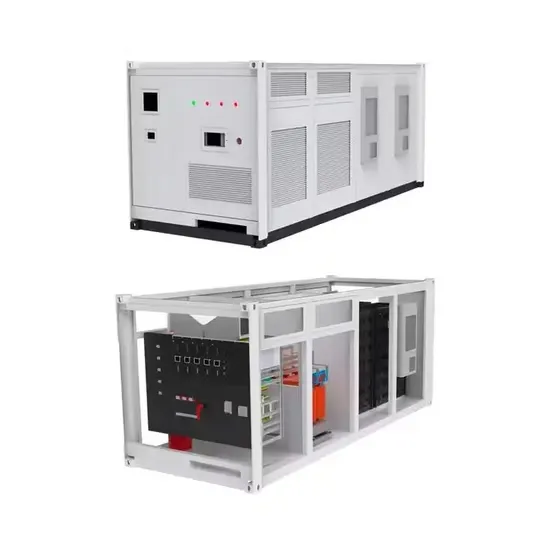
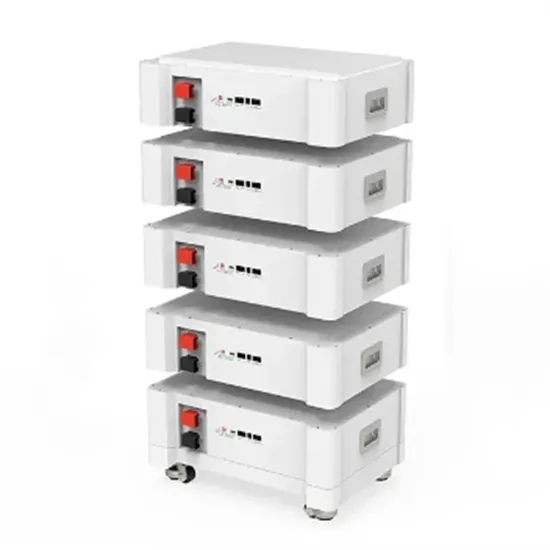
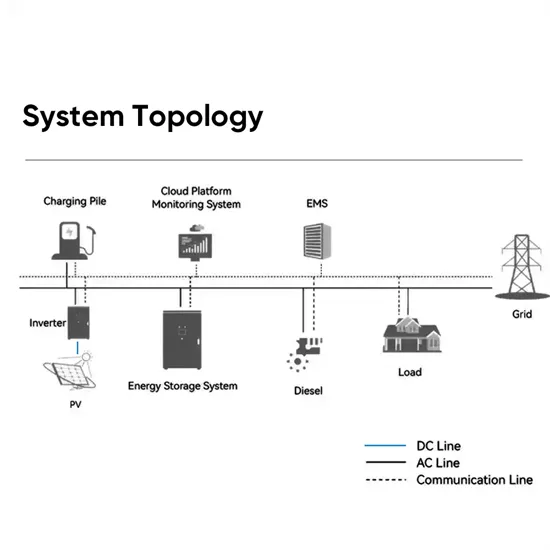
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Learn the key differences between high frequency inverters and low frequency inverters. Discover which one suits your power needs for efficiency and surge capacity.
Get Price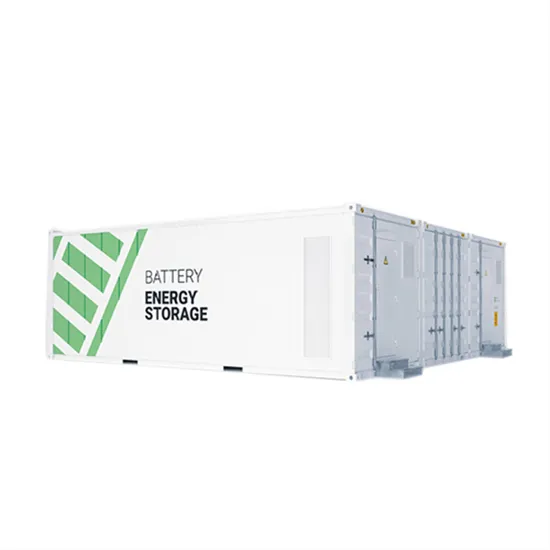
What is a High-Frequency Power Inverter?
Introduction A power inverter converts DC power into AC power for operating AC loads and equipment. High-frequency power inverters utilize high-speed switching at frequencies
Get Price
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Understanding Line-Frequency (Low-Frequency) Inverters The line-frequency inverter is the traditional, workhorse topology that has been trusted for decades. Its operation
Get Price
Technical comparison between Low Frequency Inverter VS high
Low-frequency inverters have the advantage over high-frequency inverters in two fields: peak power capacity, and reliability. Low-frequency inverters are designed to deal with higher power
Get Price
The difference between frequency converter and
The inverter is mainly composed of rectification (AC to DC), filter, inverter (DC to AC), braking unit, and so on. Frequency converters contain
Get Price
Comparing High Frequency UPS and Low Frequency UPS | Mingch
Low-Frequency Inverters vs. High-Frequency Inverters A low-frequency inverter relies on transformer-based conversion, using a heavy-duty transformer to convert DC power
Get Price
What''s the difference between a high frequency and Low frequency inverter?
The IGBT high frequency rectifier, which is used in the high frequency inverter, has a high switching rate. However, it has a tight voltage and current area during operation and has low
Get Price
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size and weight, etc., and compares
Get Price
How does a high
Now, the main difference between high - frequency and low - frequency inverters lies in how they handle the conversion process, and this difference has a bunch of implications
Get Price
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
The primary distinctions between low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters lie in their operating frequencies, design structures, and performance characteristics
Get Price
Amazon : Frequency Inverter
SUNGOLDPOWER 4000W 12V Pure Sine Wave Power Inverter DC 12V Input to AC 120V Output Converter, Low Frequency Inverter Charger for Home, RV, Truck, Off-Grid Solar Wind Power
Get Price
The difference between low frequency inverter and
It first through the high frequency DC/DC transformation technology, the low voltage DC through the high frequency transformer boost,
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
With the new technologies implemented on power inverters, a low frequency inverter can now match or even outpace high frequency in idle consumption and max THD.
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for
Get Price
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter:
Discover the disparities between high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter in this concise article, aiding your decision-making process.
Get Price
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size
Get Price
How Does a Frequency Inverter Work?
Frequency inverters can be used in home appliances. Among the home appliances that use a frequency inverter are not only motors (e.g., air
Get Price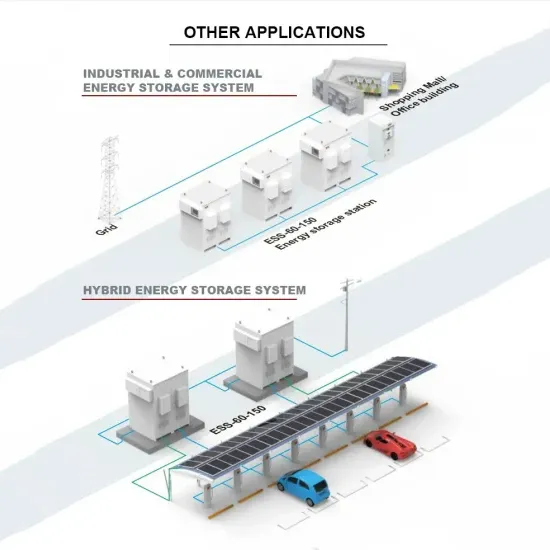
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High Frequency
In this article, we will examine the differences between low frequency or high frequency inverter. Both inverters have unique features and advantages and disadvantages,
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
With the new technologies implemented on power inverters, a low frequency inverter can now match or even outpace high frequency in idle
Get Price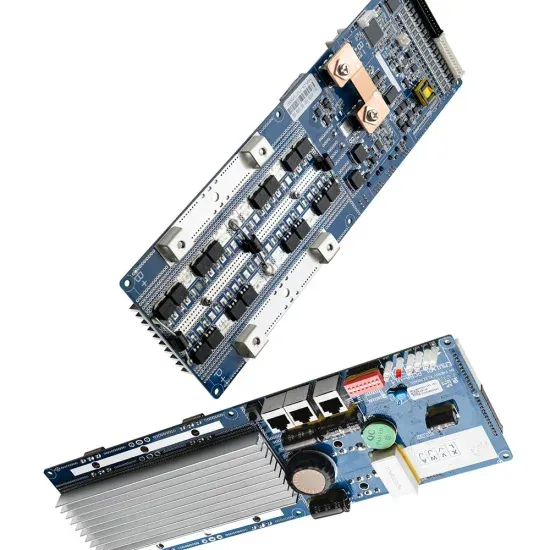
Inverters High or Low Frequency
Higher end inverters convert battery voltage to some low voltage AC. In Victron it is 8 VAC, then use a transformer to convert this to 120 VAC. The transformer is safer than direct
Get Price
Everything to Know Low Frequency Inverters
Low-frequency inverters, characterized by their use of transformers for electrical isolation, play a crucial role in a variety of high-reliability applications. This
Get Price
What is a frequency inverter?
A frequency inverter changes output voltage frequency and magnitude to vary the speed, power, and torque of a connected induction motor to meet load conditions. A typical frequency
Get Price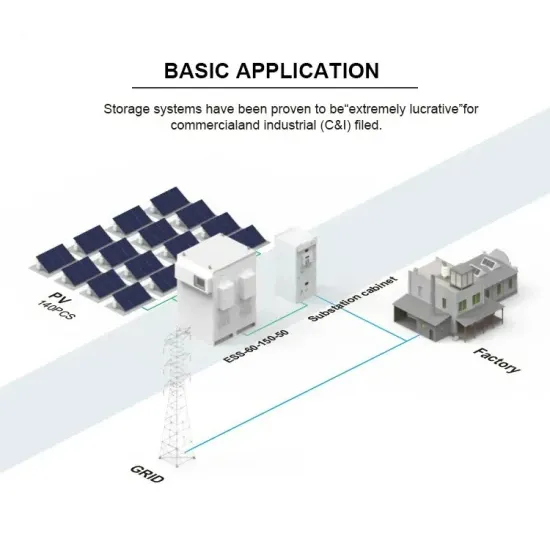
High Frequency vs. Low Frequency Inverter
A lot of the most popular AIO inverters are High Frequency Transformerless. How important is it to use the correct family of transformer (high vs. low freq) for to power devices
Get Price
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
Understand the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters with this quick article.
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get Price
Technical comparison between Low Frequency
Low-frequency inverters have the advantage over high-frequency inverters in two fields: peak power capacity, and reliability. Low-frequency inverters are
Get Price
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency
Inverters are components used to control speed or torque control for an electric motor. Inverters take AC mains and rectify it into DC. They are
Get Price
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter: How to choose
Discover the disparities between high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter in this concise article, aiding your decision-making process.
Get Price
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Convert low frequency inverter to high frequency]
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
Here is the major difference of them: Thanks to the heavy-duty transformer, low frequency inverters have much higher peak power capacity and reliability. The transformer handles higher power spikes with longer duration than high-frequency inverters when it comes to driving inductive loads such as electric motor, pump, compressor, air conditioners.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Low-frequency inverters are also best suited for those who want to power various kitchen appliances such as refrigerators, microwaves, dishwashers and ovens. Enhanced peak performance capacity and improved reliability of low frequency inverters mean that they cost more than high frequency inverters.
How do I choose a low frequency or high frequency inverter?
When deciding between a low frequency or high frequency inverter, it is important to consider the power requirements of the appliances and devices that you wish to power. Heavy-duty items, such as air conditioners and refrigerators, may require a low frequency inverter with high surge capacity.
How do high frequency power inverters convert DC to AC?
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz. Low frequency inverter circuit diagram
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
Why are high frequency inverters more efficient?
In contrast, high-frequency inverters can use smaller-sized and lighter-weight components due to their use of higher frequencies, resulting in smaller overall size and weight. Efficiency: Since the high frequency inverter uses high-frequency switches for inversion, its switching loss is relatively small, so it has higher conversion efficiency.
More related information
-
 Amorphous machine inverter high frequency and low frequency
Amorphous machine inverter high frequency and low frequency
-
 12V inverter high and low frequency
12V inverter high and low frequency
-
 Eritrea high frequency inverter
Eritrea high frequency inverter
-
 Cyprus high frequency inverter manufacturer
Cyprus high frequency inverter manufacturer
-
 Bahamas high frequency inverter installation
Bahamas high frequency inverter installation
-
 Austria high frequency power inverter
Austria high frequency power inverter
-
 Simple high frequency inverter design
Simple high frequency inverter design
-
 Number of turns of high frequency inverter
Number of turns of high frequency inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.