Difference Between MW and MWH
3 days ago· Getting MW and MWh down is key. What is MW? MW stands for Megawatt. It''s a unit for Power. Power (MW) is the speed energy is used or created right now. Think of it like
Get Price
Battery energy storage system size determination in renewable energy
Also, from Table 4.4, the BESS applications for renewable energy power plants including large-scale solar and/or wind applications are in MWh (energy capacity unit)/MW
Get Price
What is the difference between MWh and MW storage?
MW refers to the rate of energy flow, while MWh refers to the amount of energy stored. Understanding the difference between these two
Get Price
What are MW and MWh in renewable energy?
Whether you''re sizing a small off-grid system or developing a utility-scale project, understanding both MW and MWh is critical for performance, reliability, and profitability.
Get Price
Distinguishing MW from MWh in Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage projects are often labeled in the format "XX MW/XX MWh" (e.g., 100 MW/200 MWh or 125 kW/261 kWh for modular cabinet systems). The ratio of capacity to power (e.g.,
Get Price
What is the unit of solar energy mwh | NenPower
The advancement of solar technology, energy storage solutions, and regulatory frameworks contribute to the increasing importance of this unit
Get Price
Eolus to Sell 100 MW/400MWh Pome Battery Energy
Eolus has signed an agreement to sell the 100 MW/400 MWh stand-alone battery energy storage project, Pome, located in Poway, CA, U.S.
Get Price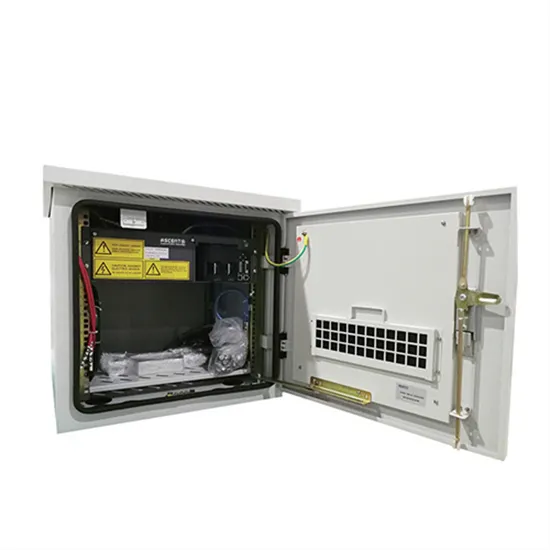
Understanding MW vs MWh: Power and Energy
Demystifying megawatts (MW) and megawatt-hours (MWh): this guide explains key energy concepts, capacity factors, storage durations, and efficiency
Get Price
US Grid-Scale Energy Storage Installations Surge,
The U.S. energy storage market set a Q2 record in 2024, with the grid-scale segment leading the way at 2,773 MW and 9,982 MWh deployed.
Get Price
MW Storage, Fluence partner on Germany''s largest
Storage specialist Fluence says its new battery-based energy storage project in Germany will be one of the largest in continental Europe,
Get Price
Energy storage mw and mwh
Demystifying megawatts (MW) and megawatt-hours (MWh): this guide explains key energy concepts, capacity factors, storage durations, and efficiency differences across power
Get Price
Prevalon Energy and Idaho Power Reach Commercial
The Happy Valley site features an 80 MW four-hour duration battery energy storage system (BESS) with a total capacity of up to 320 MWh.
Get Price
Difference Between MW and MWH
Understanding these two units'' differences is crucial for energy management, power system design, and building a commercial energy storage system. This article will delve into the
Get Price
Difference Between MW and MWH
Understanding these two units'' differences is crucial for energy management, power system design, and building a commercial energy storage system. This
Get Price
Difference Between MW and MWH
3 days ago· Getting MW and MWh down is key. What is MW? MW stands for Megawatt. It''s a unit for Power. Power (MW) is the speed energy is used or
Get Price
Understanding MW vs MWh: Power and Energy Explained
Demystifying megawatts (MW) and megawatt-hours (MWh): this guide explains key energy concepts, capacity factors, storage durations, and efficiency differences across power
Get Price
Demystifying Power Storage Platform Units: MW vs. MWh Explained
Unlike solar farms that use a single unit (like MW), battery storage platforms use MW and MWh together – a combo that confuses even seasoned engineers. But here''s the
Get Price
What are MW and MWh in a battery energy storage system?
Explore the crucial role of MW (Megawatts) and MWh (Megawatt-hours) in Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS). Learn how these key specifications determine the power delivery
Get Price
What is the difference between MWh and MW storage?
MW refers to the rate of energy flow, while MWh refers to the amount of energy stored. Understanding the difference between these two units is crucial when discussing,
Get Price
Energy Vault Announces Contract with Consumers Energy for 75 MW/300 MWh
Energy Vault awarded project by Michigan''s largest energy provider to supply two battery energy storage systems (BESS), totaling 75 MW/300 MWh, in Iosco and Bay Counties
Get Price
Measuring Battery Electric Storage System Capabilities
Power capacity or rating is measured in megawatts (MW) for larger grid-scale projects and kilowatts (kw) for customer-owned installations. Energy storage capacity: The amount of
Get Price
Difference Between MW and MWH
3 days ago· Running a business means watching energy use closely. Costs are up, and things like solar panels and battery storage are becoming common.
Get Price
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
Energy storage for electricity generation An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an
Get Price
Simulation test of 50 MW grid-connected "Photovoltaic+Energy storage
This study builds a 50 MW "PV + energy storage" power generation system based on PVsyst software. A detailed design scheme of the system architecture and energy storage
Get Price
Demystifying Power Storage Platform Units: MW vs. MWh Explained
Ever stumbled upon terms like "100MW/200MWh" in energy storage projects and felt like you''re reading hieroglyphics? You''re not alone! Unlike solar farms that use a single
Get Price
Difference Between MW and MWH
In the energy sector, MW (megawatt) and MWh (megawatt-hour) are two commonly used terms, but they represent different concepts. Understanding
Get Price
Understanding MW and MWh in Battery Energy
The MW and MWh specifications of a BESS are both important, but they serve different purposes. The MW rating determines how much power
Get Price
Understanding Power and Energy in Battery Energy Storage
Learn the key differences between power and energy in BESS. Discover how these concepts impact performance, sizing, and design of battery energy storage systems.
Get Price
Understanding MW and MWh in Battery Energy Storage Systems
The MW and MWh specifications of a BESS are both important, but they serve different purposes. The MW rating determines how much power the system can deliver at any
Get Price
6 FAQs about [The relationship between MW and MWH in energy storage projects]
What are MW and MWh in a battery energy storage system?
In the context of a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS), MW (megawatts) and MWh (megawatt-hours) are two crucial specifications that describe different aspects of the system's performance. Understanding the difference between these two units is key to comprehending the capabilities and limitations of a BESS. 1.
What does mw mean in energy storage?
In energy storage systems, MW indicates instantaneous charging/discharging capability. Example: A 1 MW system can charge/discharge 1,000 kWh (1 MWh) per hour, determining its ability to handle short-term high-power demands, such as grid frequency regulation or sudden load responses. 2. MWh (Megawatt-hour) – The “Endurance” of Energy Storage Systems
What is MWh & how does it affect a C&I energy storage system?
MWh (Megawatt-hour) measures Energy – the total amount used over time, like distance. Mixing them up can cost your c&i energy storage systems business money. Understanding this difference is key to controlling your energy bill, choosing the right size solar and battery systems, and making sure your power stays on when you need it.
What does mw stand for in power systems?
In power systems, megawatts (MW) measure instantaneous power - the rate at which energy is being generated, transmitted, or consumed at any moment. When measuring energy delivered or consumed over a period of time, we use megawatt-hours (MWh).
What is the difference between MW and MWh?
MW refers to the rate of power output or consumption at a specific moment, whereas MWh refers to the total energy accumulated over a period. Example: MW: If a power plant has a capacity of 10 MW, it can generate 10 megawatts of power at any given time. MWh: If the same power plant operates for 1 hour, it will generate 10 MWh of energy.
How much energy does a 100 MW power plant produce?
Similarly, a 100 MW power plant running for one hour delivers 100 MWh of energy. One common error we sometimes see is people writing "MW/h" when meaning MWh. MW/h would mean megawatts per hour - a rate of change of power, like saying "the power plant's output is increasing by 5 MW/h”.
More related information
-
 The relationship between new batteries and energy storage
The relationship between new batteries and energy storage
-
 Wind power projects equipped with energy storage
Wind power projects equipped with energy storage
-
 Economic calculation of energy storage projects
Economic calculation of energy storage projects
-
 How many energy storage projects are there in Lebanon
How many energy storage projects are there in Lebanon
-
 Denmark s energy storage projects for 2025
Denmark s energy storage projects for 2025
-
 Are there subsidies for energy storage projects in Poland
Are there subsidies for energy storage projects in Poland
-
 Suspend energy storage projects
Suspend energy storage projects
-
 Morocco and cooperative energy storage projects
Morocco and cooperative energy storage projects
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


