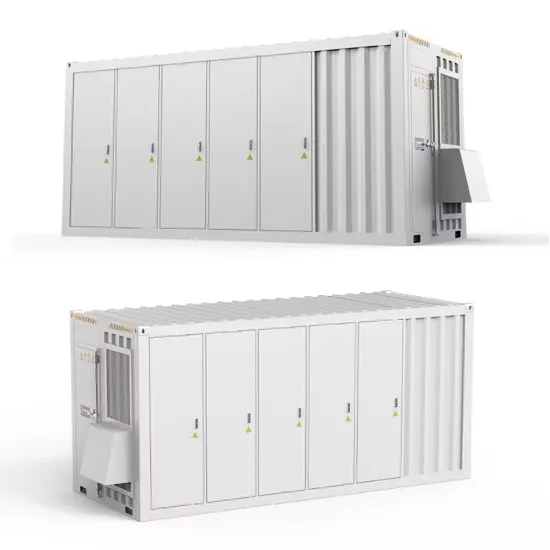
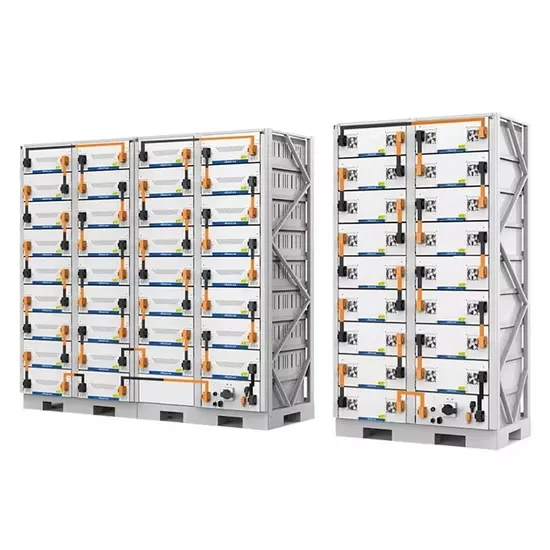
Inverter Basics | inverter
Unless you have a basic system that offers a low-voltage DC power source, the inclusion of an inverter becomes essential. An inverter
Get Price
Power inverter
OverviewInput and outputBatteriesApplicationsCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.
Get Price
Inverter Battery Voltage Chart
An inverter battery voltage chart shows the relationship between a battery''s charge level and its voltage. Battery voltage charts describe the
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The ability of an inverter to accurately convert DC to AC, operate within specified voltage and current limits, and incorporate safety and control features such as MPPT, transfer switches,
Get Price
Inverter: Types, Circuit Diagram and Applications
Current source inverters and voltage source inverts are simple than PWM inverters and are using for long time. PWM inverter needed further
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Input and Output: What is the
Input Voltage: The input voltage supplied from the DC source to the inverter follows the inverter voltage specifications, which start from 12V, 24V,
Get Price
Full Bridge Inverter – Circuit, Operation, Waveforms & Uses
What is a Full Bridge Inverter ? Full bridge inverter is a topology of H-bridge inverter used for converting DC power into AC power. The components required for conversion are two times
Get Price
Voltage Inverter : Circuit, Working and Its Applications
Inverters are used in a large number of electrical power applications. Voltage inverters are divided into three categories, Pulse-width
Get Price
Understanding inverter voltage
In the realm of power electronics, the inverter voltage is a critical parameter that dictates its performance, compatibility, and safety. Understanding the intricacies of inverter
Get Price
Understanding inverter voltage
In the realm of power electronics, the inverter voltage is a critical parameter that dictates its performance, compatibility, and safety.
Get Price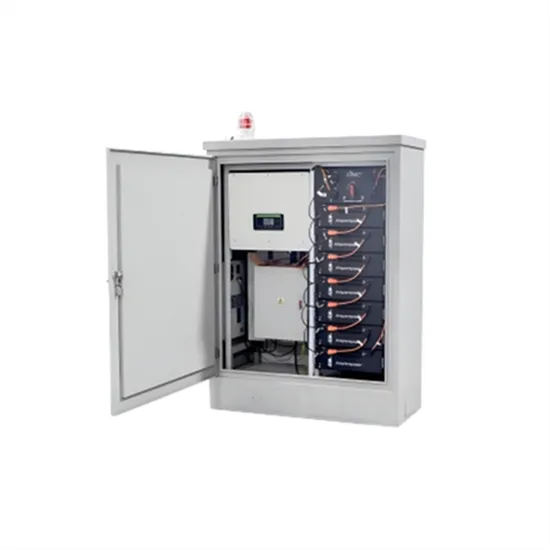
Inverter Basics | inverter
Unless you have a basic system that offers a low-voltage DC power source, the inclusion of an inverter becomes essential. An inverter takes input from a DC (direct current)
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Input and Output: What is the Relationship
Input Voltage: The input voltage supplied from the DC source to the inverter follows the inverter voltage specifications, which start from 12V, 24V, or 48V. Input Current: determines the
Get Price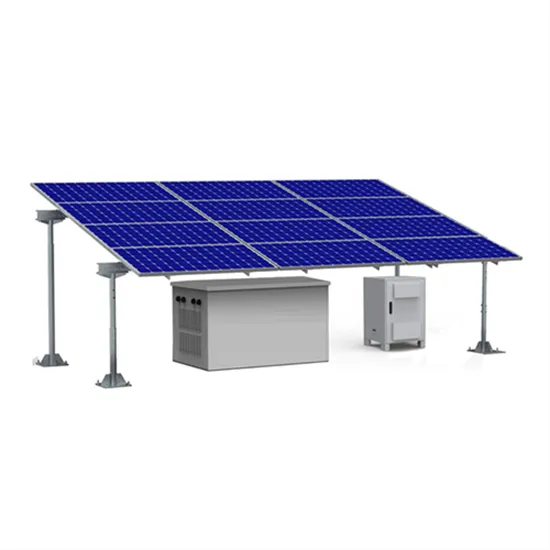
How to Test an Inverter
Precautions for inverter insulation resistance testing and voltage/current measurement Several precautions should be borne in mind when carrying out
Get Price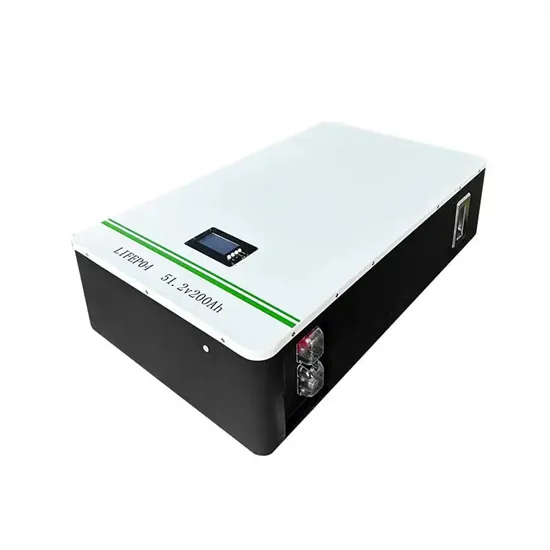
How does an inverter control current?
The two go hand-in-hand. If, on average, you''re providing slightly more current than the load sinks, the voltage will be increasing as you charge the output capacitance, since
Get Price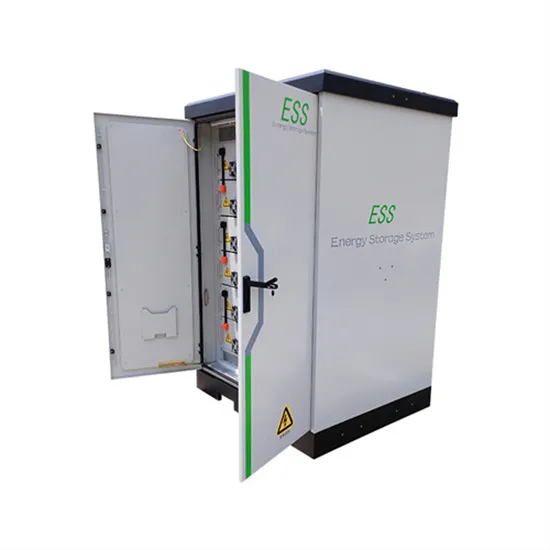
What is an Inverter? Working Principle, Types, and Applications
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). It is used in various applications like solar energy systems, power backups, and electric vehicles.
Get Price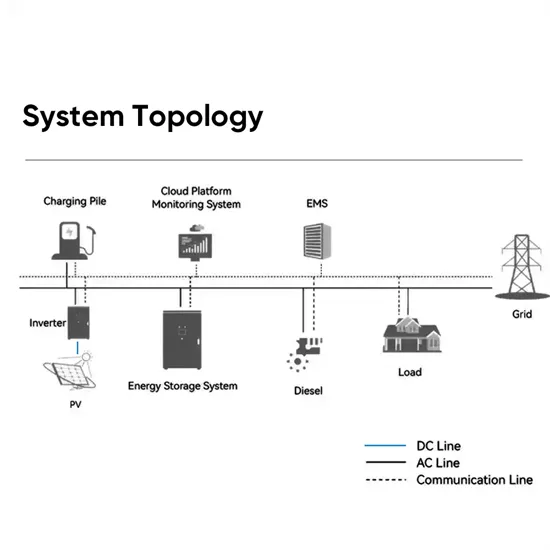
Inverter : Operating Principle,Circuit, Classification and Applications
What is an Inverter? Definition: The inverter is an electronic circuit that converts fixed DC supply to variable AC supply. The inverter is used to run the AC loads through a
Get Price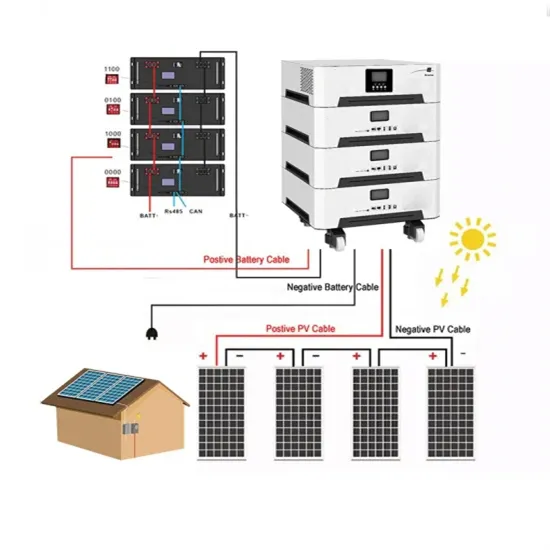
DC-to-AC Converters (Inverters): Design, Working &
The electrical circuits that transform Direct current (DC) input into Alternating current (AC) output are known as DC-to-AC Converters or
Get Price
Understanding inverter voltage
The inverter output inverter voltage is a critical aspect that must align with the standard alternating current (AC) voltage required by connected
Get Price
Introduction to Inverters
The main advantage of using AC current over DC current is that it helps to supply current to long distances without involving much cables. Block
Get Price
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
An easy-to-understand explanation of how an inverter currents DC (direct current) electricity to AC (alternating current).
Get Price
What is an Inverter? Working Principle, Types, and
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). It is used in various applications like solar energy
Get Price
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working
Get Price
Power inverter
Power inverters are primarily used in electrical power applications where high currents and voltages are present; circuits that perform the same function for electronic signals, which
Get Price
How DC/AC Power Inverters Work | HowStuffWorks
Power inverters convert direct current (DC), the power that comes from a car battery, into alternating current (AC), the kind of power supplied to your home and the power
Get Price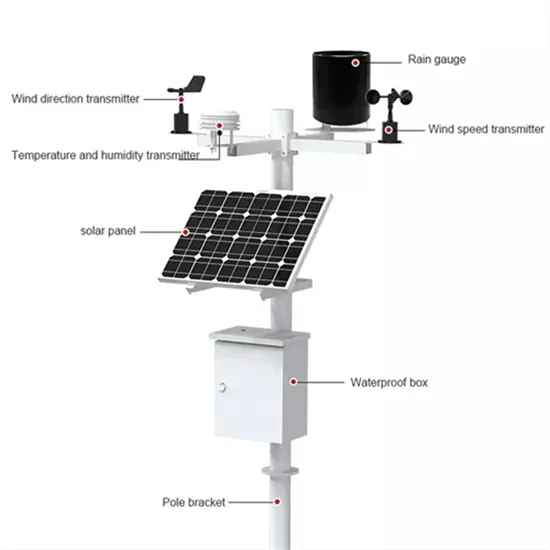
Introduction to Inverters
Inverters can also be used to change voltage levels. There are mainly five components of an inverter. They are as follows: A microcontroller
Get Price
Single Phase Inverter
Single Phase Inverter A single-phase inverter is a type of inverter that converts DC source voltage into single-phase AC output voltage at a
Get Price
What is an Inverter? Working Principle, Types, and
Voltage Source Inverter (VSI): Utilizes a constant DC voltage as input and converts it into AC. This type is commonly used in applications requiring
Get Price
Inverter Current Calculator, Formula, Inverter Calculation
The inverter draws current from a DC source to produce AC power. The inverter uses electronic circuits to switch the DC input at high frequencies, creating a form of AC voltage.
Get Price
Introduction to Inverters
Inverters can also be used to change voltage levels. There are mainly five components of an inverter. They are as follows: A microcontroller is also known as Digital
Get Price
Single Phase Full Bridge Inverter Explained
This article explains Single Phase Full Bridge Inverter, circuit diagram, various relevant waveforms & comparison between half and full
Get Price
More related information
-
 What is the inverter voltage and current
What is the inverter voltage and current
-
 What is the normal output voltage of the inverter
What is the normal output voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the inverter input voltage
What is the inverter input voltage
-
 What is a new energy high voltage inverter
What is a new energy high voltage inverter
-
 What is the voltage of the grid-connected inverter
What is the voltage of the grid-connected inverter
-
 What is the voltage of the outdoor inverter
What is the voltage of the outdoor inverter
-
 Weak current to high voltage inverter
Weak current to high voltage inverter
-
 What is the output voltage of a 12v inverter 4kw
What is the output voltage of a 12v inverter 4kw
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


