What is the inverter voltage of the energy storage
What is the inverter voltage of the energy storage system? The inverter voltage of an energy storage system refers to the electrical potential
Get Price
Understanding inverter voltage
The start inverter voltage is the minimum input voltage required for the inverter to initiate the conversion process. In the case of a 12V inverter, the start inverter voltage is
Get Price
Understanding DC/AC Ratio – HelioScope
Clipping Losses and DC/AC Ratio When the DC/AC ratio of a solar system is too high, the likelihood of the PV array producing more power than the inverter
Get Price
AC to DC & DC to AC Calculator
AC to DC Converter Calculator Enter AC voltage to convert it into DC voltage and vice versa by using this online AC to DC calculator.
Get Price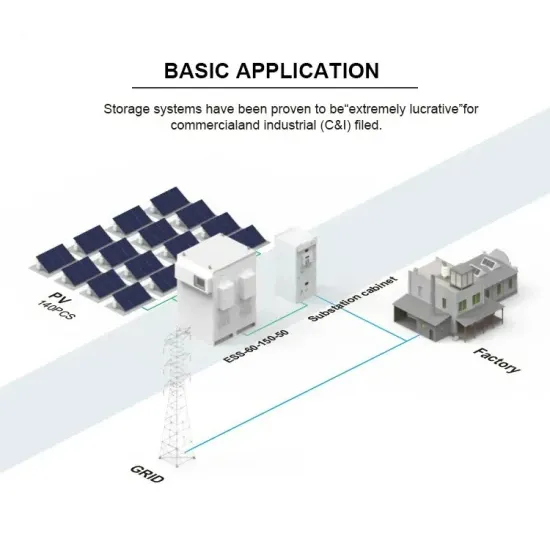
Explanation of Inverter DC Capacitance and Inrush Current
Explanation of Inverter DC Capacitance and Inrush Current What is Inverter DC Capacitance? All modern power inverters have a large capacitor bank at their DC input terminals to help provide
Get Price
Introduction to Inverters
What is an Inverter? An inverter is a device that is used to convert Direct current to Alternating Current. However the output is not a sine wave. It can be square wave, quasi
Get Price
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings
Rated voltage refers to the nominal voltage that the inverter is engineered to work with. For grid-tied systems, this is typically 220V or 230V in most countries.
Get Price
What is Inverter? – Meaning, Types and Application
The DC power input to the inverter is obtained from an existing power supply source or from a rotating alternator through a rectifier or a
Get Price
AKX00057-1
1. Inverters An inverter is a semiconductor-based power converter. An inverter that converts a direct current into an alternating current is called a DC-AC inverter. However, the
Get Price
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters: Types,
Unlock the potential of power supply with our comprehensive guide on all about inverters - discover types, benefits, and tips for the perfect
Get Price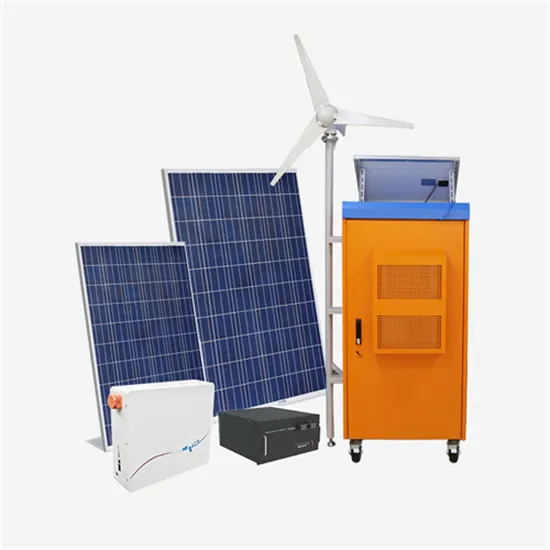
Power inverter
OverviewInput and outputBatteriesApplicationsCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
A typical power inverter device or circuit requires a stable DC power source capable of supplying enough current for the intended power demands of the system. The input voltage depends on the design and purpose of the inverter. Examples include: • 12 V DC, for smaller consumer and commercial inverters that typically run fro
Get Price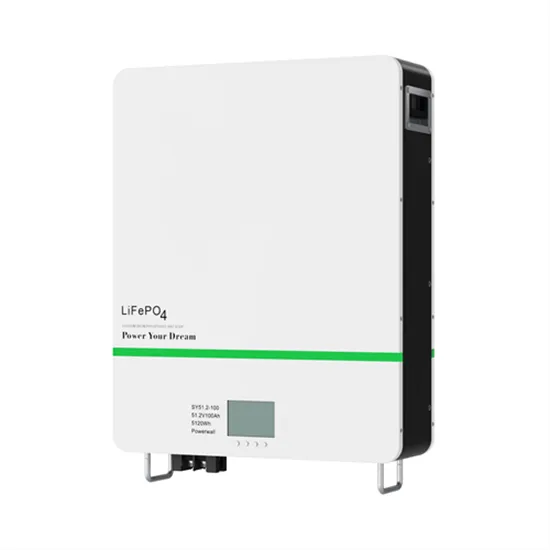
CHAPTER 2
generator. The filter capacitor across the input terminals of the inverter provides a constant dc link voltage. The inverter therefore is an adjustable-frequency voltage source. The configuration of
Get Price
Three Phase Bridge Inverter Explained
A careful observation of the above circuit diagram reveals that power circuit of a three phase bridge inverter is equivalent to three half bridge
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power calculations and inverter
Get Price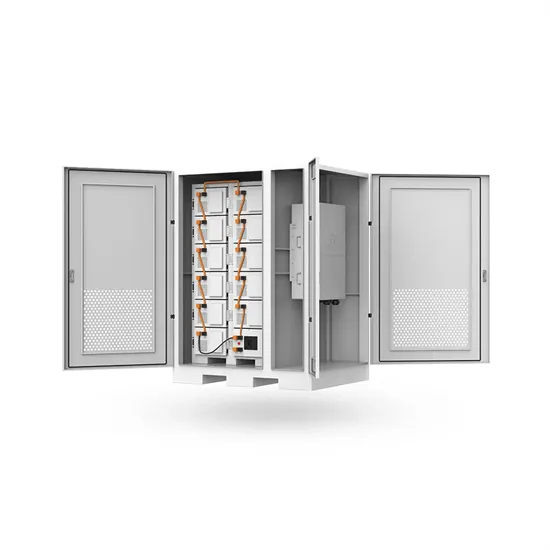
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
Get Price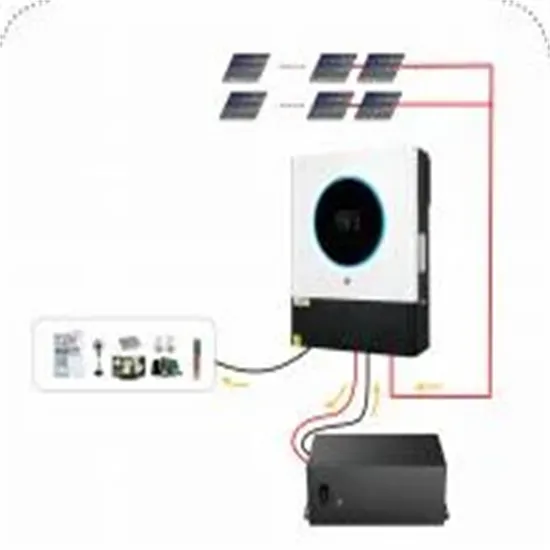
Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition, Functions,
What is the Inverter Voltage? Inverter voltage is a voltage generated by the inverter after several electrons that converts a series of
Get Price
What is the inverter voltage of the energy storage system?
What is the inverter voltage of the energy storage system? The inverter voltage of an energy storage system refers to the electrical potential generated by the inverter
Get Price
Smart PV inverter overview: IEEE 1547-2018 and UL
UL 1741 is the official industry standard for certification of inverter safety. The tests that an "advanced inverter" must pass to receive UL 1741
Get Price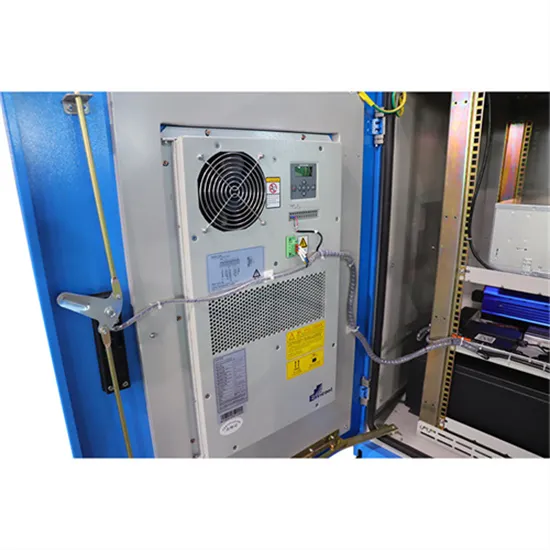
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power
Get Price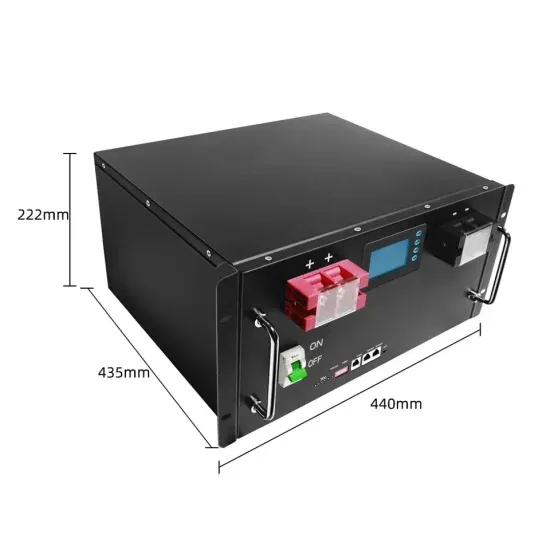
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
The output voltage of an inverter is the voltage produced when the inverter converts DC power to AC power. This AC power is then used to
Get Price
Power inverter
The AC output voltage of a power inverter is often regulated to be the same as the grid line voltage, typically 120 or 240 VAC at the distribution level, even when there are changes in the
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition, Functions, Type, and
What is the Inverter Voltage? Inverter voltage is a voltage generated by the inverter after several electrons that converts a series of direct current (DC) into alternating
Get Price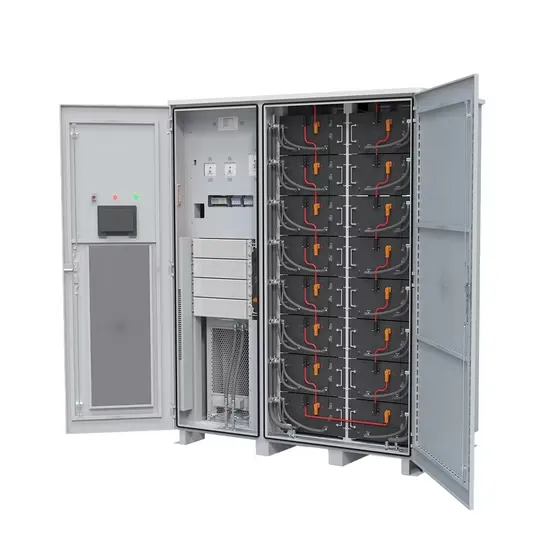
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar
Get Price
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings should you pay
Rated voltage refers to the nominal voltage that the inverter is engineered to work with. For grid-tied systems, this is typically 220V or 230V in most countries. For off-grid systems, it might be
Get Price
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
The output voltage of an inverter is the voltage produced when the inverter converts DC power to AC power. This AC power is then used to power appliances and
Get Price
SECTION 4 SWITCHED CAPACITOR VOLTAGE
In the previous section, we saw how inductors can be used to transfer energy and perform voltage conversions. This section examines switched capacitor voltage converters which accomplish
Get Price
Inverter Voltage Calculator, Formula, Inverter Voltage Calculation
Understanding and calculating inverter voltage is crucial for ensuring the correct operation and efficiency of various electronic devices and systems. Inverter voltage, V (V) in volts equals the
Get Price
What Is Inverter Voltage?
The input voltage should match your energy source (battery or solar panels), while the output voltage should correspond to the voltage standards of your region and the appliances you
Get Price
6 FAQs about [What is the inverter voltage equivalent to ]
What is inverter voltage?
Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC).
What is the AC output voltage of a power inverter?
The AC output voltage of a power inverter is often regulated to be the same as the grid line voltage, typically 120 or 240 VAC at the distribution level, even when there are changes in the load that the inverter is driving. This allows the inverter to power numerous devices designed for standard line power.
What is an example of a power inverter?
Common examples are refrigerators, air-conditioning units, and pumps. AC output voltage This value indicates to which utility voltages the inverter can connect. For inverters designed for residential use, the output voltage is 120 V or 240 V at 60 Hz for North America. It is 230 V at 50 Hz for many other countries.
What voltage is a 12V inverter?
Inverters come in various configurations, each designed for specific power systems. Common rated input voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V. The choice depends on the application, the size of the power system, and the available power source. A 12V inverter is commonly used for smaller applications, such as in vehicles or small off-grid setups.
How do you calculate inverter voltage?
Understanding and calculating inverter voltage is crucial for ensuring the correct operation and efficiency of various electronic devices and systems. Inverter voltage, V (V) in volts equals the product of DC voltage, V DC (V) in volts and modulation index, dm. Inverter voltage, V (V) = V DC (V) * dm V (V) = inverter voltage in volts, V.
Why is inverter voltage important?
Renewable Energy Systems: Calculating inverter voltage is critical for the efficient conversion of solar or wind energy into usable AC power. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Ensuring the correct inverter voltage helps maintain power stability during outages.
More related information
-
 What is the normal output voltage of the inverter
What is the normal output voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the voltage of the grid-connected inverter
What is the voltage of the grid-connected inverter
-
 What is the inverter discharge protection voltage
What is the inverter discharge protection voltage
-
 What is the maximum output voltage of the inverter
What is the maximum output voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the voltage of the outdoor inverter
What is the voltage of the outdoor inverter
-
 What is the maximum input voltage of a 48v inverter
What is the maximum input voltage of a 48v inverter
-
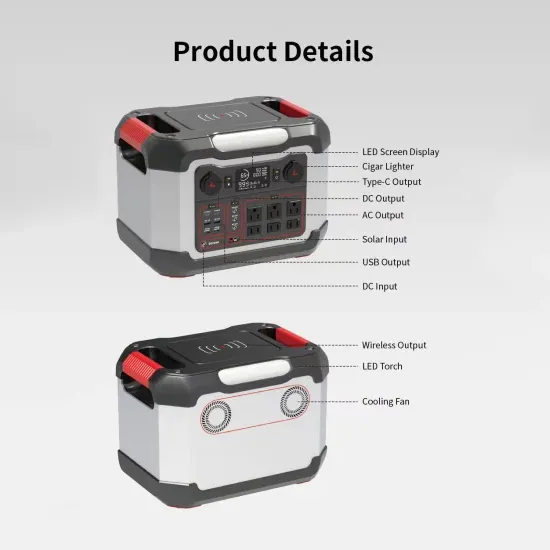 What is the inverter output voltage
What is the inverter output voltage
-
 What is the voltage of the inverter in Türkiye
What is the voltage of the inverter in Türkiye
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
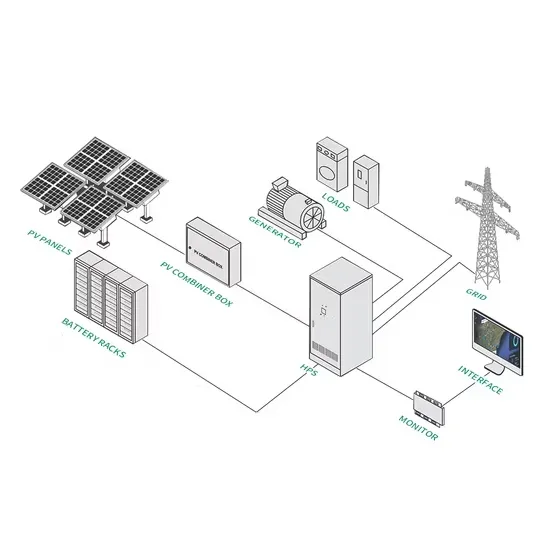
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


