Regulating Voltage: Recommendations for Smart Inverters
This report from GridLab provides an introduction to voltage regulation concepts, including advantages and disadvantages of various control modes. The authors include
Get Price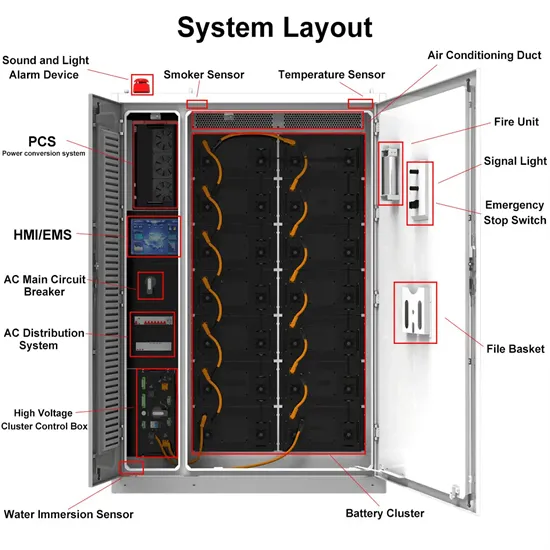
What is an Inverter and How does it work | Roboticmagazine
An inverter changes the DC current direction, to match the sinusoidal waveform and frequency (as in 50 Hz) of an AC current. In one sentence, how does an inverter work?
Get Price
4. Configuration
4.1. AC output voltage and frequency 4.2. ECO mode and ECO settings 4.3. Low battery alarm and charge detect settings 4.4. Battery settings 4.5. VE.Smart Networking 4.6. Firmware
Get Price
When a motor speed is controlled by an inverter/VFD, and it is
When a motor speed is controlled by an inverter/VFD, and it is always running at 15 hz, should the motor be wired for low voltage? I''ve been working at a food service facility for the past 2 years
Get Price
How does an inverter help stabilize voltage fluctuations?
Frequency Regulation: In some cases, inverters can participate in frequency regulation, helping to maintain grid frequency stability, which indirectly affects
Get Price
How does an inverter work?
At this time, the inverter circuit changes only the frequency, so it is called "CVVF (Constant Voltage Variable Frequency)". Last but not least, the inverter circuit
Get Price
Inverter Frequency Vs Voltage Control: Which One Drives Better
Meanwhile, inverters with frequency control (often called VFDs or Variable Frequency Drives) can regulate the AC output regarding voltage and frequency, providing more detailed control over
Get Price
Droop control strategy in inverter-based microgrids: A
To solve the disadvantages of conventional droop control, changes have been proposed using different methods such as virtual impedance loop
Get Price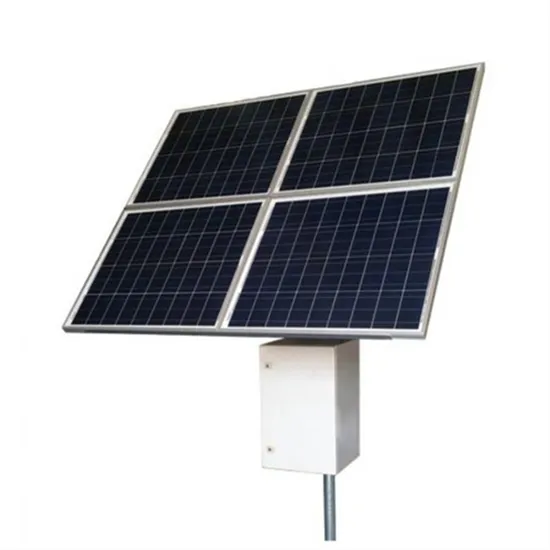
Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study
Droop-Based GFMI: Mimics the droop characteristics of synchronous generators by adjusting frequency and voltage in response to
Get Price
The difference between frequency converter and
What is a frequency converter? Introduction to frequency converter: mainly to change the frequency. The inverter is mainly composed of
Get Price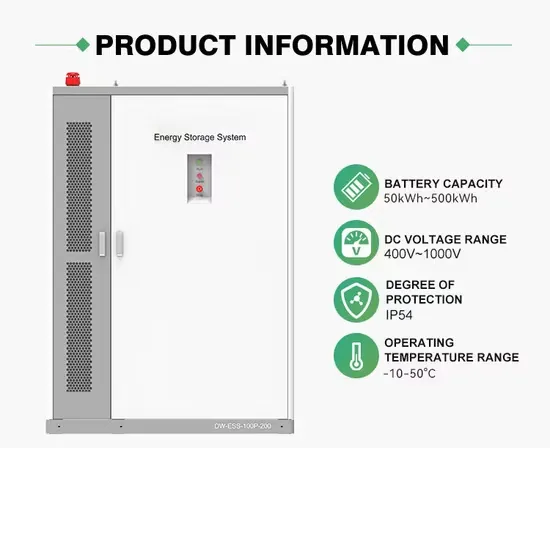
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of inverter frequency, exploring its significance, factors affecting it, and its practical implications.
Get Price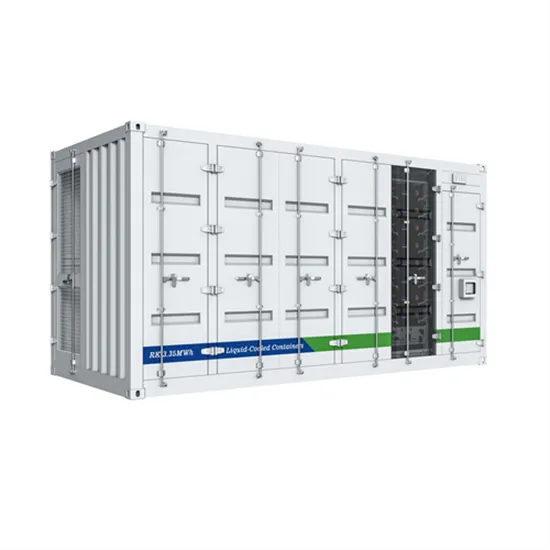
How Does a Frequency Inverter Work? | inverter
Frequency inverters used for motor control can change both voltage and frequency. The operating principle of inverters is used in a wide
Get Price
Load Control for Frequency Response
To simplify the relationship between frequency and load, note that a sudden increase in load will decrease the system frequency, and a sudden decrease in load will increase the frequency.
Get Price
FREQUENCY INVERTERS AND EVERYTHING
A frequency inverter is a device for regulating the speed of electric motors. Changes in speed are made by a simultaneous change of frequency and
Get Price
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters:
It has already been mentioned that Inverter Control providing a variable frequency supply to three phase motors should be capable of providing a variable
Get Price
Why Choose a Frequency Inverter? | inverter
The inverter adjusts the voltage and frequency of the output power supply by switching off the internal IGBT, and provides the required power supply voltage according to the actual needs
Get Price
Three Phase Inverter | Methods of Voltage Control of
The dc voltage to the inverter is normally obtained by rectifying a 50 Hz supply using a bridge rectifier. The rectifier and inverter are interconnected by means
Get Price
Understanding the Function of an Inverter
Our PWM inverters switch at a frequency of 8 kHz and can regulate the output at any point in the sine wave. Ferroresonant inverters use a modified square wave that is
Get Price
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters:
It has already been mentioned that Inverter Control providing a variable frequency supply to three phase motors should be capable of providing a variable voltage. This is required to avoid
Get Price
How does an inverter work?
At this time, the inverter circuit changes only the frequency, so it is called "CVVF (Constant Voltage Variable Frequency)". Last but not least, the inverter circuit also works in computer
Get Price
Overview of frequency control techniques in power
Power systems are rapidly transitioning towards having an increasing proportion of electricity from inverter-based resources (IBR) such
Get Price
FREQUENCY INVERTERS AND EVERYTHING ABOUT THEM
A frequency inverter is a device for regulating the speed of electric motors. Changes in speed are made by a simultaneous change of frequency and voltage, or, after reaching nominal voltage
Get Price
Understanding Frequency Inverters: A Comprehensive Guide
A frequency inverter, also known as a variable frequency drive (VFD), is an essential device used to control the speed and torque of electric motors by adjusting the input
Get Price
Does frequency shift regulation depend on the nominal inverter
Only voltage and amps will change the output powers (and also power factor) and as these are not changed when the frequency changes from 50 to 51.9 etc there is no power output change
Get Price
Advanced Inverters: (1547) Capabilities, Experiences, and
1547-2018 Active Voltage Regulation Capabilities "The DER shall provide voltage regulation capability by changes of reactive power. The approval of the Area EPS Operator shall be
Get Price
REGULATING VOLTAGE: RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
neration on distribution circuits has a voltage impact. Generation will typically raise the voltage of the circuit as it generates, with more voltage i pact from larger generators or many smaller
Get Price
How does an inverter help stabilize voltage fluctuations?
Frequency Regulation: In some cases, inverters can participate in frequency regulation, helping to maintain grid frequency stability, which indirectly affects voltage stability.
Get Price
Grid-Forming vs. Grid-Following Inverter Integration
5. Analyze frequency regulation and voltage control performance. Observe how each inverter type responds to disturbances; grid-forming inverters can help
Get Price
How Does a Frequency Inverter Work? | inverter
Frequency inverters used for motor control can change both voltage and frequency. The operating principle of inverters is used in a wide variety of fields. For example,
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Does the inverter frequency regulation voltage change ]
What is a frequency inverter used for?
Frequency inverters used for motor control can change both voltage and frequency. The operating principle of inverters is used in a wide variety of fields. For example, the power supply for computer power supplies, in which the frequency inverter is used to suppress fluctuations in reverse voltage, frequency, and momentary power outages.
What factors affect inverter frequency?
Several factors influence the inverter frequency, including the design of the power electronics, the configuration of the control circuitry, and the specifications of the utility grid. In grid-tied inverters, for instance, the inverter frequency is typically synchronized with the utility grid to ensure compatibility and seamless energy transfer.
How does a power inverter work?
On input, the inverter is powered by alternating voltage (single-phase or three-phase), the voltage in the internal circuits is regulated, and on output it is converted by a power inverter to three-phase alternating voltage at the required frequency. Depending on the type of input voltage, inverters can be classified as follows:
How does setting parameters affect the output performance of a frequency inverter?
The setting of parameters directly affects the output performance of the inverter. Input Power: The frequency inverter receives AC power through the input rectifier and converts it to DC power. The intermediate DC link smoothes the DC power to ensure the stability of the power supply.
Can a frequency inverter be used in home appliances?
Frequency inverters can be used in home appliances. Among the home appliances that use a frequency inverter are not only motors (e.g., air conditioners, etc.) but also products such as fluorescent lamps. Frequency inverters used for motor control can change both voltage and frequency.
Can inverter frequency be adjusted or programmed?
Additionally, the inverter frequency can be adjusted or programmed in certain types of inverters, allowing for versatility in different applications. However, the inherent design limitations and operating parameters of the inverter may impose constraints on the achievable inverter frequency range. 3.
More related information
-
 Single-phase inverter voltage and frequency regulation
Single-phase inverter voltage and frequency regulation
-
 The inverter high frequency voltage becomes 50hz
The inverter high frequency voltage becomes 50hz
-
 Three-phase constant voltage variable frequency inverter
Three-phase constant voltage variable frequency inverter
-
 Huawei inverter voltage change
Huawei inverter voltage change
-
 What is the voltage of a 96V household power frequency inverter
What is the voltage of a 96V household power frequency inverter
-
 Energy storage power station frequency and voltage regulation
Energy storage power station frequency and voltage regulation
-
 Medium frequency inverter output voltage
Medium frequency inverter output voltage
-
 Inverter wide voltage regulation
Inverter wide voltage regulation
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
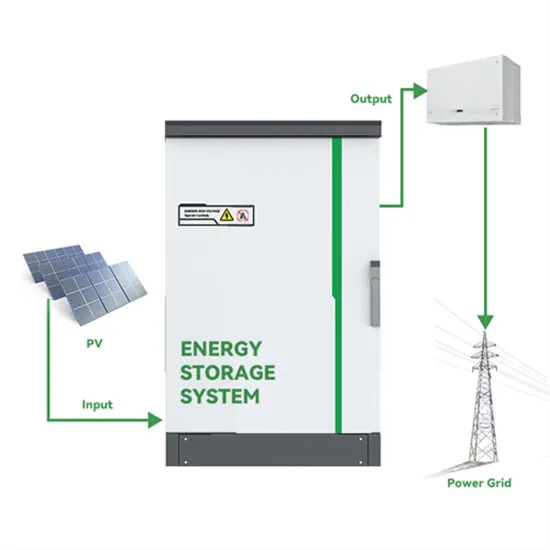
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


