FREQUENCY INVERTERS AND EVERYTHING
A frequency inverter is a device for regulating the speed of electric motors. Changes in speed are made by a simultaneous change of frequency and
Get Price
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
Understand the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters with this quick article.
Get Price
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in Modern Applications
In the world of electrical engineering and power electronics, high-frequency inverters play a crucial role in various applications, offering a wide array of advantages and benefits compared to
Get Price
High Frequency vs. Low Frequency Solar Inverters
Low-frequency inverters will take the low voltage current from the panels, and even when the sun is intense, and there are spikes in the system,
Get Price
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get Price
Common-Mode Voltage in Inverters: Effects and Reduction Methods
They use inverters to control the amplitude and frequency of the output waveform. Inverters convert DC power to AC power of a specified magnitude and frequency. The number
Get Price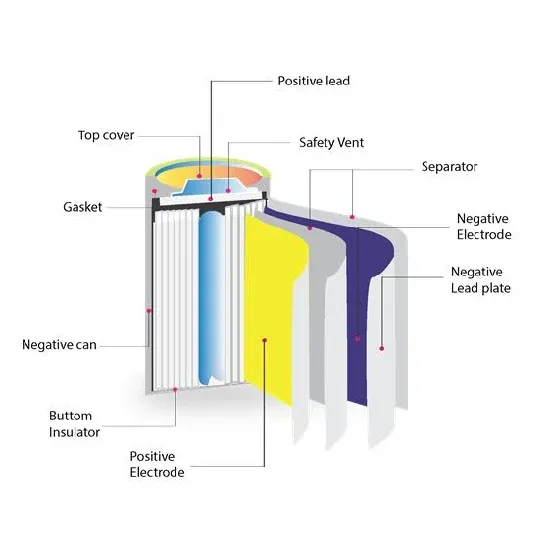
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get Price
A High-Frequency Link Single-Stage PWM Inverter With Common
This paper presents a single-stage bidirectional high-frequency transformer (HFT) link dc/ac converter topology for a three-phase adjustable magnitude and frequency PWM ac
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency Inverter: Which is
Among them, power frequency inverter and high frequency inverter are two common inverter types, each with different characteristics and application scenarios. So,
Get Price
Four-Leg Inverter Analysis for Minimizing the Common-Mode
I. INTRODUCTION In a typical three-phase power inverter drives, there exists substantial common-mode voltage between the load neutral and earth ground. PWM inverters generate
Get Price
Differential mode noise modelling and analysis
This paper proposes the prediction method of differential mode noise transmitted to the input power of a single-phase inverter in a high
Get Price
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Line-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters: A Technical Deep Dive for Engineers In the world of power electronics, the inverter is a cornerstone technology, responsible for the
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency Inverters and High
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power efficiency, space saving, or suitability
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High Frequency
There are two types of inverters, low frequency and high frequency inverters. Inverters are used in solar power systems, wind turbines, and electric vehicles. In this article,
Get Price
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
The term "high-frequency" refers to the rate at which inverter switching occurs, a fundamental characteristic of its design. It differs from low
Get Price
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
The primary distinctions between low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters lie in their operating frequencies, design structures, and performance characteristics
Get Price
Design and Implementation of A Hybrid Output EMI Filter for
Therefore, unlike the case of passive output filter, the PWM inverter is free from any limitations concerning usable switching frequency range and injection of zero voltage by space vector
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
High-frequency inverters and power-frequency inverters are the two common types of inverters. Each has its own different characteristics and applications, so which one is
Get Price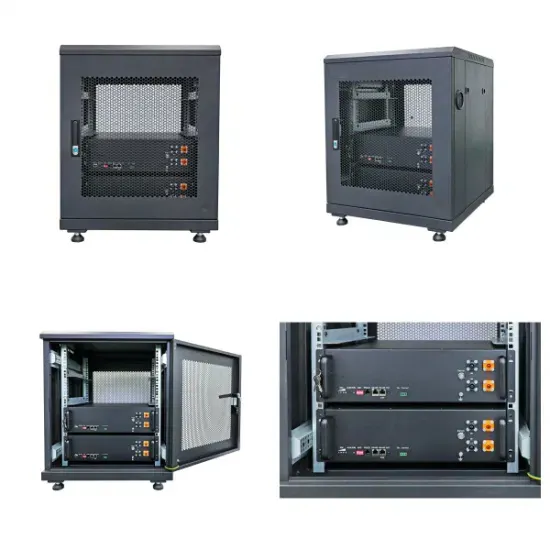
Frequency vs High-Frequency Inverters: The Best Choice for Off
Discover why frequency inverters excel in off-grid use with superior shock resistance, stable inductive load performance, and long lifespan. Make smarter choices for reliable power.
Get Price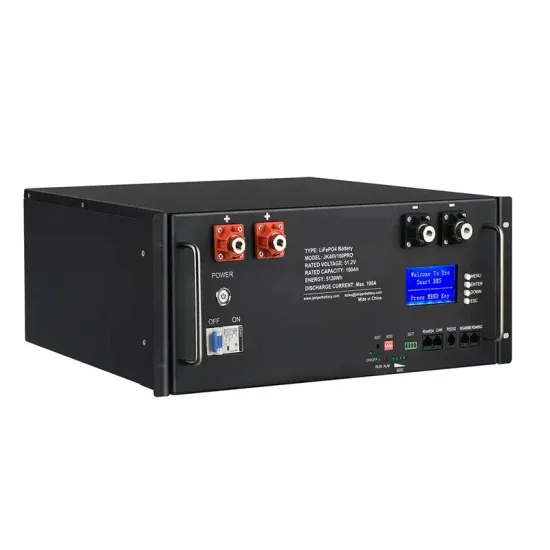
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
The term "high-frequency" refers to the rate at which inverter switching occurs, a fundamental characteristic of its design. It differs from low-frequency inverters, which operate at lower
Get Price
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power
Get Price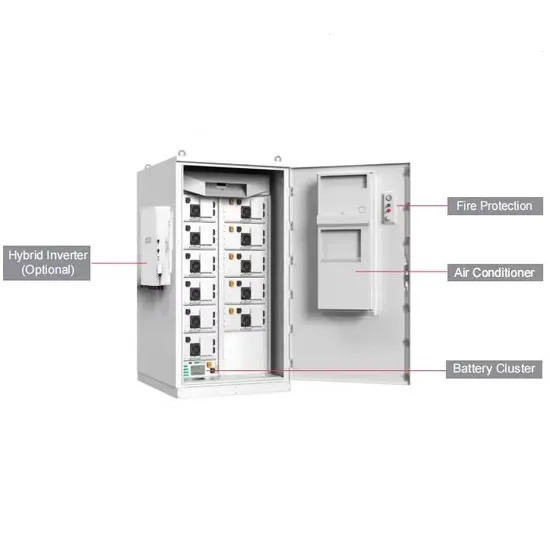
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
There are two types of power inverters on the market: low frequency inverter and high frequency inverter. No matter the inverter is high or low frequency, there are pros and
Get Price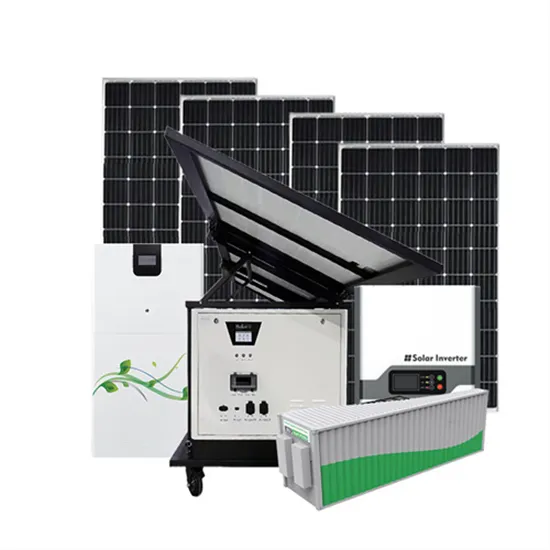
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for
Get Price
Impact of Multiple Grid-Connected Solar PV Inverters
This paper evaluates the behaviour of high-frequency harmonics in the 2–20 kHz range due to the parallel operation of multiple solar PV
Get Price
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
Among them, power frequency inverter and high frequency inverter are two common inverter types, each with different characteristics and
Get Price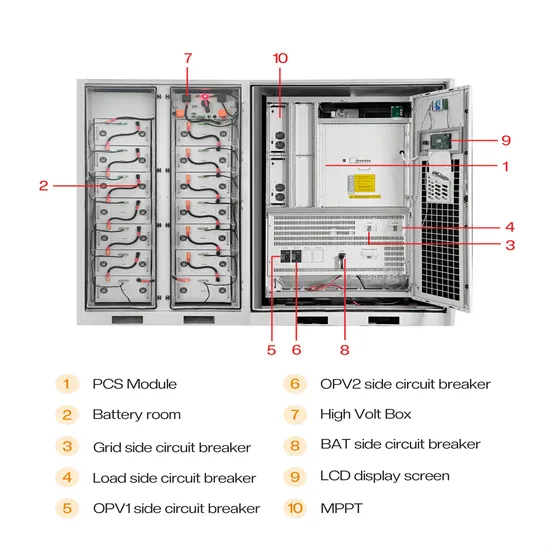
Design and Simulation of High Frequency Inverter for PV
A high frequency link photovoltaic (PV) power conditioning system which includes a high frequency resonant inverter, a rectifier, and a line commutated inverter, operating near unity
Get Price
Demystifying High Frequency vs Low Frequency
The main difference between High-frequency and Transformer-based Low-Frequency Inverters/UPS is the frequency at which they operate.
Get Price
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
There are two types of power inverters on the market: low frequency inverter and high frequency inverter. No matter the inverter is high
Get Price
Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions and
The frequency inverter is a power control equipment that applies frequency conversion technology and microelectronics technology to control
Get Price
More related information
-
 Silicon Carbide High Frequency Inverter
Silicon Carbide High Frequency Inverter
-
 Somaliland high frequency inverter structure
Somaliland high frequency inverter structure
-
 Austria high frequency power inverter
Austria high frequency power inverter
-
 High frequency inverter is also a sine wave
High frequency inverter is also a sine wave
-
 Mali high frequency inverter
Mali high frequency inverter
-
 What is the price of high frequency inverter
What is the price of high frequency inverter
-
 High frequency inverter to 24v
High frequency inverter to 24v
-
 High frequency inverter to low frequency output
High frequency inverter to low frequency output
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

