Analysis and Simulation of New Seven Level Inverter Topology
The modes of operation are outlined for 5-level inverter, as similar modes will be realized for higher levels. Simulations of seven level of the proposed inverter topology along with
Get Price
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings should you pay
Rated voltage refers to the nominal voltage that the inverter is engineered to work with. For grid-tied systems, this is typically 220V or 230V in most countries. For off-grid systems, it might be
Get Price
Two‐Level Voltage Source Inverter
This chapter focuses on pulse width modulation (PWM) schemes for the highpower two‐level inverter, where the device switching frequency is normally below 1 kHz. A carrier based
Get Price
Differences between a 2 level inverter and a 3 level inverter
There are two common types of inverters based on their output voltage levels: 2-level and 3-level inverters. In this blog let''s discuss the major differences between these two
Get Price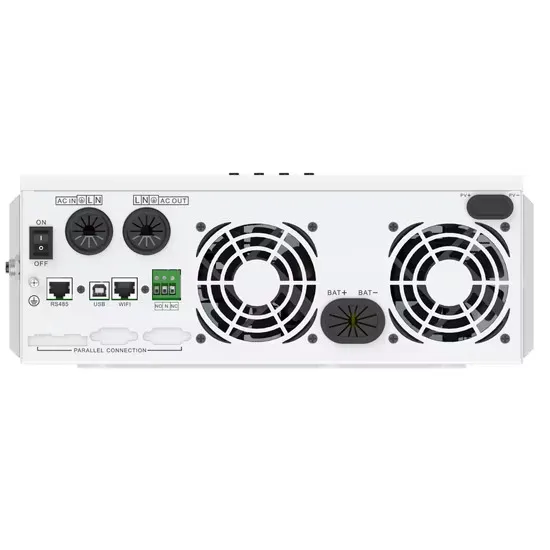
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar
Get Price
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
According to the output voltage and current phases, inverters are divided into two main categories. Single-phase inverters and three-phase inverters. These categories are briefly
Get Price
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
According to the output voltage and current phases, inverters are divided into two main categories. Single-phase inverters and three-phase inverters. These
Get Price
Power inverter
Power inverters are primarily used in electrical power applications where high currents and voltages are present; circuits that perform the same function for electronic signals, which
Get Price
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
This value is the minimum DC voltage required for the inverter to turn on and begin operation. This is particularly important for solar applications because the solar module or modules must
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Ratings and Specifications for Solar Power
Harnessing the Sun''s Potential: Demystifying Inverter Ratings In the realm of solar power, inverters serve as the gatekeepers, converting the raw energy harvested by solar panels into
Get Price
What are the differences between a 2-level inverter and a 3-level
Choosing between a two-level and a three-level inverter depends on the specific requirements of the application, including cost, efficiency, power quality, and complexity.
Get Price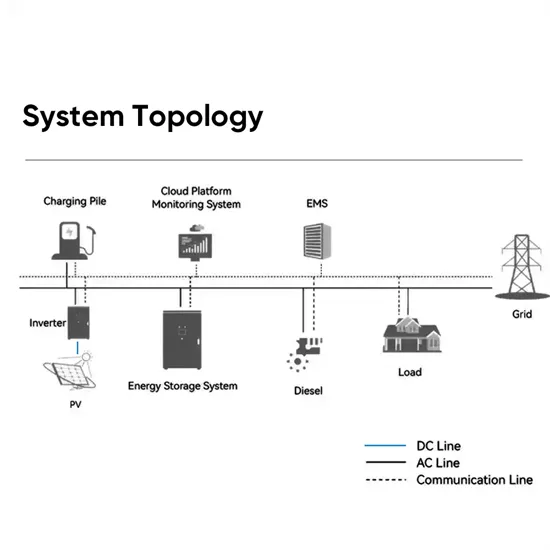
Introduction to Multilevel Inverters
Voltage on each capacitor is differing from the next as it has a ladder structure. Voltage difference between two back to back capacitors
Get Price
Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition, Functions, Type, and
Inverter voltage, uses, types of inverters based on voltage, and tips on choosing the best inverter voltage for you are mentioned in this article.
Get Price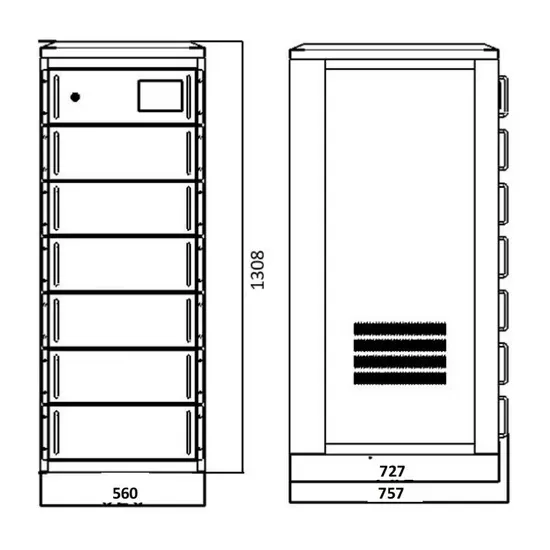
9. Inverter Settings
To set the low battery voltage level at which the inverter shuts off - To ensure long battery life, this value should be set according to your battery manufacturer specification.
Get Price
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings
Rated voltage refers to the nominal voltage that the inverter is engineered to work with. For grid-tied systems, this is typically 220V or 230V in most countries.
Get Price
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
Maximum Power Point Tracking or MPPT refers to the optimal voltage level at which the inverter can extract the most power from the solar panels. So, for efficient power
Get Price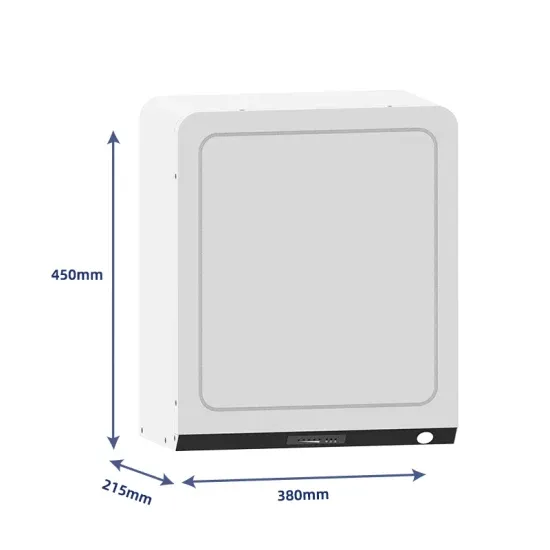
Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition, Functions,
Inverter voltage, uses, types of inverters based on voltage, and tips on choosing the best inverter voltage for you are mentioned in this article.
Get Price
Use of inverters in stand alone power systems
Some inverters can be programmed to start a generator if the battery voltage gets too low or household power demand goes above a pre-set level. Grid-connected inverters
Get Price
Introduction to multilevel voltage source inverters
Multilevel inverters (MLIs) are improved alternative devices to regular two-level inverters, to decrease dv/dt and di/dt ratios while providing an increased number of output
Get Price
Power inverter
OverviewInput and outputBatteriesApplicationsCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
A typical power inverter device or circuit requires a stable DC power source capable of supplying enough current for the intended power demands of the system. The input voltage depends on the design and purpose of the inverter. Examples include: • 12 V DC, for smaller consumer and commercial inverters that typically run fro
Get Price
CHAPTER 2
link converter. Inverters can be broadly classified into two types, voltage source and current source inverters. A voltage–fed inverter (VFI) or more generally a voltage–source inverter
Get Price
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF TWO LEVEL, THREE
Abstract: Two-level, Three- level, Five- level, and seven-level multilevel inverters are being simulated and analyzed in this paper. The schematic can be useful to photovoltaic
Get Price
Understanding inverter voltage
In the realm of power electronics, the inverter voltage is a critical parameter that dictates its performance, compatibility, and safety. Understanding the intricacies of inverter
Get Price
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
Maximum Power Point Tracking or MPPT refers to the optimal voltage level at which the inverter can extract the most power from the solar
Get Price
S13_JPE-14-05-231
Abstract Common-mode voltage (CMV) causes overvoltage stress to winding insulation and damages AC motors. CMV with high dv/dt causes leakage currents, which create noise
Get Price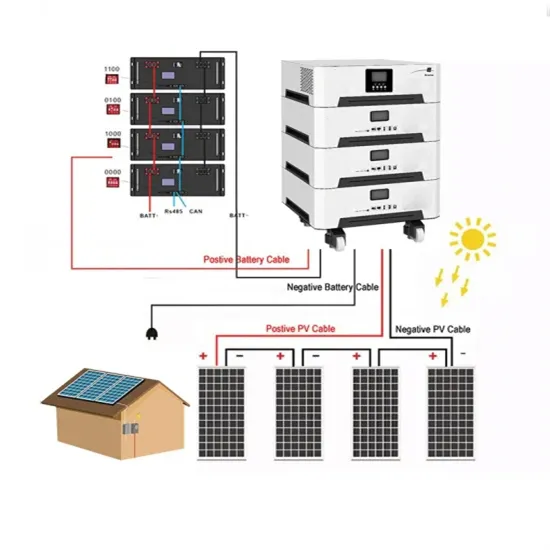
An Overview of Different Multi-level Inverters
1. INTRODUCTION The voltage source inverters produce an output voltage or current with levels either 0 or ± . They are known as the two-level inverter. To obtain the quality output voltage or
Get Price
What are the differences between a 2-level inverter
Choosing between a two-level and a three-level inverter depends on the specific requirements of the application, including cost, efficiency, power quality, and
Get Price
PWM Techniques for Two-Level Voltage Source Inverters: A
Pulse width modulation (PWM) techniques are widely used to control the switching of semiconductors in power converters. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of
Get Price
HV Multi-Level Inverter
2-level vs. 3-level inverter topology The state-of-the-art automotive inverter is 2-level topology inverter. It controls the voltage waveform of the output with 3 electric potentials of phase-to
Get Price
Differences between a 2 level inverter and a 3 level
There are two common types of inverters based on their output voltage levels: 2-level and 3-level inverters. In this blog let''s discuss the major
Get Price
More related information
-
 Wide voltage inverter power generation system
Wide voltage inverter power generation system
-
 70kw inverter voltage level
70kw inverter voltage level
-
 Inverter power AC voltage
Inverter power AC voltage
-
 Power frequency inverter secondary primary voltage
Power frequency inverter secondary primary voltage
-
 Wide voltage inverter with high power
Wide voltage inverter with high power
-
 Inverter for non-high voltage power users
Inverter for non-high voltage power users
-
 Inverter voltage is higher than the power supply voltage
Inverter voltage is higher than the power supply voltage
-
 What is the output voltage of the power inverter
What is the output voltage of the power inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

