High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
The inverter steps up the voltage using lightweight transformers or inductors, followed by the conversion to AC. Low-Frequency Inverters: Low-frequency inverters use heavy, iron-core
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for
Get Price
ZX7-400D Welding Machine Ring High Frequency
ZX7-400D Welding Machine Ring High Frequency Amorphous Main Transformer 40:5:5 IGBT Single Tube Main Accessories in online-store aliexpress .
Get Price
High Frequency Vs. Low Frequency Inverters... Which is better?
High Frequency Vs. Low Frequency? Which Inverter is better?00:00 - intro00:43 - low frequency inverters02:15 - High Frequency Inverters03:17 - Comparison
Get Price
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency
When selecting an inverter, two key factors to consider are its operating frequency and efficiency. This article will compare high-frequency and low
Get Price
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
When selecting an inverter, two key factors to consider are its operating frequency and efficiency. This article will compare high-frequency and low-frequency inverters, examining their
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
There are two types of power inverters on the market: low frequency inverter and high frequency inverter. No matter the inverter is high or low frequency, there are pros and
Get Price
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Learn the key differences between high frequency inverters and low frequency inverters. Discover which one suits your power needs for efficiency and surge capacity.
Get Price
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
When choosing an inverter, consider your specific application needs: high frequency for efficiency and compactness, low frequency for durability and high power output.
Get Price
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter: How to choose
Discover the disparities between high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter in this concise article, aiding your decision-making process.
Get Price
Amorphous Core High Frequency Main Transformer Applied for Inverter
Amorphous Core High Frequency Main Transformer Applied for Inverter Welding Machine Overview Amorphous alloy is a new type of material with excellent magnetic properties. Due to
Get Price
Low Frequency Inverter, High Frequency Inverter,
So what are the main differences between high-frequency inverters and industrial frequency inverters? 1. Low frequency inverter is superior to
Get Price
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size and weight, etc., and compares
Get Price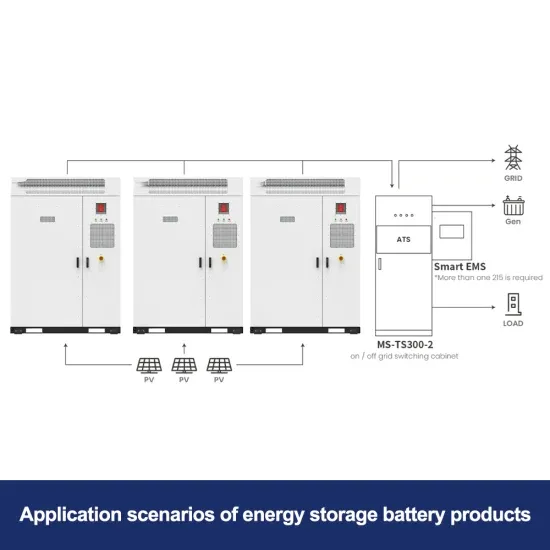
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Conclusion In conclusion, the choice between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters depends largely on the specific needs of the application. High-frequency inverters offer the
Get Price
High-Frequency Transformer Review and Design for
PDF | On Feb 1, 2019, Akrem Mohamed Elrajoubi and others published High-Frequency Transformer Review and Design for Low-Power Solid-State
Get Price
Understanding Low Frequency Power Inverters
Applications and Benefits: Why Use Low Frequency Power Inverters? Low frequency power inverters offer several benefits over their high frequency counterparts, including: – Higher
Get Price
The difference between high frequency inverter and low
High frequency inverters typically operate at frequencies above 20 kHz, while low frequency inverters operate at frequencies below 2 kHz. Another significant difference
Get Price
Vibration and noise characteristics of high-frequency amorphous
The vibration test of silicon steel, amorphous and nanocrystalline magnetic rings shows that the magnetostriction of amorphous materials is much larger than that of silicon
Get Price
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Understanding Line-Frequency (Low-Frequency) Inverters The line-frequency inverter is the traditional, workhorse topology that has been trusted for decades. Its operation
Get Price
Design of a high-frequency transformer based on
The comparison shows that while the low parasitics of the amorphous-based transformer allow for superior frequency response, they are
Get Price
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency
There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical
Get Price
The difference between high frequency inverter and
High frequency inverters typically operate at frequencies above 20 kHz, while low frequency inverters operate at frequencies below 2 kHz.
Get Price
Which is Better Low Frequency or High-frequency
Low frequency inverters are simpler, more robust and easier to control. High frequency inverters enable miniaturization, fast response, efficiency and ultra
Get Price
(PDF) Design of a high‐frequency transformer based on amorphous
The comparison shows that while the low parasitics of the amorphous‐based transformer allow for superior frequency response, they are unsuitable for long‐duration tests
Get Price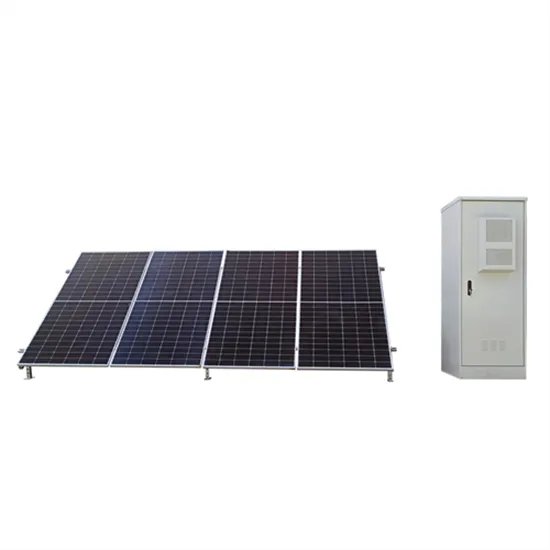
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size
Get Price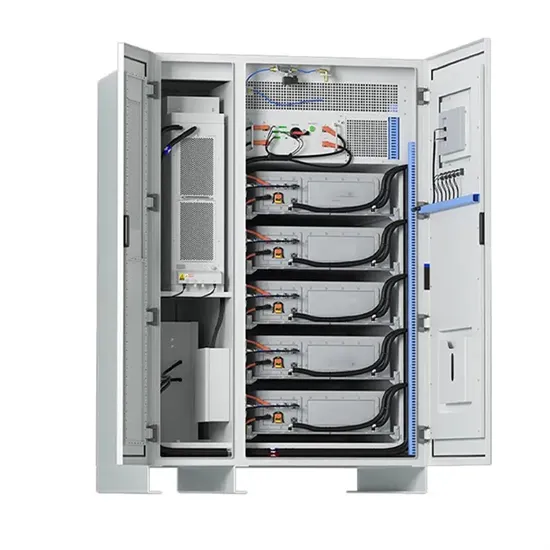
Which is Better Low Frequency or High-frequency Inverter?
Low frequency inverters are simpler, more robust and easier to control. High frequency inverters enable miniaturization, fast response, efficiency and ultra-quiet operation. The choice depends
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
There are two types of power inverters on the market: low frequency inverter and high frequency inverter. No matter the inverter is high
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get Price
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
Understand the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters with this quick article.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Amorphous machine inverter high frequency and low frequency]
What is a low frequency inverter?
Efficiency: Low-frequency inverters are known for their robustness and ability to handle high surge currents, making them suitable for powering heavy-duty appliances or equipment with high starting currents, such as motors and compressors.
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
High-frequency inverters generally have higher efficiency than low-frequency inverters. This is because the higher operating frequency reduces the size of transformers, capacitors, and other components, leading to lower power losses. Low-frequency inverters have lower efficiency due to higher losses in magnetic components and switching devices.
What are high frequency inverters used for?
Motor drives, uninterruptible power supplies, induction heating, avionics, EV charging, renewable energy integration favor high frequency inverters for their compact, lightweight and dynamic characteristics. How does efficiency compare between low frequency and high frequency inverters?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a high frequency inverter?
The main advantages of high-frequency inverters are light weight, small size, low standby power consumption, and high efficiency (relative power saving). The disadvantage is that it is not so impact-resistant (low-frequency inverter) and may not be able to carry electrical appliances such as food mixers and hand drills.
How do I choose a high-frequency or low-frequency inverter?
Choosing between a high-frequency and low-frequency inverter depends on several factors, including efficiency, size, budget, and application needs. Here’s a quick guide: Residential Users: High-frequency inverters are ideal for home use, especially in solar systems, due to their efficiency and compact size.
What are the advantages of a low frequency inverter?
Simplicity, ruggedness, low EMI, and low acoustic noise are some of the advantages of low frequency inverters. They also have higher overload capacity. What semiconductor devices are commonly used in high frequency inverters?
More related information
-
 Convert low frequency inverter to high frequency
Convert low frequency inverter to high frequency
-
 12V inverter high and low frequency
12V inverter high and low frequency
-
 Price of high frequency inverter front stage
Price of high frequency inverter front stage
-
 Is high frequency or medium frequency inverter better
Is high frequency or medium frequency inverter better
-
 Brunei high frequency inverter equipment manufacturer
Brunei high frequency inverter equipment manufacturer
-
 Bahamas high frequency inverter installation
Bahamas high frequency inverter installation
-
 Greek high frequency inverter
Greek high frequency inverter
-
 Inverter recommendation low power with high cost performance
Inverter recommendation low power with high cost performance
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


