Understanding the role of base stations (gNB vs eNB) in 5G and
Base stations are the backbone of wireless networks, facilitating communication between mobile devices and the network infrastructure. In LTE (Long Term Evolution) networks, these base
Get Price
What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless Network Infrastructure. It serves
Get Price
Investigating the Sustainability of the 5G Base Station
Abstract—5G is a high-bandwidth low-latency communication technology that requires deploying new cellular base stations. The environmental cost of deploying a 5G cellular network remains
Get Price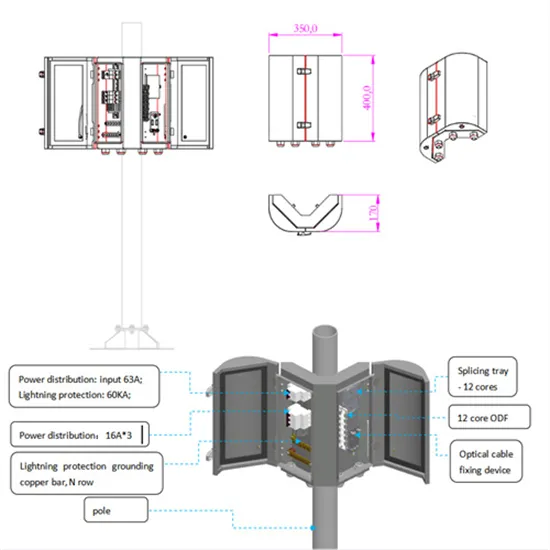
5g base station architecture
5G introduces the concept of network slicing, allowing the creation of multiple logical networks on a shared physical infrastructure. Each slice is tailored to specific
Get Price
What is 5G Base Station?
A 5G base station, also known as a 5G NodeB (gNB) in the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) standards, is a radio access point that connects user equipment (such as 5G -
Get Price
What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless
Get Price
What is a Base Station?
Base stations are central hubs of connections in different sectors and support networking, communication, and transmitting data. Integration of
Get Price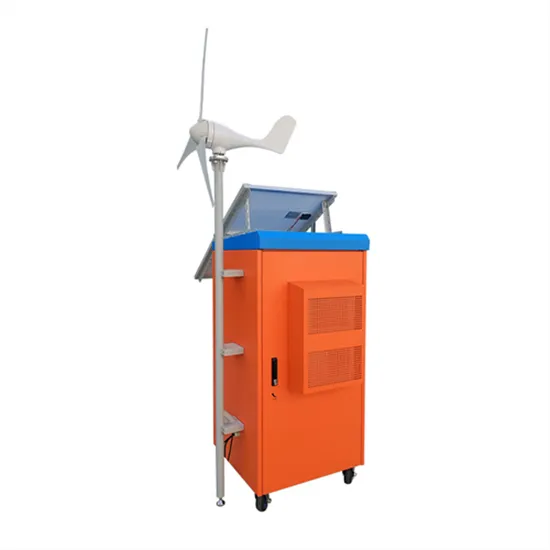
How does mobile phone communication work? 5G VS 4G Base Stations
Access networks are a key component of modern telecommunications technology. What is Access Network? How does mobile phone communication work? What is the difference between 5G
Get Price
Health Effects of 5G Base Station Exposure: A Systematic Review
The Fifth Generation (5G) communication technology will deliver faster data speeds and support numerous new applications such as virtual and augmented reality. The
Get Price
What is a 5G Base Station?
5G base stations operate by using multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) antennas to send and receive more data simultaneously
Get Price
5G base station rollout in the U.S. and China 2021
The United States (U.S.) and China are both rolling out ** infrastructure at a rapid rate, growing approximately *** times in size from
Get Price
What Is 5G Base Station?
Base stations, also called public mobile communication base stations, are interface devices for mobile devices to access the Internet. They
Get Price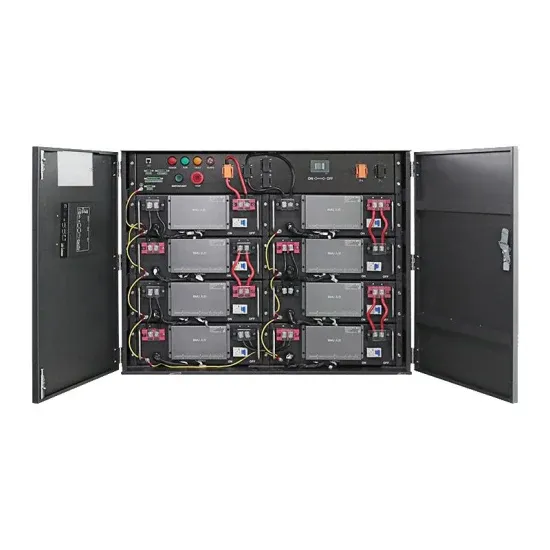
Chapter 2: Architecture — Private 5G: A Systems
To further confuse matters, 3GPP terminology often changes with each generation (e.g., a base station is called eNB in 4G and gNB in 5G). We
Get Price
WBS510 | 5GHz 300Mbps Outdoor Wireless Base
Access Where You Need It Most TP-LINK''s 5GHz 300Mbps * Outdoor Wireless Base Station is specifically designed to provide an effective
Get Price
What is a 5G Base Station?
5G base stations operate by using multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) antennas to send and receive more data simultaneously compared to previous generations of
Get Price
New Technology Allows Satellites to Act as Base
Splitting the base station Fraunhofer IIS has successfully demonstrated in the lab how satellites can be integrated into mobile
Get Price
Modeling 5G shared base station planning problem using an
A typical scenario of 5G shared BS planning is presented in this paper, in which different operators share the BSs constructed by the same tower company to reduce the
Get Price
Key technologies for 5G co-construction and shared base station
5G network consumes huge investment cost, including 5G network construction, 5G network operation and maintenance etc. Therefore, China Unicom and China Telecom.
Get Price
5G Base Station Chips: Driving Future Connectivity by 2025
The evolution of wireless technology has brought the world to the brink of a connectivity revolution. As 5G networks become the backbone of modern communication, 5G
Get Price
Learn What a 5G Base Station Is and Why It''s Important
A 5G base station is the heart of the fifth-generation mobile network, enabling far higher speeds and lower latency, as well as new levels of connectivity. Referred to as gNodeB, 5G base
Get Price
5G Base Station Architecture
Generally, UE supporting EN-DC must be capable of transmitting uplink data simultaneously across the 4G and 5G air interfaces. However, some
Get Price
5G Base Station Architecture
Generally, UE supporting EN-DC must be capable of transmitting uplink data simultaneously across the 4G and 5G air interfaces. However, some exceptions are allowed due to potential
Get Price
What is 5G base station architecture?
Before you can think about 5G network components, you need to consider the base station. To get started, find out what you need to know
Get Price
Understanding the role of base stations (gNB vs eNB) in 5G and
In LTE (Long Term Evolution) networks, these base stations are known as eNodeBs (evolved Node Bs), while in 5G networks, they are referred to as gNodeBs (next-generation Node Bs).
Get Price
5G Base Station Evolution | OpenRAN: RUs, DUs, CUs, and
From 4G to 5G technologies, Faststream has followed an evolutionary approach, with a strong emphasis on delivering able next-generation experiences and connections for our customers
Get Price
What is a base station and how are 4G/5G base
As mmWave signals, which are frequently used by 5G high-speed cell technologies, might differ from the same coverage as 4G and 3G signals,
Get Price
What is a base station and how are 4G/5G base stations different?
As mmWave signals, which are frequently used by 5G high-speed cell technologies, might differ from the same coverage as 4G and 3G signals, they will need
Get Price
The Base Station in Wireless Communications: The
Base station, also known as BTS (Base Transceiver Station), is a key device in wireless communication systems such as GSM. Equipped with
Get Price
What is 5G base station architecture?
Before you can think about 5G network components, you need to consider the base station. To get started, find out what you need to know about the architecture.
Get Price
6 FAQs about [Does 5G communication use shared base stations ]
How does a 5G base station work?
5G base stations operate by using multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) antennas to send and receive more data simultaneously compared to previous generations of mobile networks. They are designed to handle the increased data traffic and provide higher speeds by operating in higher frequency bands, such as the millimeter-wave spectrum.
What are base stations in 4G LTE networks called?
The base stations in 4G LTE networks are called either evolved Node B or eNodeB. You’ll find that eNodeB is usually abbreviated as eNB in 5G network architecture diagrams, and gNodeB as gNB. It helps to keep mind that a base station called eNB is for 4G, and gNB is for 5G.
What is the automatic data configuration model of 5G co-construction and shared base stations?
This paper focuses on the automatic data configuration model of 5G co-construction and shared base stations. By interacting with the core network and wireless network, this model can identify and match different 5G network modes such as SA and NSA (including dual-anchor scenarios and single-anchor scenarios).
What is 5G base station architecture?
5G base station architecture is characterized by its flexibility, virtualization, and the ability to support diverse services through network slicing. The separation of CU and DU, along with the introduction of cloud-based technologies, allows for more efficient resource utilization and scalability.
What frequency bands do 5G base stations use?
Utilization of Frequency Spectrum: 5g Base Stations Operate in specific Frequency Bands Allocated for 5G Communication. These bands include Sub-6 GHz Frequencies for Broader Coverage and Millimeter-Wave (Mmwave) Frequencies for Higher Data Rates.
Why do 5G base stations use MIMO & beamforming?
Both are critical for ensuring seamless communication between different network elements. 5G base stations often use Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology and beamforming to enhance spectral efficiency and coverage. Massive MIMO involves using a large number of antennas to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously.
More related information
-
 How many base stations are there for 5G communication
How many base stations are there for 5G communication
-
 What kind of electricity does Eritrea s 5G base stations use
What kind of electricity does Eritrea s 5G base stations use
-
 Are all communication base stations in Tajikistan 5G
Are all communication base stations in Tajikistan 5G
-
 Do communication base stations and wind power plants use lightning protection
Do communication base stations and wind power plants use lightning protection
-
 What is the use of wind power in communication base stations
What is the use of wind power in communication base stations
-
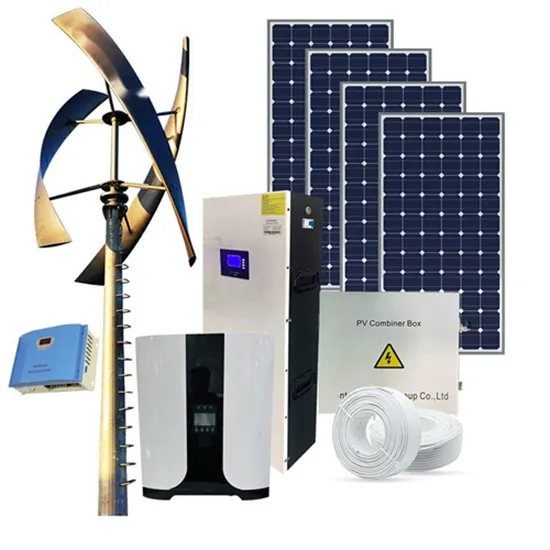 Does Huijue Battery Communication s 5G base stations receive loans from private individuals
Does Huijue Battery Communication s 5G base stations receive loans from private individuals
-
 Are all communication base stations in Turkmenistan 5G
Are all communication base stations in Turkmenistan 5G
-
 How to check 5G base stations in communication
How to check 5G base stations in communication
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


