AC Battery Voltage Explained: What You Need to Know
DC battery: Direct current (DC) is output, requiring users to connect an external inverter to use AC appliances. An AC battery includes a built-in inverter, while a DC battery
Get Price
batteries
Such modules as I see on circuits schematics are connected to the battery, before the inverter (obviously, since the inverter output voltage is different.) All the modules I see
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
This is the maximum power the inverter can supply to a load on a steady basis at a specified output voltage. The value is expressed in watts or kilowatts. Peak
Get Price
How to Connect Solar Panels to Battery Bank/Charge Controller/Inverter
Regulate Energy Flow: Connect solar panels to charge controllers correctly to optimize energy capture and protect the battery bank from overcharging. Inverter Integration:
Get Price
What is a Battery Inverter? A Comprehensive Overview
Common battery voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V, and choosing the correct voltage is essential for compatibility. Voltage Output: This parameter indicates the voltage of
Get Price
Inverter Generator Schematic: A Comprehensive
An inverter generator is a type of generator that produces AC power by converting DC power into AC power through a complex electrical circuit. This
Get Price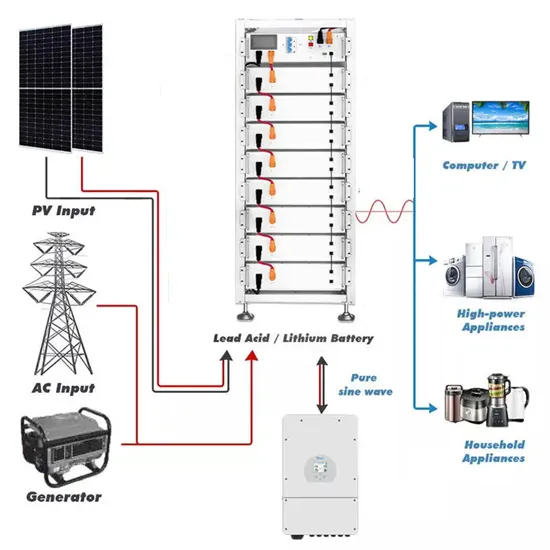
batteries
As I understand it, to calculate the current I need to divide power 500W not by inverter output 220V voltage, but by the original source voltage - that is, the battery voltage
Get Price
Power Inverters Explained
We can control the output voltage by controlling how long the switches are closed for. So, we could for example output 240v or 120v by
Get Price
Step-by-step guide: Connecting an inverter to your house wiring
Output Voltage Fluctuations: If the inverter is producing inconsistent or fluctuating output voltage, it may indicate a problem with the inverter or its connection. Check the input voltage and
Get Price
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
Solar inverter specifications include input and output specs highlighting voltage, power, efficiency, protection, and safety features.
Get Price
What is a Battery Inverter? A Comprehensive Overview
Common battery voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V, and choosing the correct voltage is essential for compatibility. Voltage Output: This
Get Price
Photovoltaic Ch 11 Electrical Integration Flashcards | Quizlet
For stand- alone systems with batteries, the inverter input current depends on battery voltage. As battery voltage decreases, the inverter input current increases to provide the same power output.
Get Price
ALL INVERTER PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
The charged DC battery is then inverted back to AC (Alternating voltage) via a step up transformer, which is what supports the load
Get Price
An Inside Look at Power Inverter Wiring
Output Section: The output section of the power inverter schematic diagram is where the AC output voltage is connected. This can be a socket or any other terminal where the AC devices
Get Price
Inverter Battery Voltage: How Many Volts Are Needed For
An inverter battery typically operates at 12V, 24V, or 48V. These voltages represent the nominal direct current (DC) needed for the inverter''s function. Selecting the
Get Price
Inverter Battery Voltage Chart
Battery voltage is crucial for ensuring compatibility with your inverter. Most inverter batteries are rated at 12 volts, while larger systems may use 24 volts. Understanding nominal
Get Price
Properly Set Up an Inverter Connection
Discover the proper Inverter Connection setup with Techfine''s GA3024MH inverter. Learn how to connect solar panels, batteries, and grid power efficiently.
Get Price
How to Choose the Right Inverter Battery Voltage for Your Needs
What is Inverter Battery Voltage? Inverter battery voltage is the electric force that drives the inverter system. It plays a big role in how well your energy setup works. The
Get Price
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
What is an inverter''s output voltage? The output voltage of an inverter is the voltage produced when the inverter converts DC power to AC power. This AC power is then
Get Price
Photovoltaic Ch 11 Electrical Integration Flashcards
For stand- alone systems with batteries, the inverter input current depends on battery voltage. As battery voltage decreases, the inverter input current
Get Price
Photovoltaic Inverters
Photovoltaic Inverters Inverters are used for DC to AC voltage conversion. Output voltage form of an inverter can be rectangle, trapezoid or
Get Price
Frequently asked questions about inverters | Mastervolt
As a rule of thumb you should divide the connected capacity by 10 for 12 volt and by 20 for 24 volt. This also includes all the power losses in the cables, fuses and the inverter. Is there a
Get Price
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
What is an inverter''s output voltage? The output voltage of an inverter is the voltage produced when the inverter converts DC power to AC
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
This is the maximum power the inverter can supply to a load on a steady basis at a specified output voltage. The value is expressed in watts or kilowatts. Peak output power. This is also
Get Price
How to Know If Inverter Battery Fully Charged?
Once the voltmeter is connected to the battery, check its display. For example, if the battery is fully charged, the voltage should be 11-13 V. If the voltmeter shows 13 volts, the
Get Price
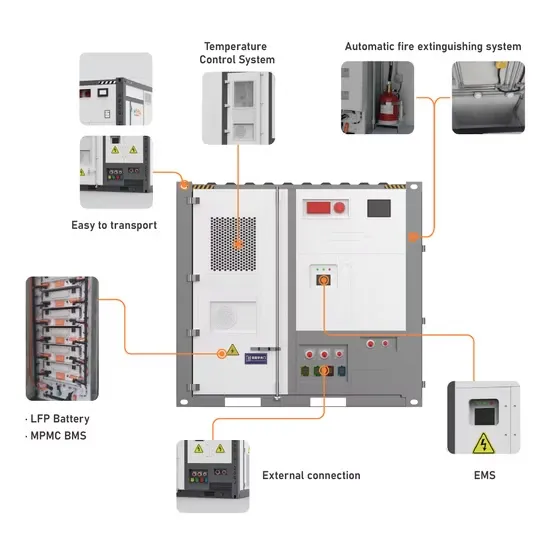
Battery Inverters: The Bridge Between Energy
Inside the battery inverter, through a series of complex circuit structures and workflows, the input DC power is filtered, chopped, inverted
Get Price
Inverter Battery Voltage: How Many Volts Are Needed For
An inverter battery typically operates at 12V, 24V, or 48V. These voltages represent the nominal direct current (DC) needed for the inverter''s function.
Get Price
Understanding inverter voltage
The inverter voltage on load varies depending on factors such as the connected devices, power consumption, and the overall health of the battery. Real-time monitoring, as
Get Price
6 FAQs about [What is the output voltage of the battery connected to the inverter ]
What is voltage input & output in a battery inverter?
Voltage Input: This parameter refers to the voltage of the battery bank that the inverter will draw power from. Common battery voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V, and choosing the correct voltage is essential for compatibility. Voltage Output: This parameter indicates the voltage of the AC power that the inverter produces.
How does battery voltage affect inverter input current?
As battery voltage decreases, the inverter input current increases to provide the same power output. At low battery voltages and peak power output, this current can be considerably higher than the inverter input current rating at the nominal battery voltage.
What voltage does a battery inverter use?
Common battery voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V, and choosing the correct voltage is essential for compatibility. Voltage Output: This parameter indicates the voltage of the AC power that the inverter produces. Standard household voltage is typically 120V or 240V, depending on your location.
Which inverter input circuit has the same maximum current?
For an interactive inverter with the PV output circuit connected directly to the inverter input, the inverter input circuit is the same as the PV output circuit and, therefore, has the same maximum current. For stand- alone systems with batteries, the inverter input current depends on battery voltage.
What is a power output in an inverter?
Power Output: This parameter, measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW), indicates the maximum power the inverter can deliver. It’s crucial to choose an inverter with a power output sufficient to handle the total power consumption of the appliances and devices you intend to power.
How much power does an inverter use?
An inverter uses a small amount of energy during the conversion process. The difference between the input power and the output power is expressed in percentages. The efficiency of modern inverters is more than 92 %. This means that a maximum of 8 % of the power consumption is used to convert battery voltage to 230V/50Hz.
More related information
-
 What is the maximum output voltage of the inverter
What is the maximum output voltage of the inverter
-
 Inverter AC output connected to voltage regulator
Inverter AC output connected to voltage regulator
-
 What kind of battery can be connected to the inverter
What kind of battery can be connected to the inverter
-
 48v battery inverter voltage regulation
48v battery inverter voltage regulation
-
 Is the substation inverter connected to the battery
Is the substation inverter connected to the battery
-
 What size inverter should I use with a 240A lithium battery
What size inverter should I use with a 240A lithium battery
-
 Household photovoltaic inverter output voltage
Household photovoltaic inverter output voltage
-
 Inverter single-phase output voltage
Inverter single-phase output voltage
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.