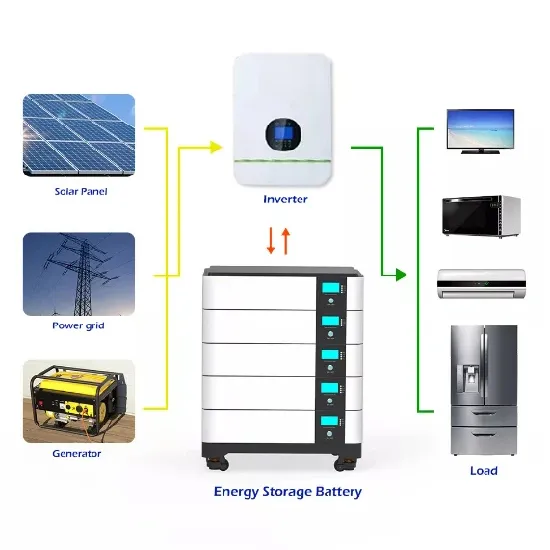
DoD SPECTRUM MANAGEMENT: A CRITICAL ANALYSIS
To establish a frequency management structure that includes a JFMO and to establish procedures to support planned and ongoing operations. The supported CCDR authorizes and
Get Price
Chapter 5 EMS Communications Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like base station, biotelemetry, cellular telephones and more.
Get Price
Communications System Technical Planning Guide
The resultant document is intended to be a simple, practical technical planning guide for Emergency Medical Service (EMS) communications.
Get Price
Communications Engineering Services
Med-Channel communications is received at EMRC via one of 24 base station sites or through interfaces with local jurisdiction''s 800 MHz systems. EMRC is the central location for
Get Price
Communications-EMT — Hopper Institute®
Communication in EMS is essential. Patients must be able to access the system, the system must be able to dispatch units, EMTs must have a means of communicating with medical direction
Get Price
Guide for the Selection of Communication Equipment for
Common radio messages are transmitted over the RF band between 0.05 MHz and 900 MHz. Most public safety communications radios (portable, mobile, base station, and repeaters)
Get Price
C8: Communications [5/5/03]
Other than a means of voice communication, base station contact over the UHF radio or cellular phone line provides a two fold purpose: It gives ALS personnel the capability of transmitting an
Get Price
Chapter 4 Communication and Documentation
allocating specific radio frequencies for use by EMS providers, licensing base stations and assigning appropriate radio call signs for those stations, establishing licensing standards and
Get Price
EMT: Communication and Documentation Flashcards | Quizlet
A special base station radio that receives messages and signals on one frequency and then automatically retransmits them on a second frequency.
Get Price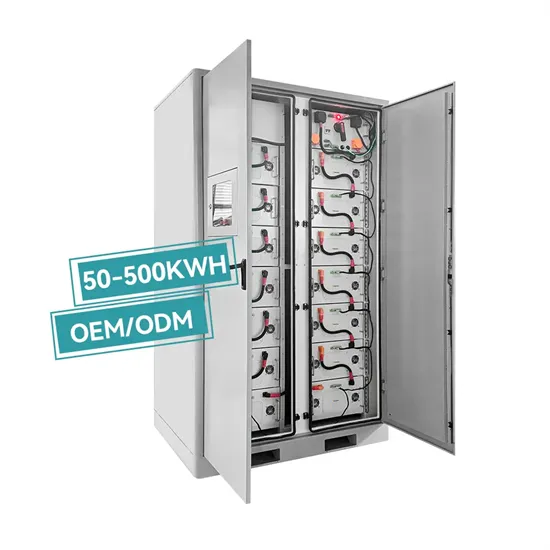
Microsoft Word
Beyond the immediate communication and coordination of EMS services, it is essential for an ECC to align with the interoperable communications technologies deployed by
Get Price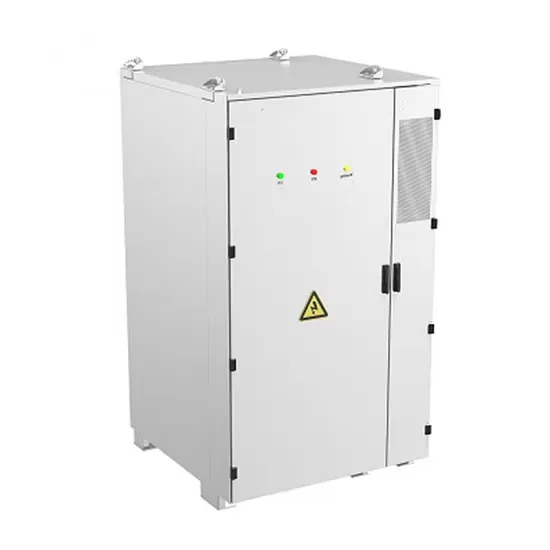
C8: Communications [5/5/03]
"The use of cellular telephones is permitted provided that the ambulance also has VHF or UHF radio back-up on a frequency assigned by IDPH; and permission of the EMS Resource
Get Price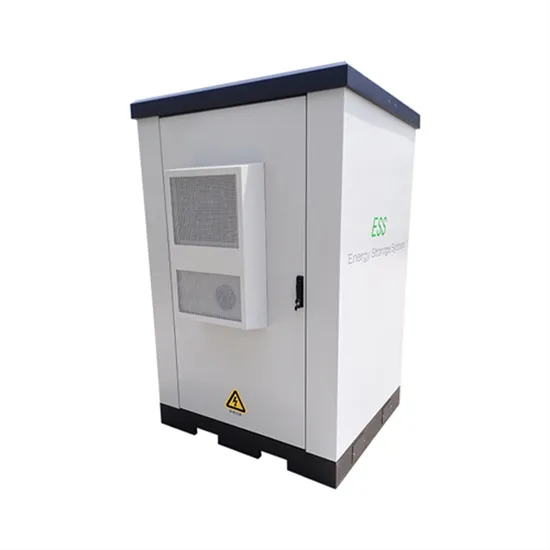
EMT Chapter 4: Communication Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Base Station, Cellular Telephone, Channel and more.
Get Price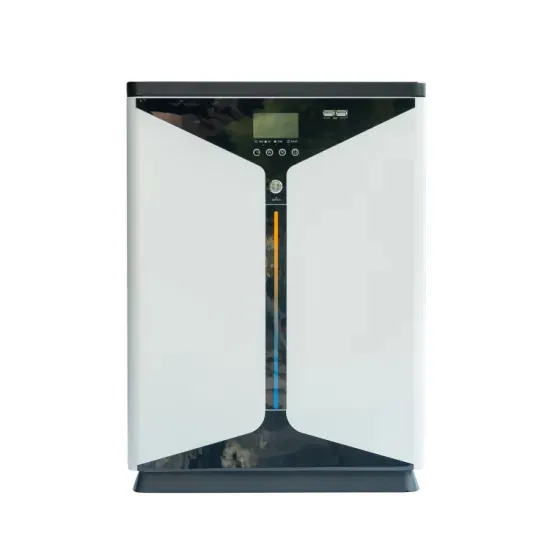
Effective Communication in EMS Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
Effective communication is a crucial aspect of Emergency Medical Services (EMS), ensuring the accurate and timely relay of information. This guide synthesizes multiple perspectives on
Get Price
EMSCOM
Provide a base station communications back-up for dispatching, direct phone line patching and coordinating EMS information in cases where local base station control fails or is not available.
Get Price
Boston_EMS_Policies_and_Procedures.pdf
Basic components of a communications system generally include (1) portable and mobile transceivers; (2) base stations; and (3) central and remote control consoles. Special Features
Get Price
Chapter 5 (Worksheet) EMT Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Dispatch, Base Station, Radio Medical Report and more.
Get Price
Boston_EMS_Policies_and_Procedures.pdf
Point-to-Point communications for coordination of critical transfers, mutual assistance and mass casualty incident management will normally be conducted on VHF radio frequency 155.280 MHz.
Get Price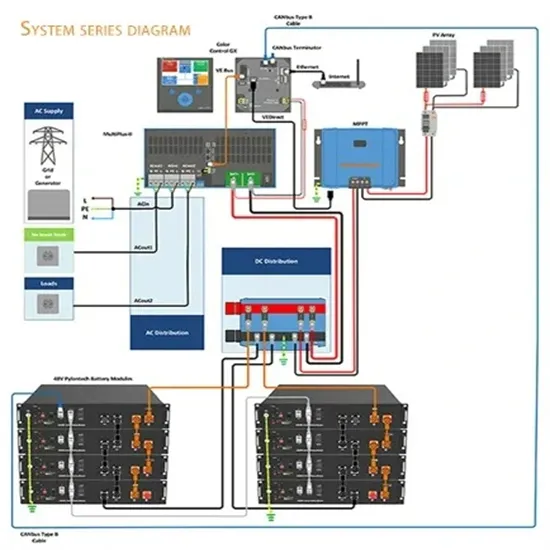
EMS Chapter 4
A special base station radio that receives messages and signals on one frequency and then automatically retransmits them on a second frequency.
Get Price
E74
Effective verbal communication is a daily challenge for EMS providers. Therapeutic communication requires etiquette and special understanding when providing care to a variety
Get Price
Wisconsin Emergency Medical Services Communication Plan
Concerning EMS communications specifically, the concept of back-up communications as applied to base station or other fixed radio equipment means they must provide the following capabilities:
Get Price
Chapter 5 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The initial communication EMTs receive about an emergency call comes from a. the hospital b. the
Get Price
CHP 15 post test Flashcards | Quizlet
The FCC licenses individual base station operations, assigns radio call signs, approves equipment for use, establishes limitations for transmitter power output, assigns radio
Get Price
CHAPTER 4 Communications and Documentation
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A special base station radio that receives messages and signals on one frequency and then automatically retransmits them on
Get Price
Statewide EMS Operations & Communications Resource
This Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Operations and Communications Resource Manual has been developed by the State of California Emergency Medical Services
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Communication Base Station EMS and Frequency Management]
Why is communication important in EMS?
Communication in EMS is essential. Patients must be able to access the system, the system must be able to dispatch units, EMTs must have a means of communicating with medical direction and receiving facility, and EMTs must be able to communicate vital information to other personnel.
How do I select a EMS base station Radio?
To select a channel on an EMS base station radio, you should set the channel selector on the local primary channel as used in your area. The channel select button must be depressed in order to transmit on the selected frequency.
What frequency does EMS radio communication take place in?
EMS radio communication takes place in the VHF low band, VHF high band, and UHF band. VHF low band is the radio frequencies from 32-50 megahertz (MHz). They are able to follow the shape of the earth allowing communication over long distances. These frequencies are more susceptible to interference from, weather, buildings, and electrical equipment.
What CTCSS tone do EMS med radios use?
For this reason, all New Mexico EMSCOM UHF radios on the EMS MED channels should be using CTCSS tone 136.5. Types of Stations: A base station transmits directly to mobiles and portables. If the base station is at some distance away from the operator, it is known as a remote base station.
What is the purpose of the EMSCOM manual for?
This manual is provided for the use of all services that may have occasion to use the New Mexico Emergency Medical Services Communications (EMSCOM) System. The intended purpose of the manual is to provide a basic understanding of the capabilities and proper utilization of the State EMSCOM system. Maintenance policies are also included.
What are the main functions of the EMSCOM system?
The EMSCOM system's main functions are to provide communications between ambulance/rescue and hospital emergency rooms to allow notification of incoming injured patients to health care facilities.
More related information
-
 Latvian communication base station EMS equipment
Latvian communication base station EMS equipment
-
 5G communication base station energy management construction in Swaziland
5G communication base station energy management construction in Swaziland
-
 Hungarian communication base station EMS battery
Hungarian communication base station EMS battery
-
 Is the communication base station EMS a device
Is the communication base station EMS a device
-
 Communication base station EMS foreign countries
Communication base station EMS foreign countries
-
 Communication base station wind and solar hybrid BMS management system
Communication base station wind and solar hybrid BMS management system
-
 How many communication base station EMS companies are there in the world
How many communication base station EMS companies are there in the world
-
 Floor communication base station EMS construction
Floor communication base station EMS construction
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


