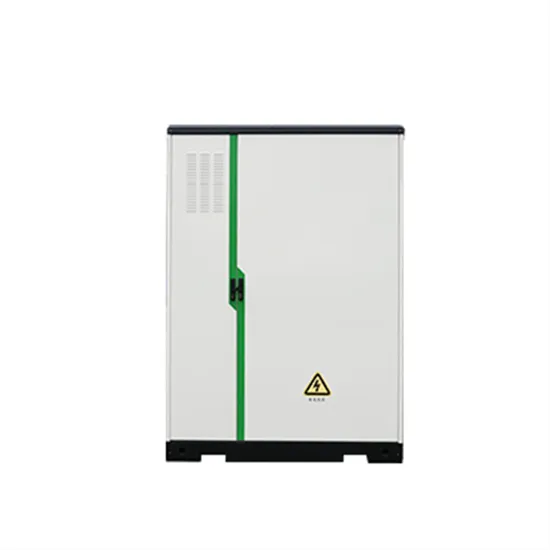
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get Price
Whats is a High Voltage Hybrid inverter? What are
Explore the pivotal differences between high and low voltage hybrid inverters and how these variations can influence your choice in sustainable
Get Price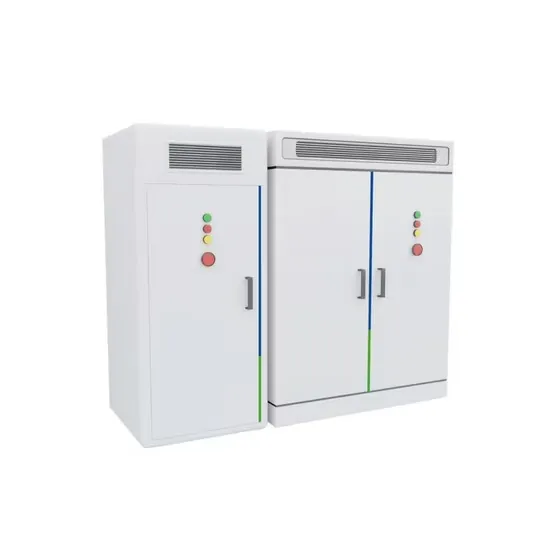
High Bus Voltage Error on MUST 5KVA Inverter
Just installed a new 48V 5KVA inverter with 4x 100Ah gel batteries. Backup DB has 25A input and output breakers with 3-way bypass switch and 125A DC circuit breaker.
Get Price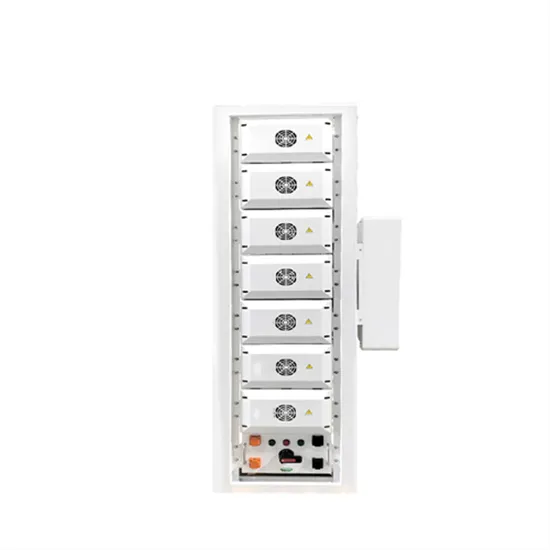
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
You''ll learn what high-voltage and low-voltage inverters do, how they work, and where each type is best used. We''ll also talk about the benefits and drawbacks of each, along
Get Price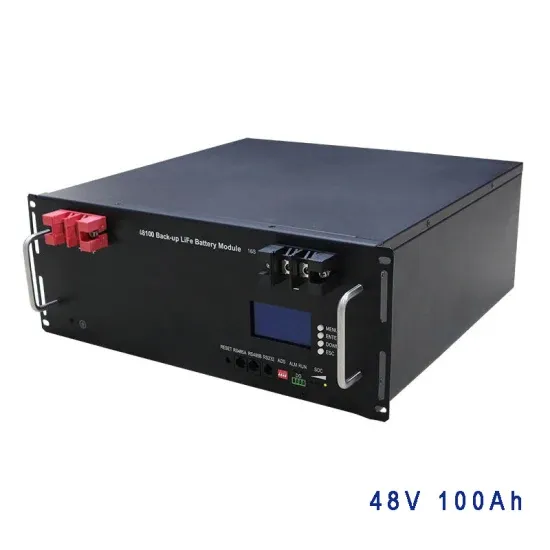
How to Address Inverter Low Voltage Issues for
Inverters play a crucial role in industrial automation and energy management, ensuring seamless operation and efficiency. However, voltage
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What Is The
Understanding the relationship between input and output inverters is key to better understanding how does inverter works and functions. The relationship
Get Price
power supply
Low voltage and high current means you need to spend more on copper/cables. Going for a higher voltage saves money on copper up until you reach issues with cable
Get Price
Lower the Volts, higher the Amps, and vice versa?
"the lower the Volts, the higher the Amps" is what applies when you alter the load to consume the same power on a new voltage. Here, the constant (as a desired result) is the
Get Price
Understanding inverter startup voltage.
Meaning that each individual string has to be of a certain size to reach the inverter start up voltage separately. For example; inverter start up voltage 90v. So each string has to
Get Price
High Voltage vs. Low Voltage: What''s the Best Choice
When choosing an inverter for a low-voltage home energy storage systems, it is important to select an inverter with a voltage range that includes
Get Price
6 FAQs about [What does high voltage and low voltage mean in inverters ]
What is the difference between high voltage and low voltage inverters?
A high voltage array can use smaller cross-section cables to connect it to the inverter, or can be sited further from the inverter, than a low voltage array. For 'reasonable' voltages, in the several 10s to several 100s range, there's not a lot of difference between the efficiency of commercial inverters.
Is there a difference between a commercial inverter and a high voltage?
For 'reasonable' voltages, in the several 10s to several 100s range, there's not a lot of difference between the efficiency of commercial inverters. Comparably higher voltage is more preferable when given choice between different voltages.
What happens if the input is low (0) in an inverter?
When the input to an inverter is LOW (0), the output is inverted, meaning it becomes HIGH (1).
What is a low voltage & high voltage?
According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), voltage is divided into two categories: 600 volts or less (low voltage) and greater than 600 volts (high voltage). Live parts of 50 volts or more must be guarded against accidental contact.
Why do inverters have two input voltage options?
The third and most distinctive advantage is the higher efficiency of inverters at higher input voltages. If you see the datasheet of the inverters with two input voltage options they are more efficient in converting higher input voltage to mains voltage than converting lower input voltage to the same mains voltage.
Does a high voltage array have a problem?
The "problem" is not so much on the inverter side as it is on the supply side. (Generally speaking, each inverter may have their own issues) A high voltage array can use smaller cross-section cables to connect it to the inverter, or can be sited further from the inverter, than a low voltage array.
More related information
-
 What are the advantages of high voltage inverters
What are the advantages of high voltage inverters
-
 Two high voltage inverters can be used in series
Two high voltage inverters can be used in series
-
 The difference between high voltage and low voltage energy storage batteries
The difference between high voltage and low voltage energy storage batteries
-
 Inverter high current voltage becomes low
Inverter high current voltage becomes low
-
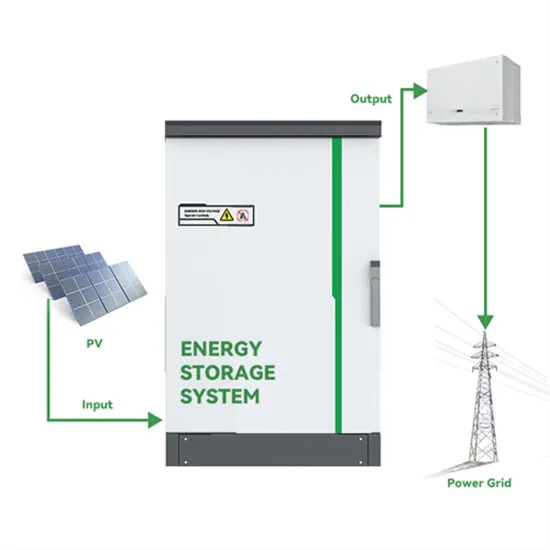 Is the communication base station inverter high voltage or low voltage
Is the communication base station inverter high voltage or low voltage
-
 Can the inverter convert high voltage to low voltage
Can the inverter convert high voltage to low voltage
-
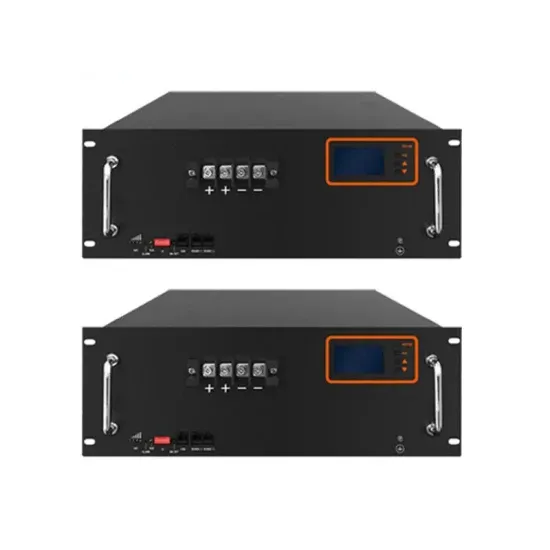 What is the best DC voltage for photovoltaic inverters
What is the best DC voltage for photovoltaic inverters
-
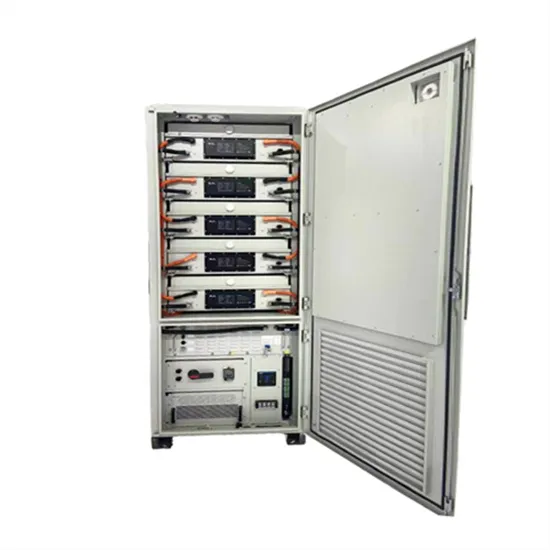 220v high voltage power station energy storage
220v high voltage power station energy storage
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


