Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline vs Thin-Film Solar
Find the differences between Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-film solar panels in our comprehensive guide. Learn their pros and cons, cost
Get Price
Crystalline and Thin Film Solar Panels | The Difference
Crystalline Silicon Solar Panels c-Si solar panels can be grouped into two categories — monocrystalline solar cells and polycrystalline cells — which rely
Get Price
Monocrystalline silicon
A silicon ingot Monocrystalline silicon, often referred to as single-crystal silicon or simply mono-Si, is a critical material widely used in modern electronics and
Get Price
The Difference Between Monocrystalline Silicon and
However, there is not much difference between polycrystalline silicon solar panels and monocrystalline silicon solar panels in use, and the life and stability are very good.
Get Price
Differences between monocrystalline and bicrystalline photovoltaic panels
Monocrystalline photovoltaic panels have a photoelectric conversion efficiency of approximately 18%, up to 24%. In contrast, polycrystalline photovoltaic panels have a
Get Price
Monocrystalline vs Amorphous Solar Panels: A Comprehensive
Amorphous solar panels operate similarly to their monocrystalline counterparts, by using the photovoltaic effect. However, the key difference between amorphous and
Get Price
The difference between monocrystalline silicon and
As early as 20 years ago, monocrystalline silicon cells broke through the technical barrier of more than 20% photoelectric conversion efficiency. The cost of polycrystalline silicon
Get Price
What''s the Difference Between Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline Panels?
What is a monocrystalline solar panel? Monocrystalline panels, which are darker in color and made out of the highest-grade silicon, are more energy efficient than polycrystalline panels.
Get Price
The Difference Between Polycrystalline Silicon And
The main differences between monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon lie in their structure, properties, and applications.
Get Price
Solar panel types and differences: monocrystalline silicon
The four corners of monocrystalline silicon cells show a rounded shape with no pattern on the surface. Polycrystalline silicon cells have four corners with square corners and a pattern on the
Get Price
CdTe vs. Crystalline Silicon Panels: Benefits & Applications
Crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar panels, either monocrystalline or polycrystalline panels, are the dominant panel technology, widely adopted from residential to C&I projects.
Get Price
The difference between monocrystalline silicon and
Overall, monocrystalline silicon is suitable for high demand electronic and semiconductor fields, while polycrystalline silicon is more
Get Price
What are the differences between monocrystalline and
At first glance we can differentiate a solar panel made of monocrystalline silicon from one made of polycrystalline silicon if we look at the shape and color of its cells.
Get Price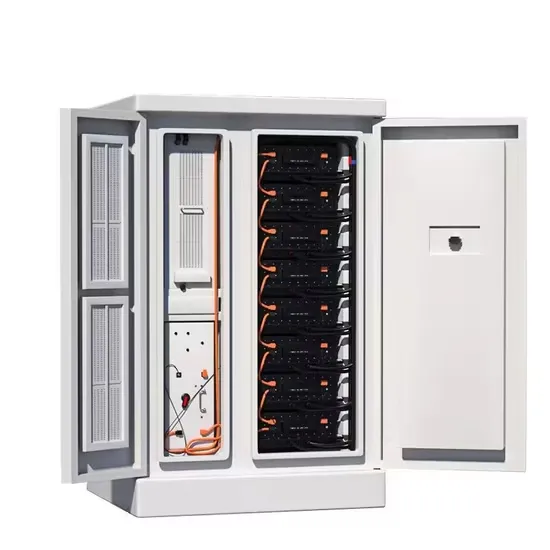
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MONOCRYSTALLINE AND
In the field of solar energy, monocrystalline silicon is also used to make photovoltaic cells due to its ability to absorb radiation. Monocrystalline silicon consists of silicon in which the crystal
Get Price
What is the Difference between Thin-Film and
The Difference between Crystalline Silicon and Thin Film Solar Panels Thin film and crystalline solar panels differ in cost, efficiency, size, etc.
Get Price
Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline: Which One Is the
Usually, a monocrystalline solar panel will have either 60 or 72 solar cells depending on how big the panel is. Mono silicon panels for
Get Price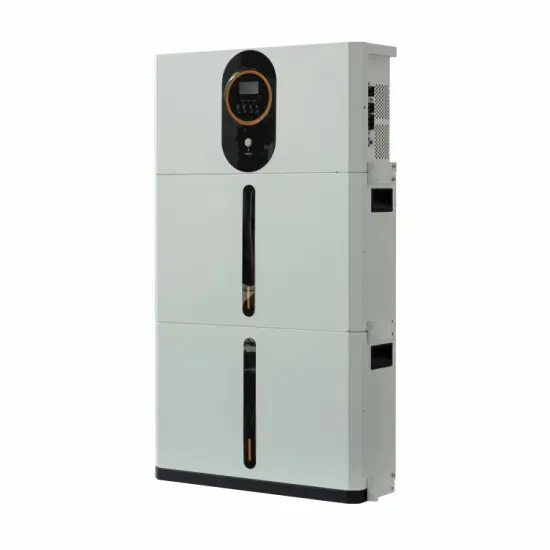
Bifacial vs Monofacial Solar Panels: Working,
Learn about the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of monofacial solar panels and bifacial solar panels. Explore which one is better
Get Price
The Difference Between Polycrystalline Silicon And
The Difference Between Polycrystalline Silicon And Monocrystalline Silicon in Photovoltaic Panels Dec 13, 2024 Leave a message
Get Price
Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline Silicon: Which Solar Cell Is
Two of the most common types of solar cells available today are monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon cells. Each type has distinct characteristics, benefits, and
Get Price
Solar panel types and differences: monocrystalline
The four corners of monocrystalline silicon cells show a rounded shape with no pattern on the surface. Polycrystalline silicon cells have four corners with
Get Price
The difference between monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline
Overall, monocrystalline silicon is suitable for high demand electronic and semiconductor fields, while polycrystalline silicon is more suitable for solar cells and certain
Get Price
Monocrystalline vs Polycrystalline Panels: Which Is
When choosing the best solar panel for home, most homeowners and businesses find themselves debating between Monocrystalline vs
Get Price
Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline Solar Panels:
Here''s what to know about the main types of solar panels. Defining monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels The difference between the
Get Price
Differences between monocrystalline and bicrystalline
Monocrystalline photovoltaic panels have a photoelectric conversion efficiency of approximately 18%, up to 24%. In contrast, polycrystalline photovoltaic panels have a
Get Price
Differences Between Polycrystalline Silicon and Monocrystalline Silicon
Polycrystalline silicon can be used as a raw material for pulling monocrystalline silicon, and the main differences between polycrystalline silicon and monocrystalline silicon
Get Price
The Difference Between Polycrystalline Silicon And Monocrystalline
The main differences between monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon lie in their structure, properties, and applications. Monocrystalline silicon is composed of a single
Get Price
Differences Between Polycrystalline Silicon and
Polycrystalline silicon can be used as a raw material for pulling monocrystalline silicon, and the main differences between polycrystalline
Get Price
Monocrystalline vs Amorphous Solar Panels
The main difference between Amorphous and Monocrystalline Solar Panels is that one is flexible and the other isn''t. Amorphous panels can be bent to match the lines of a surface with difficult
Get Price
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MONOCRYSTALLINE AND BICRYSTALLINE
In the field of solar energy, monocrystalline silicon is also used to make photovoltaic cells due to its ability to absorb radiation. Monocrystalline silicon consists of silicon in which the crystal
Get Price
6 FAQs about [The difference between bicrystalline silicon and monocrystalline silicon photovoltaic panels]
What is the difference between a monocrystalline and a polycrystalline solar cell?
Monocrystalline silicon solar cells (M-Si) are made of a single silicon crystal with a uniform structure that is highly efficient. Polycrystalline silicon solar cells (P-Si) are made of many silicon crystals and have lower performance. Thin-film cells are obtained by depositing several layers of PV material on a base.
What is the difference between monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon?
Polycrystalline silicon and single crystal silicon can be distinguished from each other in appearance, but true identification must be determined by analyzing the crystal plane orientation, conductivity type, and resistivity. Monocrystalline silicon cells have high cell conversion efficiency and good stability, but are costly.
Why is monocrystalline silicon used in photovoltaic cells?
In the field of solar energy, monocrystalline silicon is also used to make photovoltaic cells due to its ability to absorb radiation. Monocrystalline silicon consists of silicon in which the crystal lattice of the entire solid is continuous. This crystalline structure does not break at its edges and is free of any grain boundaries.
What are monocrystalline silicon solar panels?
Monocrystalline silicon sun-energy panels are more widely used in solar rooftop systems. These panels are commonly preferred for large-scale solar PV installations. Such solar panels are used in different sectors such as industrial, commercial, or residential.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of monocrystalline silicon solar cells?
Advantages: 1. High conversion efficiency: Monocrystalline silicon solar cells have high photoelectric conversion efficiency, which can better convert solar energy into electrical energy. 2. Low photoelectric conversion loss: Compared with polycrystalline silicon, monocrystalline silicon has lower photoelectric conversion loss.
Are monocrystalline silicon cells expensive?
Monocrystalline silicon cells have high cell conversion efficiency and good stability, but are costly. As early as 20 years ago, monocrystalline silicon cells broke through the technical barrier of more than 20% photoelectric conversion efficiency.
More related information
-
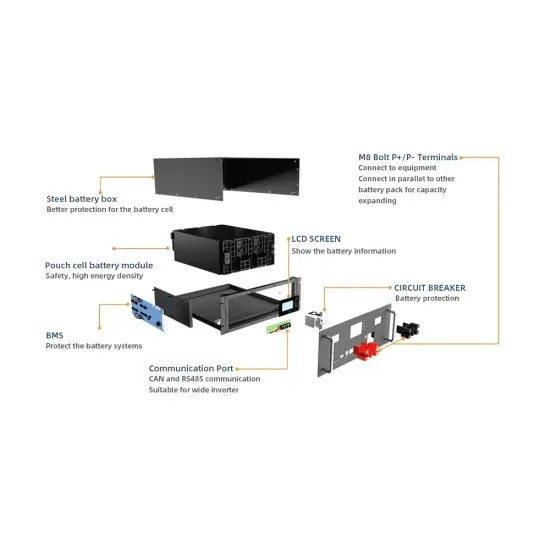 The difference between monocrystalline photovoltaic panels and bicrystalline photovoltaic panels
The difference between monocrystalline photovoltaic panels and bicrystalline photovoltaic panels
-
 Connection of monocrystalline silicon photovoltaic panels
Connection of monocrystalline silicon photovoltaic panels
-
 What are the monocrystalline silicon panels in photovoltaic plants
What are the monocrystalline silicon panels in photovoltaic plants
-
 Comparison of monocrystalline silicon and thin film photovoltaic panels
Comparison of monocrystalline silicon and thin film photovoltaic panels
-
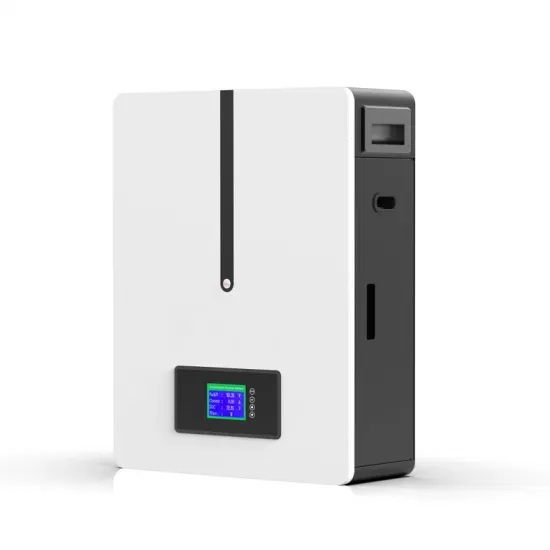 Photovoltaic power generation production of monocrystalline silicon panels
Photovoltaic power generation production of monocrystalline silicon panels
-
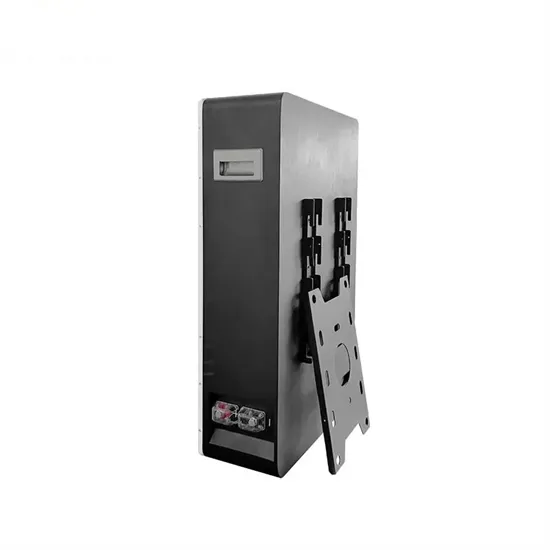 Photovoltaic monocrystalline silicon solar panels
Photovoltaic monocrystalline silicon solar panels
-
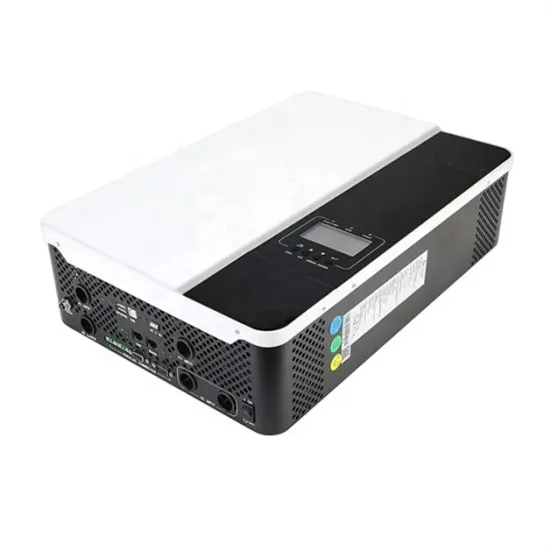 Monocrystalline silicon on solar photovoltaic panels
Monocrystalline silicon on solar photovoltaic panels
-
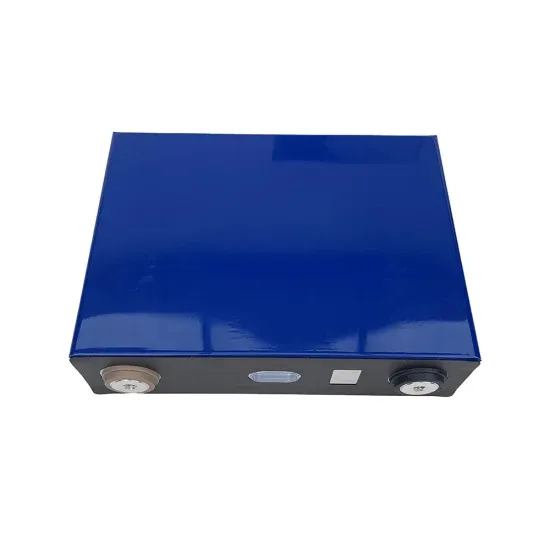 Size and weight of monocrystalline silicon photovoltaic panels
Size and weight of monocrystalline silicon photovoltaic panels
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with a 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with a 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


